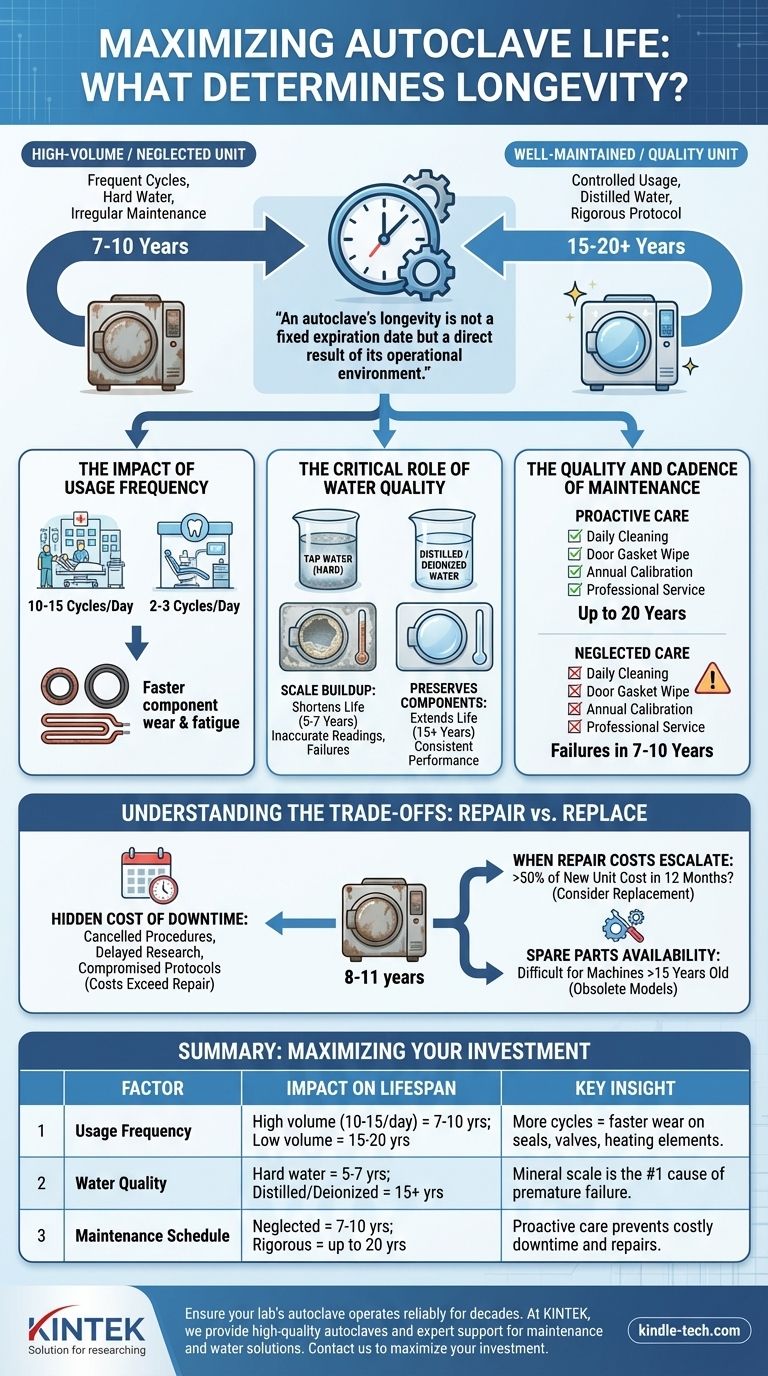
Determining an autoclave's lifespan is not a simple matter of a single number, as it depends heavily on build quality, usage patterns, and, most critically, the quality of its maintenance. A well-maintained, high-quality autoclave can reliably function for 15 to 20 years, while a neglected unit in a high-volume setting may begin to fail in as few as 7 to 10 years.
An autoclave's longevity is not a fixed expiration date but a direct result of its operational environment. The single most important factor within your control is the commitment to a rigorous maintenance schedule and the use of high-purity water.

The Key Factors That Define Autoclave Longevity
An autoclave is a complex piece of equipment where several variables interact to determine its functional lifespan. Understanding these factors is key to maximizing your investment.
The Impact of Usage Frequency
The number of cycles an autoclave runs directly correlates to wear and tear on its core components. Gaskets, seals, valves, and heating elements all have a finite operational life.
A unit in a busy hospital sterile processing department running 10-15 cycles per day will naturally experience component fatigue faster than a unit in a small dental office running 2-3 cycles per day.
The Critical Role of Water Quality
This is arguably the most significant and often overlooked factor in autoclave health. Using tap water or water with high mineral content is the fastest way to shorten an autoclave's life.
Minerals like calcium and magnesium, present in hard water, will precipitate out during the steam generation process. This creates scale buildup inside the chamber, plumbing lines, and on critical sensors, acting like plaque in an artery.
This buildup forces the machine to work harder, leads to inaccurate temperature readings, and can cause catastrophic failures in the heating elements and solenoid valves. The consistent use of distilled or deionized water is non-negotiable for longevity.
The Quality and Cadence of Maintenance
Proactive maintenance is the difference between a 10-year lifespan and a 20-year lifespan. This includes both daily user tasks and professional annual servicing.
Regular user maintenance involves cleaning the chamber, wiping the door gasket, and ensuring filters are clear. Professional annual or semi-annual maintenance includes calibrating sensors, testing safety valves, and inspecting internal wiring and plumbing for wear.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Repair vs. Replace
As an autoclave ages, you will inevitably face the decision of whether to continue repairing it or invest in a replacement. The choice is not just about the cost of a single repair.
The Hidden Cost of Downtime
For any medical, dental, or research facility, a non-functional autoclave can bring operations to a halt. The cost of downtime—cancelled appointments, delayed research, or compromised sterilization protocols—can quickly exceed the cost of a repair or even a new unit.
When Repair Costs Escalate
An isolated repair on a 7-year-old machine may be a sound financial decision. However, when an 11-year-old machine requires its third major repair in a year, you must consider the total cost of ownership.
Track repair expenses over a 12-month period. If the cumulative cost of repairs and downtime approaches 50% of a new unit's price, replacement is often the more prudent long-term choice.
Availability of Spare Parts
For machines older than 15 years, sourcing the correct spare parts can become difficult and expensive. Manufacturers eventually discontinue support for older models, making a simple repair impossible and forcing a replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your strategy for managing your autoclave should align with your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximizing lifespan: Implement a strict daily maintenance protocol and mandate the exclusive use of distilled or deionized water.
- If your primary focus is financial planning: Budget for autoclave replacement on a 10- to 15-year cycle, especially in high-volume environments, to avoid being forced by an unexpected catastrophic failure.
- If your primary focus is operational reliability: Track the frequency of service calls for any machine over 8 years old; an increasing trend is a clear indicator that it is time to plan for replacement.
Ultimately, proactive care and informed planning are the keys to managing the lifecycle of this mission-critical equipment.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Lifespan | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Usage Frequency | High-volume use (10-15 cycles/day) shortens lifespan to 7-10 years; low-volume use extends it to 15-20 years. | More cycles = faster wear on seals, valves, and heating elements. |
| Water Quality | Hard water causes scale buildup, leading to failures in 5-7 years; distilled/deionized water preserves components for 15+ years. | Mineral scale is the #1 cause of premature failure. |
| Maintenance Schedule | Neglected units fail in 7-10 years; rigorous daily/annual maintenance can double the lifespan to 20 years. | Proactive care prevents costly downtime and repairs. |
Ensure your lab’s autoclave operates reliably for decades. At KINTEK, we understand that your laboratory’s efficiency depends on durable, well-maintained equipment. Our range of high-quality autoclaves and consumables is designed for longevity, and our expert support team provides guidance on maintenance protocols and water purification solutions to maximize your investment. Don’t let unexpected downtime disrupt your workflow—contact us today to discuss your sterilization needs and keep your lab running smoothly.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What precautions should be taken during autoclave in laboratory? A Complete Safety Guide to Prevent Burns and Explosions
- What types of items and materials can be processed in a laboratory autoclave? Essential Guide for Lab Safety
- How do you use an autoclave in a microbiology lab? Master Sterilization for Lab Safety & Accuracy
- What role do laboratory autoclaves play in pectin extraction? Optimize Prebiotic Yield from Citrus and Apple Biomass



















