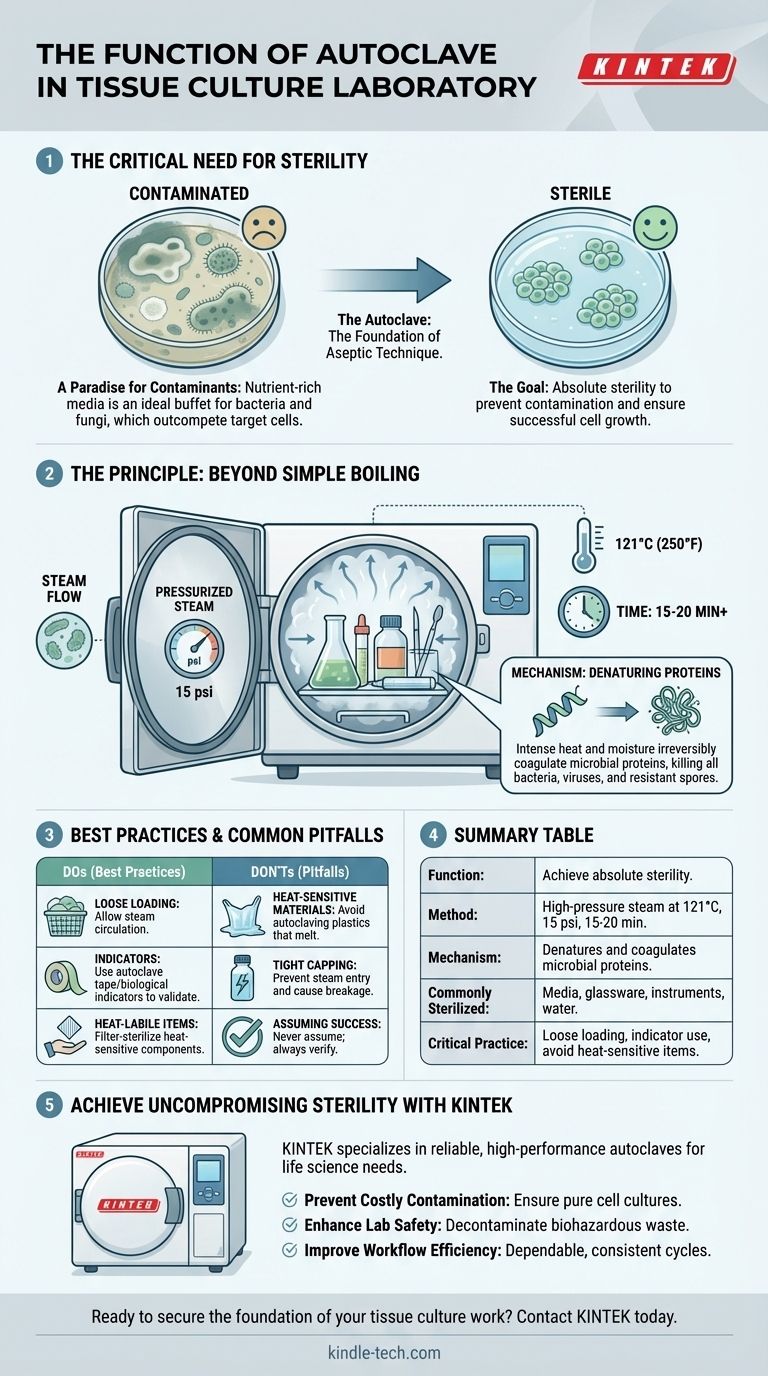
In a tissue culture laboratory, the function of an autoclave is to achieve absolute sterility for all media, glassware, and instruments used in the process. It uses high-pressure steam to reach temperatures that kill all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, and highly resistant spores, which would otherwise contaminate and destroy the delicate cell cultures.
The success of any tissue culture experiment hinges on maintaining a completely sterile, or aseptic, environment. The autoclave is not just a cleaning device; it is the primary tool that makes this sterile environment possible by reliably eliminating all potential contaminants.
The Critical Need for Sterility in Tissue Culture
The foundational goal of tissue culture is to grow cells outside of a living organism. This requires a nutrient-rich environment that, unfortunately, is also a perfect breeding ground for unwanted microbes.
A Paradise for Contaminants
The culture medium you prepare is packed with sugars, amino acids, and vitamins. While essential for your cells, this is an ideal buffet for bacteria and fungi, which grow much faster than animal or plant cells.
The Consequence of Contamination
A single bacterial or fungal spore can rapidly take over a culture dish. This contamination will outcompete your target cells for nutrients, change the pH of the medium, and release toxic byproducts, leading to the complete failure of your experiment.
The Principle of Autoclaving: Beyond Simple Boiling
An autoclave achieves sterilization through a combination of high heat, pressure, and steam, a method far more effective than simple boiling.
Pressurized Steam: The Key to High Temperatures
At normal atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). An autoclave is a sealed chamber that increases the pressure, allowing the steam inside to reach much higher temperatures—typically 121°C (250°F).
Heat and Time: The Lethal Combination
This superheated steam effectively penetrates and transfers heat to all items within the chamber. A standard sterilization cycle runs at 121°C and 15 psi (pounds per square inch) of pressure for at least 15-20 minutes, ensuring sufficient time to kill even the most heat-resistant spores.
Denaturing Proteins: The Mechanism of Killing
The intense heat and moisture from the steam irreversibly denatures and coagulates the essential proteins and enzymes within microorganisms. This process is lethal and absolute, ensuring no microbe can survive or reproduce.
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
While highly effective, an autoclave's success depends on proper use. Missteps can lead to incomplete sterilization and compromise your work.
Heat-Sensitive Materials Cannot Be Autoclaved
Many plastics will melt at 121°C. Furthermore, certain critical components of culture media, like some antibiotics or growth factors, are heat-labile (destroyed by heat) and must be filter-sterilized, not autoclaved.
Proper Loading is Essential for Steam Penetration
Items must be packed loosely to allow steam to circulate freely around and inside every object. Capping bottles too tightly will prevent steam from entering and can even cause the bottle to shatter under pressure changes. Lids should always be left slightly loose.
Routine Validation Ensures Performance
Never assume a cycle was successful. Use autoclave indicator tape on every run, which changes color to confirm it reached the target temperature. For critical applications, periodic use of biological indicators containing heat-resistant spores confirms the autoclave's killing power.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The autoclave is a foundational tool, and using it correctly is directly tied to your experimental outcomes and lab safety.
- If your primary focus is successful cell growth: Always autoclave your media (without heat-labile components), water, glassware, and metal instruments to create the aseptic environment your cells need to thrive.
- If your primary focus is lab safety and containment: Use the autoclave to decontaminate all biohazardous waste, including used culture plates and contaminated lab equipment, before disposal.
- If your primary focus is efficiency: Plan your work to run full, properly loaded autoclave cycles instead of many small, inefficient ones, and always separate heat-stable from heat-sensitive items beforehand.
Ultimately, mastering the principles of autoclaving is a non-negotiable step toward achieving consistent and reliable results in tissue culture.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Achieve absolute sterility to prevent contamination of delicate cell cultures. |
| Sterilization Method | High-pressure steam at 121°C (250°F) and 15 psi for 15-20 minutes. |
| Mechanism | Denatures and coagulates microbial proteins, killing all bacteria, viruses, and spores. |
| Commonly Sterilized Items | Culture media (without heat-labile components), glassware, metal instruments, water. |
| Critical Best Practices | Loose loading for steam penetration, using indicator tape, avoiding heat-sensitive materials. |
Achieve Uncompromising Sterility in Your Lab with KINTEK
Your tissue culture research demands a perfectly sterile environment to succeed. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable, high-performance autoclaves and lab equipment designed specifically for the rigorous needs of life science laboratories.
We understand that contamination can mean the loss of weeks of valuable work. Our autoclaves are engineered to deliver consistent, validated sterilization cycles, giving you the confidence that your media, glassware, and instruments are truly sterile.
Let us help you protect your research:
- Prevent Costly Contamination: Ensure your cell cultures remain pure and your experiments yield reliable data.
- Enhance Lab Safety: Safely decontaminate biohazardous waste before disposal.
- Improve Workflow Efficiency: With equipment you can depend on cycle after cycle.
Ready to secure the foundation of your tissue culture work? Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect sterilization solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of autoclave in microbiology lab? Achieve Sterile Conditions with 121°C
- What are the settings for autoclave sterilization? Ensure Reliable Sterility with Proper Parameters
- What are the 4 principles of autoclave? Master Steam Sterilization for Your Lab
- Why is the standard autoclave temperature set to 121? The Science of Effective Sterilization
- What is the size of a laboratory autoclave? A Guide to Choosing the Right Capacity



















