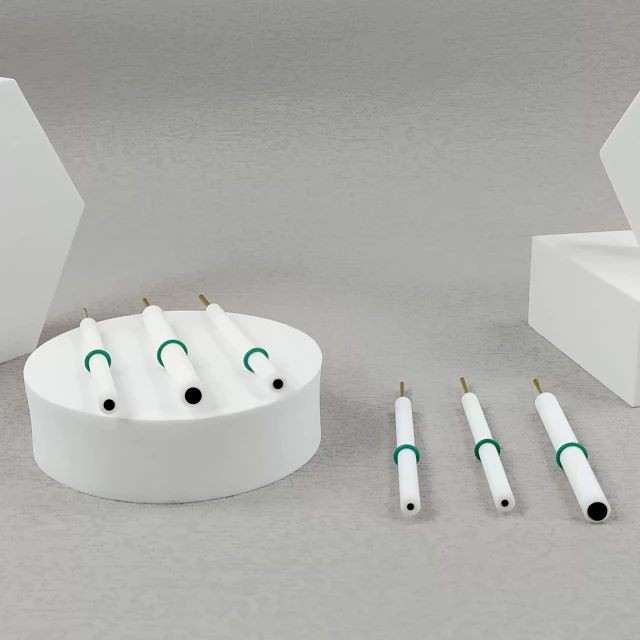

Electrochemical Consumables
Glassy Carbon Electrochemical Electrode
Item Number : ELEGC
Price varies based on specs and customizations
$54.90 / set
- Specification
- Inner diameter 2~6mm, can be customized
- Applicable temperature range
- 0 ~ 60℃
- Rod material
- PTFE
- Material
- glassy carbon > 99.99%
Shipping:
Contact us to get shipping details Enjoy On-time Dispatch Guarantee.
Why Choose Us
Easy ordering process, quality products, and dedicated support for your business success.
The glassy carbon electrode is made from high-quality materials and is safe and durable. It can be customized according to specific needs and is capable of accommodating complete models.
Technical specifications
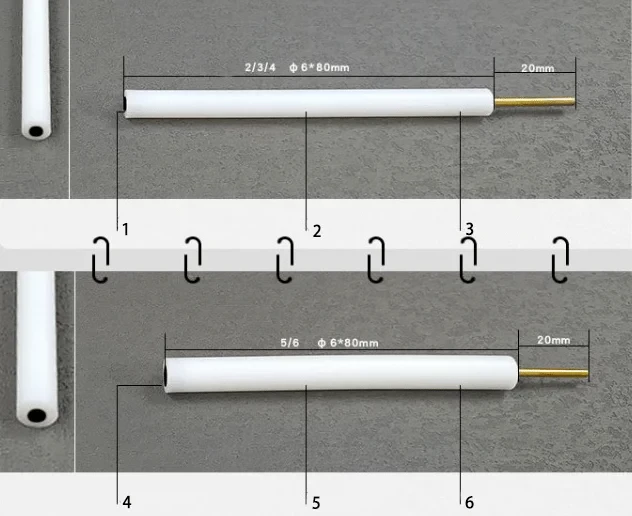
| Specification | Inner diameter 2~6mm, can be customized |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Rod material | PTFE |
| Material | Imported glassy carbon > 99.99% |
Detail & Parts
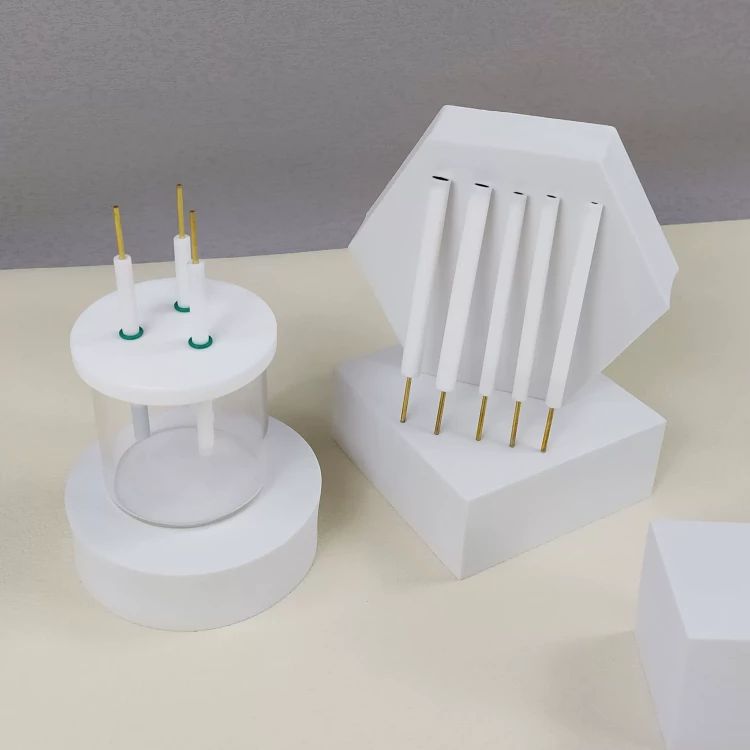


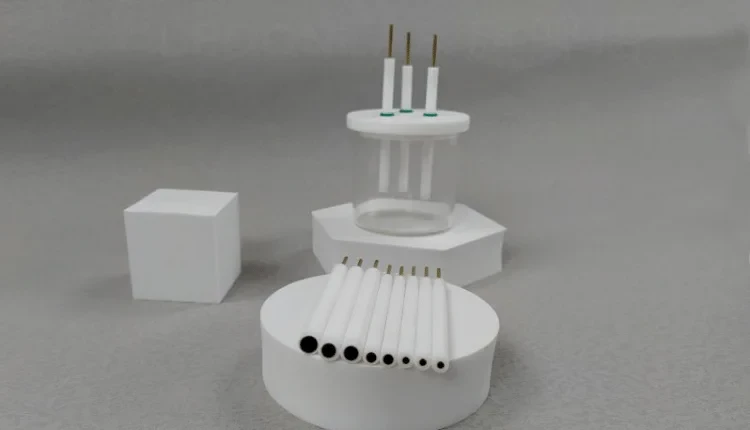
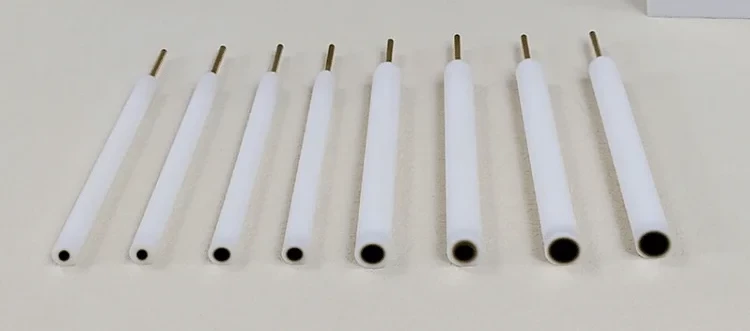
Designed for You
KinTek provide deep custom made service and equipment to worldwide customers, our specialized teamwork and rich experienced engineers are capable to undertake the custom tailoring hardware and software equipment requirements, and help our customer to build up the exclusive and personalized equipment and solution!
Would you please drop your ideas to us, our engineers are ready for you now!
Trusted by Industry Leaders

FAQ
What Is An Electrode In Electrochemistry?
What Is The Function Of Auxiliary Electrode?
What Are The 3 Electrodes In Electrochemistry?
What Is The Difference Between Auxiliary And Reference Electrode?
What Are The Different Types Of Electrochemical Electrodes?
What Materials Are Commonly Used For Auxiliary Electrodes?
What Materials Are Commonly Used For Electrochemical Electrodes?
How Do Auxiliary Electrodes Affect The Performance Of An Electrochemical Cell?
What Factors Should Be Considered When Selecting An Electrochemical Electrode?
Why Are Auxiliary Electrodes Necessary In Electrochemical Systems?
How Can Electrochemical Electrodes Be Used In Various Applications?
Are There Any Limitations Or Considerations When Using Auxiliary Electrodes?
4.8 / 5
The glassy carbon electrode arrived promptly and was packaged with care. I highly recommend this product.
4.9 / 5
I'm very impressed with the quality of this electrode. It's well-made and durable, and it's producing excellent results in my experiments.
4.7 / 5
This electrode is a great value for the price. It's performing just as well as more expensive electrodes I've used in the past.
5.0 / 5
I'm very happy with this electrode. It's easy to use and clean, and it's giving me very consistent results.
4.8 / 5
This electrode is a great addition to my lab. It's helping me get more accurate and reliable results in my experiments.
4.9 / 5
I'm very impressed with the performance of this electrode. It's sensitive and responsive, and it's helping me get better data in my research.
5.0 / 5
This electrode is a game-changer for my lab. It's helping me get faster and more accurate results, which is saving me time and money.
4.7 / 5
I'm very happy with this electrode. It's well-made and durable, and it's giving me very consistent results.
4.8 / 5
This electrode is a great value for the price. It's performing just as well as more expensive electrodes I've used in the past.
4.9 / 5
I'm very impressed with the quality of this electrode. It's well-made and durable, and it's producing excellent results in my experiments.
5.0 / 5
This electrode is a great addition to my lab. It's helping me get more accurate and reliable results in my experiments.
4.8 / 5
I'm very happy with this electrode. It's easy to use and clean, and it's giving me very consistent results.
4.9 / 5
I'm very impressed with the performance of this electrode. It's sensitive and responsive, and it's helping me get better data in my research.
5.0 / 5
This electrode is a game-changer for my lab. It's helping me get faster and more accurate results, which is saving me time and money.
REQUEST A QUOTE
Our professional team will reply to you within one business day. Please feel free to contact us!
Related Products

Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
Discover our Glassy Carbon Sheet - RVC. Perfect for your experiments, this high-quality material will elevate your research to the next level.

Conductive Carbon Cloth Carbon Paper Carbon Felt for Electrodes and Batteries
Conductive carbon cloth, paper, and felt for electrochemical experiments. High-quality materials for reliable and accurate results. Order now for customization options.

Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
Elevate your experiments with our Metal Disk Electrode. High-quality, acid and alkali resistant, and customizable to fit your specific needs. Discover our complete models today.

Side Window Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
Experience reliable and efficient electrochemical experiments with a side window optical electrolytic cell. Boasting corrosion resistance and complete specifications, this cell is customizable and built to last.

Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
Experience optimal performance with our Water Bath Electrolytic Cell. Our double-layer, five-port design boasts corrosion resistance and longevity. Customizable to fit your specific needs. View specs now.

Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer CaF2 Substrate Window Lens
A CaF2 window is an optical window made of crystalline calcium fluoride. These windows are versatile, environmentally stable and resistant to laser damage, and they exhibit a high, stable transmission from 200 nm to about 7 μm.
Related Articles

Innovations in Electrochemical Electrodes Technology
Recent advancements in nanotechnology and materials science have led to significant improvements in electrochemical devices, making them more efficient, durable, and cost-effective.

The Future of Electrochemical Electrodes
The latest trends and developments in electrode materials and their implications for the future of electrochemistry.

How to Make Your Own Ag/AgCl Reference Electrode for Electrochemical Experiments
A reference electrode is an electrode with a stable and well-defined potential that is used as a reference point to measure the potential of other electrodes. Reference electrodes are commonly used in electrochemical experiments to determine the potential difference between two electrodes.

Electrode Fixture Guide: Types, Design, and Applications
Discover the comprehensive guide to electrode fixtures, covering various types, design considerations, and their indispensable role in industries like electroplating, welding, and electrochemical cells.

Understanding Saturated Calomel Reference Electrodes: Composition, Uses, and Considerations
Explore the detailed guide on saturated calomel reference electrodes, including their composition, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. Ideal for researchers and lab technicians.

Pseudo-Reference Electrodes When and How to Use Them
Reference electrodes are an essential component in electrochemical measurements. They are used to establish a stable and reproducible potential for the working electrode and provide a reference point for the measurement. The reference electrode should have a stable and well-defined potential, which is independent of the solution's composition and the working electrode's potential.

Glymercury Electrode: Composition, Characteristics, and Applications
An in-depth look at the glymercury electrode, its composition, characteristics, and applications in analytical chemistry.

Design and Application of Reference Electrodes in Lithium Batteries
An in-depth analysis of the design, features, and applications of reference electrodes in lithium batteries.

The Invisible Architecture of Accuracy: Mastering Electrode Installation
Master the lifecycle of electrode installation—from inspection to alignment and maintenance—to ensure safety and reproducibility in electrochemical experiments.

Exploring Rotating Electrode Technology in Electrochemistry
An in-depth analysis of rotating electrode technology, its applications, and its impact on electrochemical reactions under different flow conditions.

The Art of Resistance: Why Your Electrolytic Cell Needs Breathing Room
Short circuits in electrolytic cells aren't just accidents; they are geometry failures. Learn how to control the electrical path and protect your lab equipment.

The Art of the Non-Spontaneous: Precision in Electrolytic Circuits
Mastering the electrolytic cell setup requires more than connecting wires. It demands a systematic approach to polarity, purity, and power control.