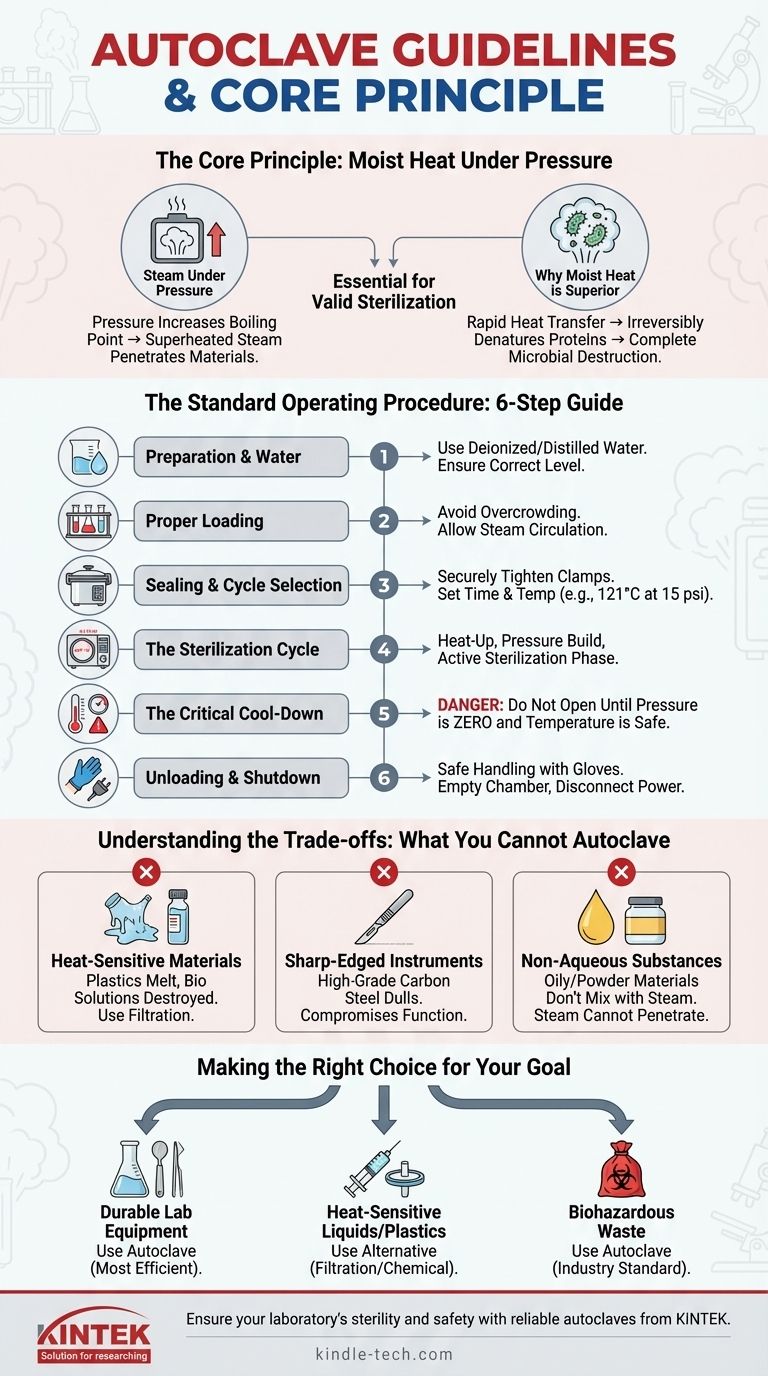
A guideline for an autoclave is a systematic procedure for using pressurized steam to achieve sterility. The core process involves adding water, properly loading materials, sealing the chamber, running a cycle at a specific temperature and pressure (typically 121°C at 15 psi), and allowing a complete cool-down before safely unloading the sterilized items.
The central principle of autoclaving is not just applying heat, but using moist heat under pressure. Understanding this allows you to determine what can and cannot be safely sterilized, preventing damaged equipment and ensuring complete microbial destruction.

The Core Principle: How an Autoclave Achieves Sterility
An autoclave's effectiveness comes from its unique combination of physical forces. It is far more effective than simply boiling or using dry heat.
Steam Under Pressure
The sealed chamber of an autoclave allows pressure to increase significantly. This rise in pressure allows water to boil at a much higher temperature than normal, creating superheated steam that can effectively penetrate materials.
Why Moist Heat is Superior
Moist heat is exceptionally efficient at killing microbes. The hot water vapor rapidly transfers heat and irreversibly denatures essential proteins and enzymes within microorganisms, rendering them non-functional and ensuring their destruction.
The Standard Operating Procedure: A Step-by-Step Guide
Following a consistent procedure is critical for both safety and effectiveness. While specific models vary, the fundamental steps remain the same.
Step 1: Preparation and Water Level
Before use, ensure the autoclave has the required amount of deionized or distilled water. Using the correct water level is essential for generating enough steam for the entire cycle.
Step 2: Proper Loading Technique
Place items inside the chamber without overcrowding them. Proper spacing is crucial to allow steam to circulate freely and reach all surfaces of the items being sterilized.
Step 3: Sealing and Cycle Selection
Close the autoclave lid and ensure the safety clamps are securely tightened to create a perfect seal. Set the appropriate time and temperature or select a pre-programmed cycle based on the load (e.g., liquids, glassware, waste).
Step 4: The Sterilization Cycle
Once started, the autoclave will heat up, build pressure, and hold the target temperature for the designated duration. This is the active phase where sterilization occurs.
Step 5: The Critical Cool-Down Phase
After the cycle completes, the chamber must be allowed to cool and depressurize completely. Attempting to open an autoclave while it is still under pressure is extremely dangerous and can cause severe burns or explosive boiling of liquids.
Step 6: Unloading and Shutdown
Once the pressure gauge reads zero and the temperature has dropped to a safe level, you can open the door and carefully remove the items. After use, empty the chamber and disconnect the power if it will not be used again soon.
Understanding the Trade-offs: What You Cannot Autoclave
An autoclave is a powerful tool, but it is not suitable for all materials. Attempting to sterilize incompatible items can result in damaged equipment or failed sterilization.
Heat-Sensitive Materials
Many plastics will melt or deform under the high heat and pressure. Additionally, sensitive biological solutions such as vaccines, serums, or certain protein media will be destroyed and must be sterilized using other methods like filtration.
Sharp-Edged Instruments
The high heat can cause the fine edges of high-grade carbon steel instruments, like certain scalpels or scissors, to become dull, compromising their function.
Non-Aqueous and Oily Substances
Autoclaving relies on moist heat. Oily substances, powders, and other materials that do not mix with water cannot be sterilized effectively because the steam cannot penetrate them.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your sterilization method based on the material and your objective.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing durable lab equipment (glassware, stainless steel tools, media): The autoclave is the most efficient, economical, and reliable method.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive liquids or plastics: You must use an alternative method, such as sterile filtration for liquids or chemical sterilization for solids.
- If your primary focus is decontaminating biohazardous waste: The autoclave is the industry standard for rendering biological waste safe for disposal.
Mastering the autoclave protocol is fundamental to ensuring safety, validity, and success in any sterile environment.
Summary Table:
| Key Step | Purpose | Critical Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation & Water | Generate sufficient steam | Use deionized/distilled water |
| Loading | Ensure steam penetration | Avoid overcrowding; allow space for circulation |
| Cycle Selection | Achieve sterility for specific loads | Standard cycle: 121°C at 15 psi |
| Cool-Down | Ensure user safety | Never open until pressure is zero and temperature is safe |
| Unloading | Safe handling of sterile items | Use heat-protective gloves |
Ensure your laboratory's sterility and safety with reliable autoclaves from KINTEK.
Proper sterilization is non-negotiable for valid results and user protection. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, providing autoclaves designed for precise temperature control, uniform steam penetration, and long-lasting performance. Our solutions are trusted by laboratories worldwide to meet stringent sterilization protocols efficiently and safely.
Let KINTEK be your partner in laboratory excellence. Contact our experts today to find the perfect autoclave solution for your specific needs, from routine glassware sterilization to biohazard waste decontamination.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment
- What is the primary function of a laboratory autoclave in the pre-treatment of medical plastic waste for liquid fuel?
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave equipped with a stirring device for molten salt testing? Dynamic Accuracy



















