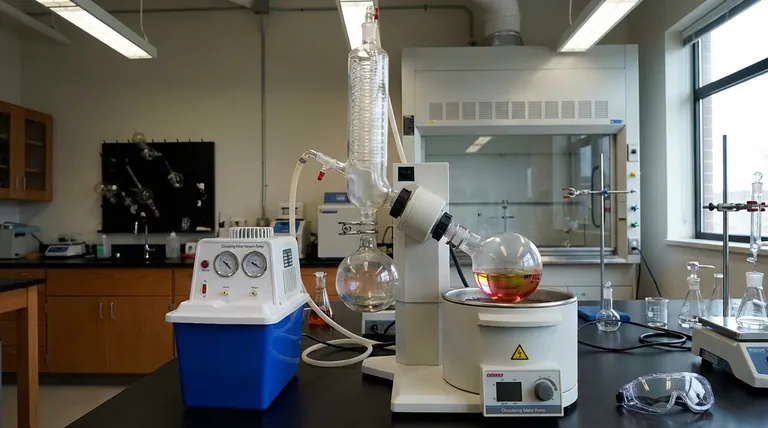
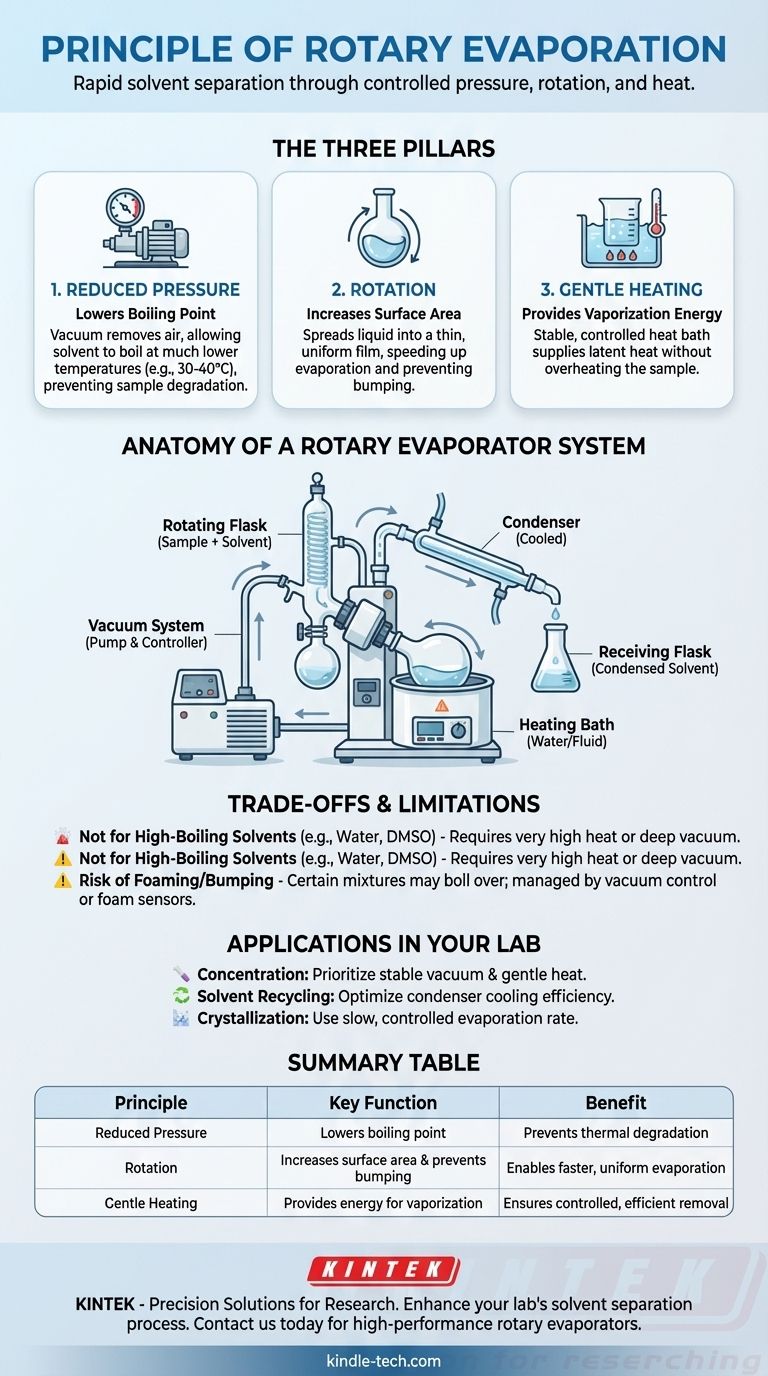
At its core, the principle of rotary evaporation is to rapidly separate a solvent from a sample by manipulating three key physical factors. It works by increasing the sample's surface area through rotation, lowering the solvent's boiling point by reducing pressure with a vacuum, and applying gentle, controlled heat to accelerate the process.
By creating a vacuum, a rotary evaporator allows a solvent to boil at a much lower temperature than normal. This gentle heating, combined with constant rotation to increase surface area, enables fast and efficient solvent removal without damaging the temperature-sensitive compounds left behind.

The Three Pillars of Rotary Evaporation
To truly understand how a rotary evaporator works, you must grasp the interplay of three scientific principles. The machine is designed to optimize each one for gentle and rapid separation.
Principle 1: Reducing Pressure Lowers the Boiling Point
A liquid boils when its vapor pressure equals the pressure of the environment around it. A vacuum pump is used to remove air from the system, drastically lowering the ambient pressure inside.
Because of this reduced pressure, the solvent requires far less heat energy to reach its boiling point. This is the most critical principle, as it allows for evaporation at low temperatures (e.g., 30-40°C) that will not degrade or alter a sensitive chemical sample.
Principle 2: Rotation Increases Surface Area and Prevents Bumping
The sample is held in a round-bottom flask that is continuously rotated by a motor. This rotation spreads the liquid into a thin, uniform film on the inner surface of the flask.
This action dramatically increases the surface area available for evaporation, making the process much faster and more efficient. It also ensures even heat distribution and prevents "bumping"—the violent boiling that can occur when a liquid is heated unevenly, which can lead to sample loss.
Principle 3: Gentle Heating Provides Energy
Evaporation is an endothermic process, meaning it requires an input of energy, known as the latent heat of vaporization. A heated fluid bath, typically filled with water, provides this energy in a stable and controlled manner.
The temperature of the bath is kept just high enough to encourage evaporation at the reduced pressure but low enough to protect the integrity of the target compound.
Anatomy of a Rotary Evaporator System
The principles are put into practice by a system of interconnected components, each with a specific job.
The Rotating Flask and Heating Bath
This is where the separation occurs. The round-bottom flask contains the initial solution (solvent + sample) and is partially submerged in the heated water bath while it rotates.
The Vacuum System
A vacuum pump is connected to the glassware to remove air and maintain the low-pressure environment essential for low-temperature boiling. A vacuum controller allows for precise pressure management.
The Condenser and Receiving Flask
As the solvent evaporates, its vapor travels into a cooled condenser. The condenser, often chilled with a circulating fluid like ethylene glycol, causes the vapor to turn back into a liquid. This purified, condensed solvent then drips into a separate receiving flask for collection or disposal.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, a rotary evaporator is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
Not Ideal for High-Boiling-Point Solvents
Solvents with very high boiling points, like water or DMSO, require either a very deep vacuum or higher temperatures to evaporate efficiently. Applying high heat can defeat the primary purpose of using a rotovap for gentle separation.
The Risk of Foaming and Bumping
Although rotation minimizes bumping, certain mixtures are prone to foaming or boiling over, especially when the vacuum is first applied. This can be managed with careful vacuum control or specialized accessories like a foam sensor.
Volatility of the Target Compound
If the compound you wish to isolate is also volatile, it may co-evaporate with the solvent, leading to product loss. This requires a delicate balance of temperature and vacuum depth to ensure only the desired solvent is removed.
How to Apply This to Your Lab Work
Your specific goal determines how you should optimize the rotary evaporation process.
- If your primary focus is concentrating a solution: Prioritize a stable vacuum and a gentle temperature differential to efficiently remove the solvent without degrading your target compound.
- If your primary focus is solvent distillation and recycling: Optimize the condenser's cooling efficiency to ensure maximum recovery of the vaporized solvent in the receiving flask.
- If your primary focus is crystallization: Use a very slow and controlled evaporation rate by finely adjusting the vacuum to allow large, well-defined crystals to form from the supersaturated solution.
Understanding these core principles transforms the rotary evaporator from a simple machine into a precision instrument for chemical separation.
Summary Table:
| Principle | Key Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced Pressure | Lowers solvent boiling point | Prevents thermal degradation of samples |
| Rotation | Increases surface area & prevents bumping | Enables faster, more uniform evaporation |
| Gentle Heating | Provides energy for vaporization | Ensures controlled, efficient solvent removal |
Ready to enhance your lab's solvent separation process?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance rotary evaporators and lab equipment designed for precision and reliability. Whether you're concentrating solutions, recycling solvents, or crystallizing compounds, our systems provide the gentle, efficient evaporation your sensitive samples require.
Contact us today to find the perfect rotary evaporation solution for your laboratory needs. Let our experts help you optimize your workflow and achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How is a circulating water vacuum pump utilized for hydrogen production residues? Optimize Your Solid-Liquid Separation
- What are the advantages of a water circulating vacuum pump? Superior Durability for Demanding Lab Environments
- What is the purpose of the compression chamber in a vacuum pump? The Heart of Vacuum Generation
- Why is a water circulating vacuum pump suitable for handling flammable or explosive gases? Inherent Safety Through Isothermal Compression
- What can I use a vacuum pump for? Powering Industrial Processes from Packaging to Automation



















