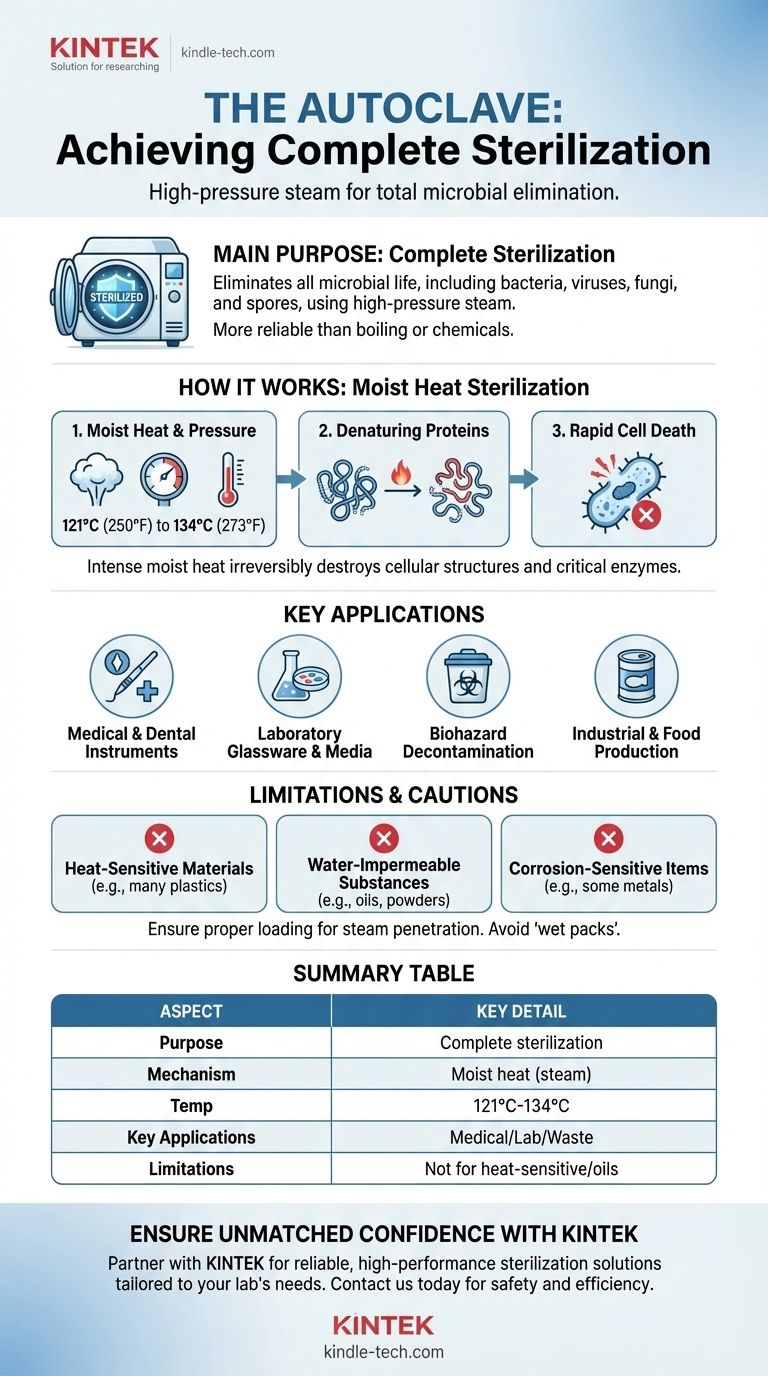
In short, the main purpose of an autoclave is to achieve complete sterilization. It uses high-pressure steam to eliminate all forms of microbial life—including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and even highly resistant spores—from equipment, liquids, and waste materials.
The autoclave is not merely a cleaning device; it is a precision instrument designed for sterilization. It leverages the physical properties of steam under pressure to achieve a level of microbial destruction that is far more reliable and effective than simple boiling or chemical disinfectants.
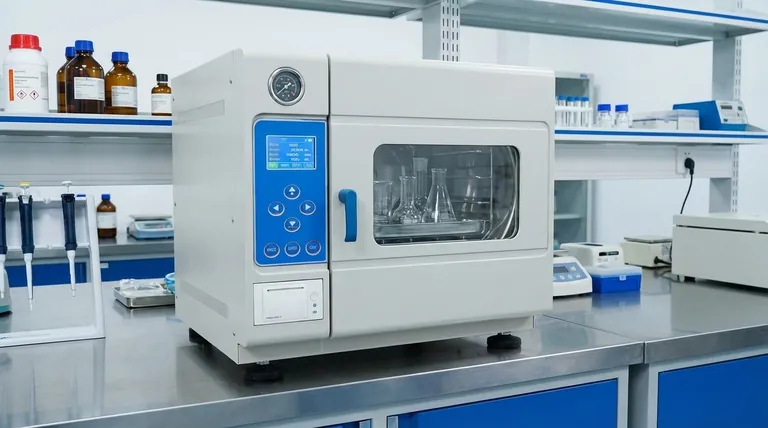

How Autoclaves Achieve Sterilization
An autoclave operates on a principle known as moist heat sterilization. This method is considered the gold standard in many scientific and medical fields for its exceptional effectiveness and reliability.
The Principle of Moist Heat
Moist heat, in the form of saturated steam, is significantly more efficient at transferring thermal energy than dry heat. This allows it to penetrate materials and kill microorganisms much more quickly and at lower temperatures than a dry heat oven.
The process works by subjecting the items inside the chamber to steam at a temperature well above the boiling point of water.
The Role of Pressure and Temperature
By increasing the pressure inside its sealed vessel, an autoclave can raise the boiling point of water. This allows it to create steam at temperatures typically ranging from 121°C (250°F) to 134°C (273°F).
These extreme temperatures are lethal to almost all forms of life, but the key is the combination of heat and moisture delivered by the steam.
The Mechanism: Denaturing Proteins
The intense, moist heat irreversibly coagulates and denatures essential proteins and enzymes within microbial cells. This process destroys the cellular structure and disrupts critical metabolic functions, leading to rapid cell death.
This is why autoclaving is effective against even the most resilient organisms, such as bacterial spores, which can survive boiling and many chemical treatments.
Key Applications and Use Cases
The reliability of steam sterilization makes the autoclave an indispensable tool across numerous industries.
Medical and Laboratory Settings
In hospitals, clinics, and dental offices, autoclaves are used to sterilize surgical instruments, dental tools, and other reusable medical devices to prevent patient infections.
In microbiology and research labs, they are essential for sterilizing glassware, plasticware, and culture media to avoid contamination of experiments.
Decontamination of Biohazardous Waste
Before disposal, infectious materials like used petri dishes, live cultures, and medical waste must be rendered non-hazardous.
Autoclaving is the most dependable method for decontaminating this biohazardous waste, ensuring that all infectious agents are destroyed.
Industrial and Production Roles
In food production, autoclaves are used to sterilize canned goods, achieving commercial sterility and extending shelf life. They are also used in manufacturing settings where sterile conditions are paramount, such as in the production of pharmaceuticals.
Understanding the Limitations and Trade-offs
While powerful, the autoclave is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is crucial for safe and effective operation.
Not Suitable for All Materials
The high heat and moisture will damage or destroy certain items. Autoclaves cannot be used for:
- Heat-sensitive materials, such as many types of plastics that would melt.
- Water-impermeable substances, like oils, waxes, or powders, as the steam cannot penetrate them to ensure sterilization.
- Corrosion-sensitive instruments, as repeated exposure to steam can cause rust or dull sharp edges.
The Importance of Proper Loading
For sterilization to be successful, steam must be able to circulate freely and contact every surface of the items being processed.
Overpacking the chamber or using sealed containers will create air pockets and prevent proper steam penetration, leading to sterilization failure. This is one of the most common user errors.
The Risk of Wet Packs
A successful cycle should result in a dry load. "Wet packs"—items that are still damp or wet at the end of a cycle—are considered unsterile because moisture can compromise the sterile barrier and harbor microbial growth.
Modern autoclaves often feature a jacketed chamber, where an outer jacket is filled with steam to preheat the inner chamber walls, which helps minimize condensation and prevent wet packs.
How to Apply This to Your Task
Your choice of sterilization method must be guided by the material you are processing and your ultimate goal.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-resistant, steam-permeable items like glassware, surgical steel, or culture media: The autoclave is the most reliable and effective method available.
- If your primary focus is decontaminating biohazardous waste: Steam sterilization via an autoclave is the industry standard for rendering waste non-infectious before disposal.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive materials, oils, or powders: You must use an alternative, such as ethylene oxide (EtO) gas, gamma irradiation, or dry heat sterilization, as autoclaving is not suitable.
Ultimately, the autoclave's purpose is to provide an unmatched level of confidence that an item is truly sterile and free from all living microorganisms.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Complete sterilization of equipment, liquids, and waste. |
| Mechanism | Moist heat sterilization using high-pressure steam. |
| Typical Temperature | 121°C (250°F) to 134°C (273°F). |
| Key Applications | Medical instrument sterilization, lab decontamination, biohazardous waste treatment. |
| Limitations | Not suitable for heat-sensitive materials, oils, powders, or water-impermeable substances. |
Ensure Unmatched Sterilization Confidence in Your Lab
Understanding the critical role of an autoclave is the first step. Implementing the right sterilization solution for your specific needs is what ensures safety, compliance, and success in your work.
KINTEK is your trusted partner for all laboratory sterilization needs. We specialize in providing high-quality autoclaves and lab equipment designed for reliability and performance. Whether you are setting up a new research facility, a clinical practice, or need to upgrade your current decontamination processes, we have the expertise and products to support you.
Let us help you achieve complete peace of mind with a sterilization solution tailored to your laboratory's unique requirements.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your autoclave needs and ensure your lab operates with the highest standards of safety and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the most common sterilization technique used in labs? Mastering the Autoclave for Unmatched Safety
- What are the considerations for autoclave? Ensure Sterilization Success and Safety
- Do liquids boil in an autoclave? How to Safely Sterilize Media Without Boil-Over
- How do you autoclave lab equipment? A Step-by-Step Guide to Sterile Results
- Can autoclave sterilize liquid? Master Safe and Effective Liquid Sterilization



















