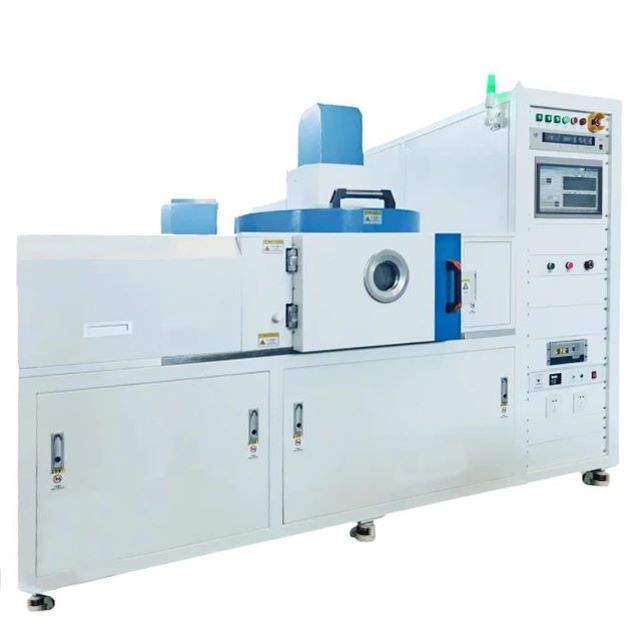

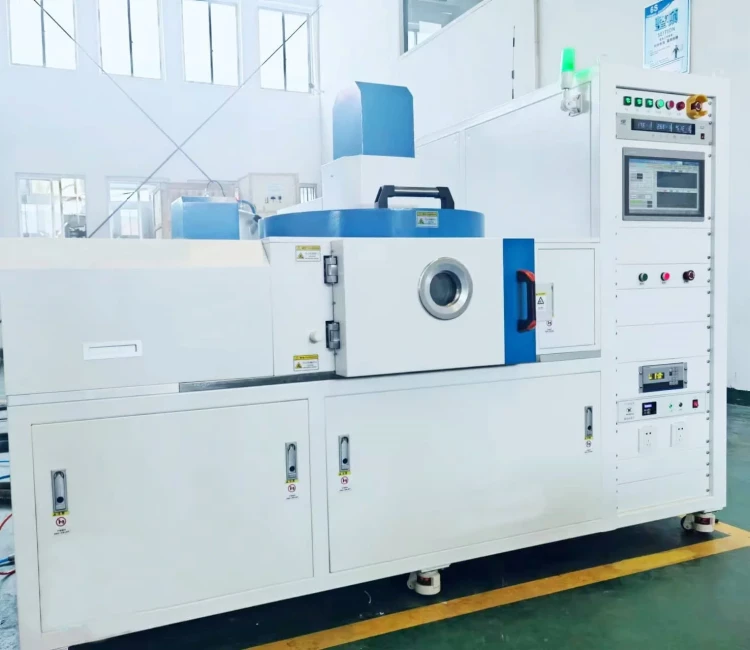
CVD & PECVD Furnace
RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
Item Number : KT-RFPE
Price varies based on specs and customizations
- Frequency
- RF frequency 13.56MHZ
- Heating temperature
- max 200°C
- Vacuum chamber dimensions
- Ф420mm × 400 mm
Shipping:
Contact us to get shipping details Enjoy On-time Dispatch Guarantee.
Why Choose Us
Easy ordering process, quality products, and dedicated support for your business success.
Introduction
Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (RF PECVD) is a thin-film deposition technique that uses plasma to enhance the chemical vapor deposition process. This process is used to deposit a wide variety of materials, including metals, dielectrics, and semiconductors. RF PECVD is a versatile technique that can be used to deposit films with a wide range of properties, including thickness, composition, and morphology.
Applications
RF-PECVD, a revolutionary technique in the realm of thin-film deposition, finds widespread applications in diverse industries, including:
- Fabrication of optical components and devices
- Manufacturing of semiconductor devices
- Production of protective coatings
- Development of microelectronics and MEMS
- Synthesis of novel materials
Components and Functions
Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (RF PECVD) is a technique used to deposit thin films on substrates by utilizing a radio frequency generator to create a plasma that ionizes precursor gases. The ionized gases react with each other and deposit onto the substrate, forming a thin film. RF PECVD is commonly used to deposit Diamond-like Carbon (DLC) films on germanium and silicon substrates for applications in the 3-12um infrared wavelength range.
Comprising a vacuum chamber, vacuum pumping system, cathode and anode targets, RF source, inflatable gas mixing system, computer control cabinet system, and more, this apparatus enables seamless one-button coating, process storage and retrieval, alarm functions, signal and valve switching, as well as comprehensive process operation logging.
Details and Examples
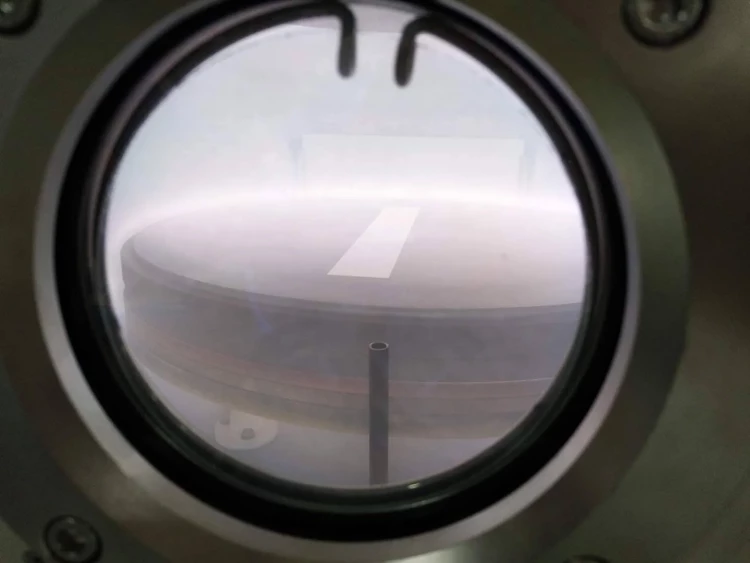


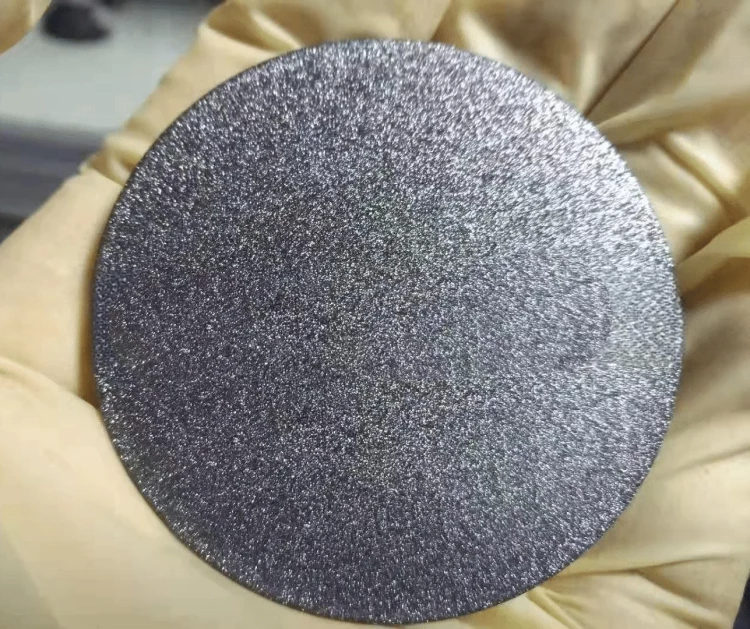
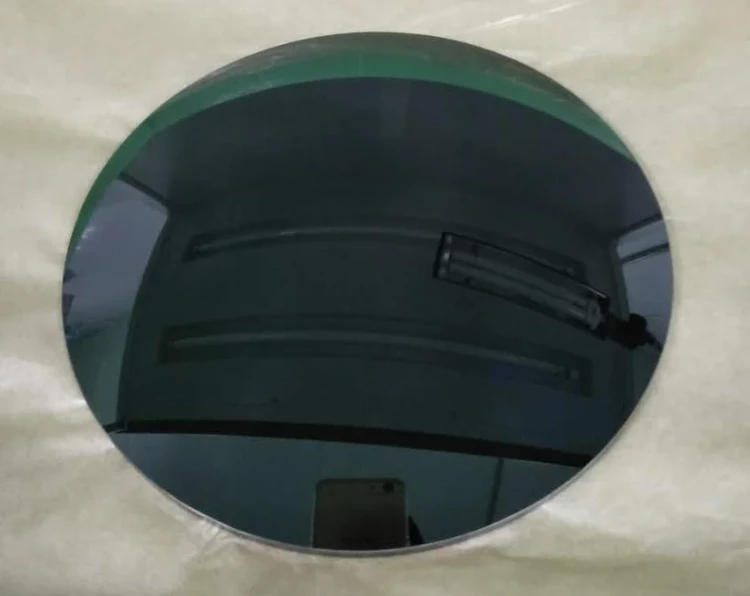
Features
RF-PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition features:
- One-button coating: Simplifies the coating process, making it easy for users to operate.
- Process storage and retrieval: Allows users to save and recall process parameters, ensuring consistent results.
- Alarm functions: Alerts users to any issues or errors during the coating process, minimizing downtime.
- Signal and valve switching: Provides precise control over the coating process, enabling users to achieve the desired results.
- Comprehensive process operation logging: Records all process parameters, making it easy to track and analyze the coating process.
- Vacuum chamber, vacuum pumping system, cathode and anode targets, RF source, inflatable gas mixing system, computer control cabinet system: Ensures a stable and controlled environment for the coating process.
Advantages
- High-quality film deposition at low temperature, suitable for temperature-sensitive substrates.
- Precise control over film thickness and composition.
- Uniform and conformal film deposition on complex geometries.
- Low particle contamination and high purity films.
- Scalable and cost-effective process for high-volume production.
- Environmentally friendly process with minimal hazardous waste generation.
Technical specifications
Main equipment part
| Equipment form |
|
| Vacuum chamber |
|
| Host skeleton |
|
| Water cooling system |
|
| Control cabinet |
|
Vacuum system
| Ultimate vacuum |
|
| Restore vacuum time |
|
| Pressure rise rate |
|
| Vacuum system configuration |
|
| Vacuum system measurement |
|
| Vacuum system operation | There are two modes of vacuum manual and vacuum automatic selection;
|
| Vacuum test |
|
Heating system
- Heating method: iodine tungsten lamp heating method;
- Power regulator: digital power regulator;
- Heating temperature: maximum temperature 200°C, power 2000W/220V, controllable and adjustable display, ±2°C control;
- Connection method: fast insertion and quick retrieval, metal shielding cover for anti-fouling, and isolated power supply source to ensure the safety of personnel.
RF radio frequency power supply
- Frequency: RF frequency 13.56MHZ;
- Power: 0-2000W continuously adjustable;
- Function: fully automatic impedance matching function adjustment, fully automatic adjustment to keep the reflection function very low working, internal reflection within 0.5% , with manual and automatic conversion adjustment function;
- Display: with bias voltage, CT capacitor position, RT capacitor position, set power, reflective function display , with communication function, communicate with touch screen, set and display parameters on configuration software, tune line display etc.
Cathode anode target
- Anode target: φ300mm copper substrate is used as the cathode target, the temperature is low when working, and no cooling water is needed;
- Cathode target: φ200mm copper water-cooled cathode target, the temperature is high when working, and the interior is cooled water, to ensure consistent temperature during work, the maximum distance between the anode and the cathode target is 100-250mm.
Inflation control
- Flowmeter: Four-way British flowmeter is used, the flow rate is 0-200SCCM, with pressure display, communication setting parameters, and gas type can be set;
- Stop valve: Qixing Huachuang DJ2C-VUG6 stop valve, works with the flow meter, mixes the gas, fills it into the chamber through the annular inflation device, and flows evenly through the target surface;
- Pre-stage gas storage bottle: mainly a flushing conversion bottle, which vaporizes the C4H10 liquid, and then enters the front-stage pipeline of the flowmeter. The gas storage bottle has a pressure digital display DSP instrument, which performs pressure over pressure and low pressure alarm prompts;
- Mixed gas buffer bottle: The buffer bottle is mixed with four gases in the latter stage. After mixing, it is output from the buffer bottle all the way to the bottom of the chamber and all the way to the top, and one of them can be closed independently;
- Inflating device: the uniform gas pipeline at the outlet of the gas circuit of the chamber body, which is evenly charged to the target surface to make the coating uniform is better.
Control system
- Touch screen: take TPC1570GI touch screen as host computer + keyboard and mouse;
- Control software: tabular process parameter setting, alarm parameter display, vacuum parameter display and curve display, RF power supply and DC direct current power supply parameter setting and display, all valve and switch working state records, process records, alarm records, vacuum record parameters , can be stored for about half a year, and the process operation of the whole equipment is saved in 1 second to save the parameters;
- PLC: Omron PLC is used as the lower computer to collect data of various components and in-position switches, control valves and various components, and then perform data interaction, display and control with configuration software. This is more secure and reliable;
- Control status: one-button coating, automatic vacuuming, automatic constant vacuum, automatic heating, automatic multi-layer process deposition, automatic completion of pick-up and other work;
- Advantages of touch screen: touch screen control software cannot be changed, stable operation is more convenient and flexible, but the amount of stored data is limited, parameters can be directly exported, and when there is a problem with the process; 6. Alarm: adopt the sound and light alarm mode, and record the alarm in the configuration alarm parameter library. It can be queried at any time in the future, and the saved data can be queried and called at any time.
Constant vacuum
- Butterfly valve constant vacuum: DN80 butterfly valve cooperates with Inficon CDG025 capacitive film gauge to work constant vacuum, the disadvantage is that the valve port is easy to be polluted and difficult to clean;
- Valve Position Mode: Set the position control mode.
Water, electricity, gas
- The main inlet and outlet pipes are made of stainless steel and equipped with emergency water inlets;
- All water-cooled pipes outside the vacuum chamber adopt stainless steel quick-change fixed joints and plastic high-pressure ( High-quality water pipes, which can be used for a long time without leaking or breaking), and the water inlet and outlet plastic high-pressure water pipes should be displayed in two different colors and correspondingly marked; brand Airtek;
- All water-cooled tubes inside the vacuum chamber are made of high-quality SUS304 material;
- The water and gas circuits are respectively installed with safe and reliable, high-precision display water pressure and air pressure instruments .
- Equipped with 8P chiller for water flow of carbon film machine.
- Equipped with a set of 6KW hot water machine, when the door is opened, hot water will flow through the room.
Security protection requirements
- The machine is equipped with an alarm device;
- When the water pressure or air pressure does not reach the specified flow rate, all vacuum pumps and valves are protected and cannot be started, and an alarm sound and red signal light prompt;
- When the machine is in normal working process, when the water pressure or air pressure is suddenly insufficient, all valves will be automatically closed, and an alarm sound and red signal light will appear;
- When the operating system is abnormal (high voltage, ion source, control system), there will be an alarm sound and a red signal light prompt;
- The high voltage is turned on, and there is a protection alarm device.
Working environment requirements
- Ambient temperature: 10~35℃;
- Relative humidity: not more than 80%;
- The environment around the equipment is clean and the air is clean. There should be no dust or gas that can cause corrosion of electrical appliances and other metal surfaces or cause electrical conduction between metals.
Equipment power requirements
- Water source: industrial soft water, water pressure 0.2~0.3Mpa, water volume~60L/min , water inlet temperature≤25°C; water pipe connection 1.5 inches;
- Air source: air pressure 0.6MPa;
- Power supply: three-phase five-wire system 380V, 50Hz, voltage fluctuation range: line voltage 342 ~ 399V, phase voltage 198 ~ 231V; frequency fluctuation range: 49 ~ 51Hz; equipment power consumption: ~ 16KW; grounding resistance ≤ 1Ω;
- Hoisting requirements: self-provided 3-ton crane, hoisting door not less than 2000X2200mm
Warnings
Operator safety is the top important issue! Please operate the equipment with cautions. Working with inflammable& explosive or toxic gases is very dangerous, operators must take all necessary precautions before starting the equipment. Working with positive pressure inside the reactors or chambers is dangerous, operator must fellow the safety procedures strictly. Extra caution must also be taken when operating with air-reactive materials, especially under vacuum. A leak can draw air into the apparatus and cause a violent reaction to occur.
Designed for You
KinTek provide deep custom made service and equipment to worldwide customers, our specialized teamwork and rich experienced engineers are capable to undertake the custom tailoring hardware and software equipment requirements, and help our customer to build up the exclusive and personalized equipment and solution!
Would you please drop your ideas to us, our engineers are ready for you now!
Trusted by Industry Leaders

FAQ
What Is PECVD Method?
What Is PECVD Used For?
What Are The Advantages Of PECVD?
What Is The Difference Between ALD And PECVD?
What Is The Difference Between PECVD And Sputtering?
4.7 / 5
RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition is a great tool for depositing high-quality thin films. We've been using it for several months now and have been very happy with the results.
4.8 / 5
RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition has been a lifesaver in our lab. It's allowed us to produce high-quality thin films quickly and easily.
4.9 / 5
We are very satisfied with the RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition. It's a well-built system that produces high-quality results. The customer service is also excellent.
5.0 / 5
RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition is a game-changer for our research. It's allowed us to explore new possibilities that we never thought possible.
4.7 / 5
We've been using RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition for a few months now and have been very impressed with its performance. It's a powerful tool that has helped us to achieve great results.
4.8 / 5
RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition is a great investment for any lab. It's easy to use and produces high-quality results. I highly recommend it.
4.9 / 5
We're very happy with our RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition. It's a reliable system that has helped us to improve our research.
5.0 / 5
RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition is a top-of-the-line system. It's a must-have for any lab that wants to stay ahead of the curve.
4.7 / 5
We've been using RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition for a few years now and have been very happy with it. It's a versatile system that can be used for a variety of applications.
4.8 / 5
RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition is a great value for the money. It's a powerful system that can be used for a variety of applications.
4.9 / 5
We're very satisfied with the RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition. It's a well-built system that produces high-quality results. The customer service is also excellent.
5.0 / 5
RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition is a game-changer for our research. It's allowed us to explore new possibilities that we never thought possible.
4.7 / 5
We've been using RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition for a few months now and have been very impressed with its performance. It's a powerful tool that has helped us to achieve great results.
4.8 / 5
RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition is a great investment for any lab. It's easy to use and produces high-quality results. I highly recommend it.
4.9 / 5
We're very happy with our RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition. It's a reliable system that has helped us to improve our research.
5.0 / 5
RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition is a top-of-the-line system. It's a must-have for any lab that wants to stay ahead of the curve.
4.7 / 5
We've been using RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition for a few years now and have been very happy with it. It's a versatile system that can be used for a variety of applications.
4.8 / 5
RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition is a great value for the money. It's a powerful system that can be used for a variety of applications.
4.9 / 5
We're very satisfied with the RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition. It's a well-built system that produces high-quality results. The customer service is also excellent.
REQUEST A QUOTE
Our professional team will reply to you within one business day. Please feel free to contact us!
Related Products

Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
KT-PE12 Slide PECVD System: Wide power range, programmable temp control, fast heating/cooling with sliding system, MFC mass flow control & vacuum pump.

915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine and its multi-crystal effective growth, the maximum area can reach 8 inches, the maximum effective growth area of single crystal can reach 5 inches. This equipment is mainly used for the production of large-size polycrystalline diamond films, the growth of long single crystal diamonds, the low-temperature growth of high-quality graphene, and other materials that require energy provided by microwave plasma for growth.

Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
Learn about Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine, the microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition method used for growing diamond gemstones and films in the jewelry and semi-conductor industries. Discover its cost-effective advantages over traditional HPHT methods.

Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
Get your exclusive CVD furnace with KT-CTF16 Customer Made Versatile Furnace. Customizable sliding, rotating, and tilting functions for precise reactions. Order now!

Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
Discover our Glassy Carbon Sheet - RVC. Perfect for your experiments, this high-quality material will elevate your research to the next level.

Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
Discover the benefits of Spark Plasma Sintering Furnaces for rapid, low-temperature material preparation. Uniform heating, low cost & eco-friendly.

Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
Evaporation boat sources are used in thermal evaporation systems and are suitable for depositing various metals, alloys and materials. Evaporation boat sources are available in different thicknesses of tungsten, tantalum and molybdenum to ensure compatibility with a variety of power sources. As a container, it is used for vacuum evaporation of materials. They can be used for thin film deposition of various materials, or designed to be compatible with techniques such as electron beam fabrication.

VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
A hydrogen peroxide space sterilizer is a device that uses vaporized hydrogen peroxide to decontaminate enclosed spaces. It kills microorganisms by damaging their cellular components and genetic material.

Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
Elevate your experiments with our Metal Disk Electrode. High-quality, acid and alkali resistant, and customizable to fit your specific needs. Discover our complete models today.

1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
Discover our KT-12A Pro Controlled atmosphere furnace - high precision, heavy duty vacuum chamber, versatile smart touch screen controller, and excellent temperature uniformity up to 1200C. Ideal for both laboratory and industrial application.

Lab Infrared Press Mold
Easily release samples from our lab infrared press mold for accurate testing. Ideal for battery, cement, ceramics, and other sample preparation research. Customizable sizes available.

XRF & KBR steel ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
Produce perfect XRF samples with our steel ring lab powder pellet pressing mold. Fast tableting speed and customizable sizes for accurate molding every time.

Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
Explore the benefits of Non-Consumable Vacuum Arc Furnace with high melting point electrodes. Small, easy to operate & eco-friendly. Ideal for laboratory research on refractory metals & carbides.

Glassy Carbon Electrochemical Electrode
Upgrade your experiments with our Glassy Carbon Electrode. Safe, durable, and customizable to fit your specific needs. Discover our complete models today.

Side Window Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
Experience reliable and efficient electrochemical experiments with a side window optical electrolytic cell. Boasting corrosion resistance and complete specifications, this cell is customizable and built to last.

Narrow Band Pass Filters for Precision Applications
A narrow bandpass filter is an expertly engineered optical filter specifically designed to isolate a narrow range of wavelengths while effectively rejecting all other wavelengths of light.
Related Articles

Understanding PECVD: A Guide to Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
PECVD is a useful technique for creating thin film coatings because it allows for the deposition of a wide variety of materials, including oxides, nitrides, and carbides.

Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD): A Comprehensive Guide
Learn everything you need to know about Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD), a thin film deposition technique used in the semiconductor industry. Explore its principles, applications, and benefits.

How to Achieve High Quality Single-Crystal Diamond with MPCVD
Microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition (MPCVD) is a popular technique for producing high-quality single-crystal diamond.

The Role of Plasma in PECVD Coatings
PECVD (Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition) is a type of thin film deposition process that is widely used for creating coatings on various substrates. In this process, a plasma is used to deposit thin films of various materials onto a substrate.

An Introduction to Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Chemical vapor deposition, or CVD, is a coating process that involves the use of gaseous reactants to produce thin films and coatings of high quality.

A Step-by-Step Guide to the PECVD Process
PECVD is a type of chemical vapor deposition process that uses plasma to enhance the chemical reactions between the gas-phase precursors and the substrate.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a versatile thin-film deposition technique widely used in various industries. Explore its advantages, disadvantages, and potential new applications.

Why PECVD is Essential for Microelectronic Device Fabrication
PECVD (Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition) is a popular thin film deposition technique used in microelectronics device fabrication.

Comparing the Performance of PECVD and HPCVD in Coating Applications
Although both PECVD & HFCVD are used for coating applications, they differ in terms of deposition methods, performance, and suitability for specific applications.

Key Materials for Successful CVD Processes
The success of CVD processes is dependent on the availability and quality of precursors used during the process.

A Comprehensive Guide to PECVD Equipment Maintenance
Proper maintenance of PECVD equipment is crucial to ensure its optimal performance, longevity, and safety.

Understanding the PECVD Method
PECVD is a plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition process that is widely used in the production of thin films for various applications.