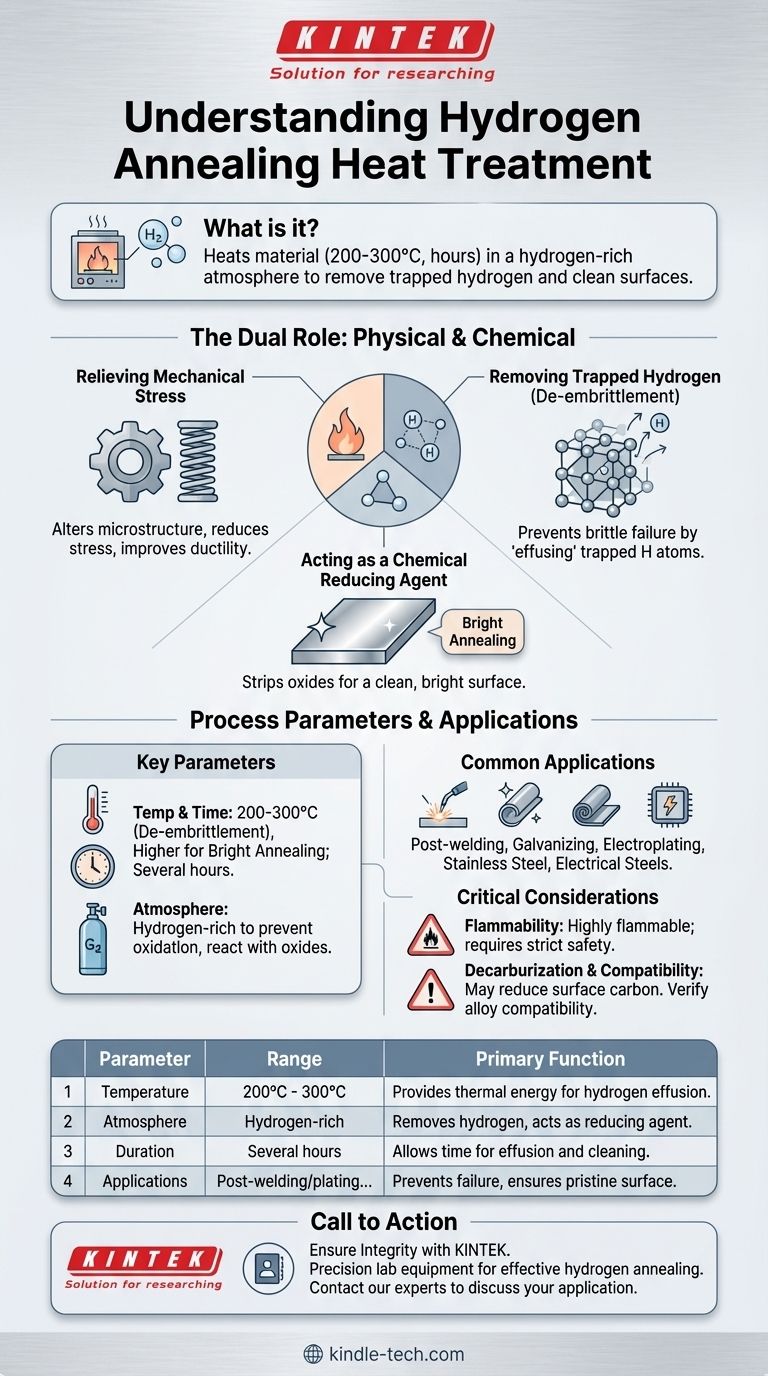
In short, hydrogen annealing is a heat treatment where a material is heated between 200°C and 300°C for several hours within a furnace filled with a hydrogen-rich atmosphere. This process is primarily designed to remove trapped hydrogen atoms that can cause metal to become brittle, a phenomenon known as hydrogen embrittlement. It is commonly performed after processes like welding, coating, or galvanizing, which can introduce hydrogen into the material.
The core purpose of hydrogen annealing is twofold: it physically removes trapped hydrogen to prevent material failure while also chemically cleaning the metal's surface by using hydrogen as a reducing agent to remove oxides.

The Dual Role of Hydrogen Annealing
Unlike standard annealing which primarily targets a material's internal structure, hydrogen annealing adds a crucial chemical component to the process. It addresses both the physical stress within the metal and the chemical composition of its surface.
Relieving Mechanical Stress
Like all annealing processes, this treatment heats a metal to alter its microstructure. This reduces internal stresses, lowers hardness, and significantly improves ductility. The material becomes less prone to cracking and easier to form or machine.
Removing Trapped Hydrogen (De-embrittlement)
The defining feature is its ability to combat hydrogen embrittlement. During welding or electroplating, tiny hydrogen atoms can diffuse into the metal's crystal lattice. These trapped atoms create immense internal pressure points, making an otherwise tough material fragile.
By heating the part in the furnace, the hydrogen atoms gain enough thermal energy to diffuse back out of the material, a process called effusion. This effectively removes the source of the embrittlement.
Acting as a Chemical Reducing Agent
The hydrogen atmosphere is not inert; it is highly reactive. At high temperatures, hydrogen vigorously reacts with oxygen. This means it strips oxides (like rust) from the surface of the metal, leaving it perfectly clean and bright.
This "bright annealing" effect is critical for materials like stainless steel or electrical steels, where a pristine, oxide-free surface is essential for performance and appearance.
Understanding the Process Parameters
The effectiveness of the treatment depends on carefully controlling the environment and timing.
Key Parameters: Temperature and Time
For the specific goal of removing hydrogen, a relatively low temperature range of 200°C to 300°C is sufficient. The process is maintained for several hours to allow adequate time for the hydrogen to escape.
For bright annealing intended to modify grain structure, temperatures are significantly higher, often exceeding the material's recrystallization point while remaining below its melting point.
The Controlled Atmosphere
The entire process must occur in an enclosed furnace where air is replaced with a hydrogen-rich atmosphere. This prevents oxygen from reacting with the hot metal, which would create scale and defeat the purpose of achieving a clean surface.
Common Applications
The method is predominantly used immediately after fabrication processes that are known to introduce hydrogen. Key applications include parts that have been recently welded, galvanized, or electroplated. It is also essential for producing high-purity metals and achieving the specific surface properties required in electrical steels and certain stainless steels.
Critical Considerations and Trade-offs
While powerful, hydrogen annealing carries unique risks and is not a universal solution.
The Flammability of Hydrogen
Hydrogen gas is extremely flammable and requires specialized furnace equipment and rigorous safety protocols. Managing this risk is a primary operational concern and cost factor.
Unintended Decarburization
Hydrogen can react with carbon in steel alloys, removing it from the surface. While this decarburization is sometimes desirable, it can also unintentionally soften the surface of a part that requires high hardness, which must be carefully managed.
Material Compatibility
The process is most effective for ferrous metals like steel and some non-ferrous metals like copper. However, its interaction with other alloys must be evaluated to ensure it does not have unintended negative metallurgical effects.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this process correctly, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is preventing post-fabrication brittleness: Use a low-temperature (200-300°C) hydrogen bake-out immediately after welding or plating to drive out trapped hydrogen.
- If your primary focus is achieving a pristine, oxide-free surface: Employ a higher-temperature bright annealing process where the hydrogen atmosphere acts as a reducing agent.
- If your primary focus is general stress relief and softening: Hydrogen annealing will achieve this, but if an oxide-free surface is not required, a simpler annealing process in an inert gas or vacuum may be a safer and more cost-effective alternative.
Ultimately, hydrogen annealing is a specialized tool used when controlling both the physical properties and surface chemistry of a metal is absolutely critical.
Summary Table:
| Key Parameter | Typical Range | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 200°C - 300°C (for de-embrittlement) | Provides thermal energy for hydrogen to diffuse out. |
| Atmosphere | Hydrogen-rich gas | Removes hydrogen and acts as a reducing agent for oxides. |
| Duration | Several hours | Allows sufficient time for hydrogen effusion and surface cleaning. |
| Common Applications | Post-welding, post-electroplating, stainless steel, electrical steels | Prevents failure and ensures a pristine, oxide-free surface. |
Ensure the integrity and performance of your metal components.
Hydrogen embrittlement can lead to catastrophic and unexpected material failure. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and furnace solutions needed for effective hydrogen annealing and other critical heat treatments. Our expertise ensures you can safely and reliably remove trapped hydrogen, achieve bright, clean surfaces, and relieve internal stresses.
Contact our experts today at [#ContactForm] to discuss your specific application and find the right solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is an industrial furnace with hydrogen atmosphere control necessary for the pre-sintering of Fe-Cr-Al materials?
- What is hydrogen atmosphere heat treatment? Achieve Superior Surface Purity & Brightness
- What is the use of hydrogen in furnace? A Key to Oxygen-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What are the primary benefits of using hydrogen firing for sintering parts? Achieve Peak Density & Corrosion Resistance
- What are the effects of hydrogen (H2) in a controlled furnace environment? Mastering Reduction and Risk



















