The principle of an evaporator vacuum pump revolves around creating a low-pressure environment within the rotary evaporator system. This reduction in pressure lowers the boiling point of the solvent, enabling evaporation at lower temperatures, which is crucial for preserving heat-sensitive compounds. The pump removes air and gas molecules from the system, maintaining a vacuum that facilitates efficient evaporation and condensation. Diaphragm vacuum pumps, often used in rotary evaporators, operate by mechanically oscillating a diaphragm to create periodic changes in the pumping chamber's volume, allowing gas molecules to be drawn in and expelled. This process ensures a dry, oil-free vacuum, making it suitable for sensitive applications.
Key Points Explained:
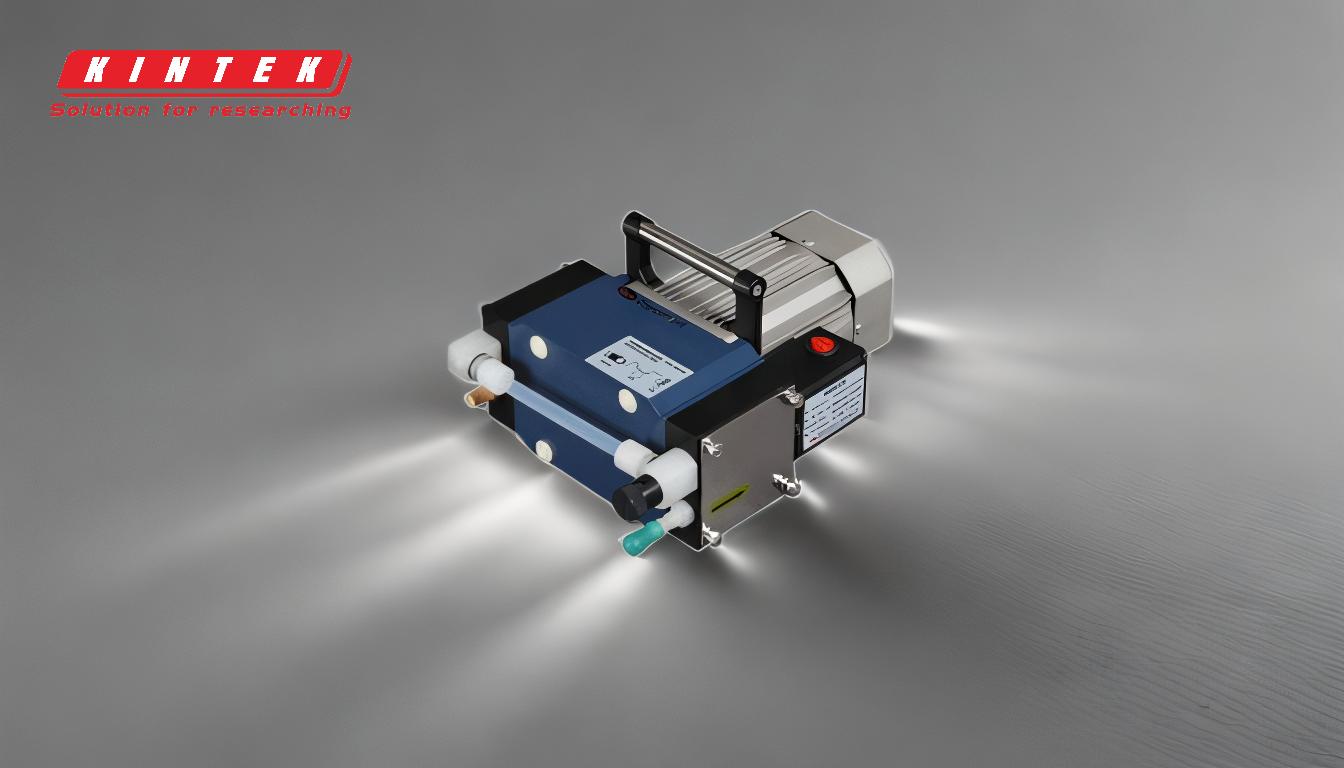
-
Purpose of the Vacuum Pump in a Rotary Evaporator:
- The primary role of the vacuum pump is to lower the pressure inside the rotary evaporator, creating a vacuum. This reduces the boiling point of the solvent, allowing it to evaporate at lower temperatures. This is particularly important for heat-sensitive compounds, as it minimizes the risk of thermal degradation.
-
Mechanism of Pressure Reduction:
- Vacuum pumps remove gas molecules or air particles from the sealed volume of the rotary evaporator. This alters the pressure within the system, creating a partial or full vacuum. The natural flow of gas molecules from high-pressure to low-pressure areas is exploited to achieve this.
-
Lowering the Boiling Point:
- By reducing the vapor pressure within the system, the vacuum pump enables the solvent to boil at a lower temperature. This not only speeds up the evaporation process but also ensures that the sample is not exposed to high temperatures, which could otherwise cause damage or degradation.
-
Types of Vacuum Pumps:
- Diaphragm vacuum pumps are commonly used in rotary evaporators. These pumps operate by oscillating a diaphragm, which periodically changes the volume of the pumping chamber. This action draws in gas molecules during the expansion phase and expels them during the compression phase. The diaphragm provides a hermetic seal, ensuring that the system remains free of oil and lubricants, which is essential for maintaining the purity of the sample.
-
Operation of Diaphragm Vacuum Pumps:
- The diaphragm is tensioned between the pump head and the casing wall. It is moved in an oscillating manner by a connecting rod and an eccentric. Valves are arranged so that during the expansion phase, the chamber is open to the intake line, and during compression, it is linked to the exhaust line. This creates a continuous pumping action, maintaining the vacuum within the system.
-
Integration with Rotary Evaporator:
- The vacuum pump works in conjunction with the rotary evaporator’s vacuum controller, allowing the user to preset a specific pressure. This ensures precise control over the evaporation process, making it more efficient and reproducible.
-
Maintaining the Vacuum:
- Once the vacuum pump evacuates the air from the rotary evaporator, it continues to maintain the vacuum inside the system. This is crucial for the continuous evaporation and condensation process, ensuring that the solvent is efficiently removed from the sample.
-
Industrial Applications:
- In industrial settings, vacuum pumps operate over a wide pressure range, typically from 1.3 to 13.3 mbar. As the pressure decreases, removing additional molecules becomes more challenging, requiring the system to be highly efficient and capable of operating under varying pressure conditions.
By understanding these key points, one can appreciate the critical role that vacuum pumps play in the operation of rotary evaporators. Their ability to create and maintain a vacuum not only enhances the efficiency of the evaporation process but also ensures the integrity of sensitive compounds, making them indispensable in both laboratory and industrial settings.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Lowers pressure to reduce solvent boiling point, preserving heat-sensitive compounds. |
| Mechanism | Removes gas molecules to create a vacuum, enabling lower-temperature evaporation. |
| Types of Pumps | Diaphragm pumps are commonly used, providing oil-free, dry vacuum operation. |
| Operation | Oscillating diaphragm creates volume changes, drawing in and expelling gas molecules. |
| Integration | Works with vacuum controllers for precise pressure control and reproducibility. |
| Industrial Applications | Operates at 1.3–13.3 mbar, ensuring efficiency across varying pressure ranges. |
Discover how an evaporator vacuum pump can optimize your processes—contact us today for expert advice!









