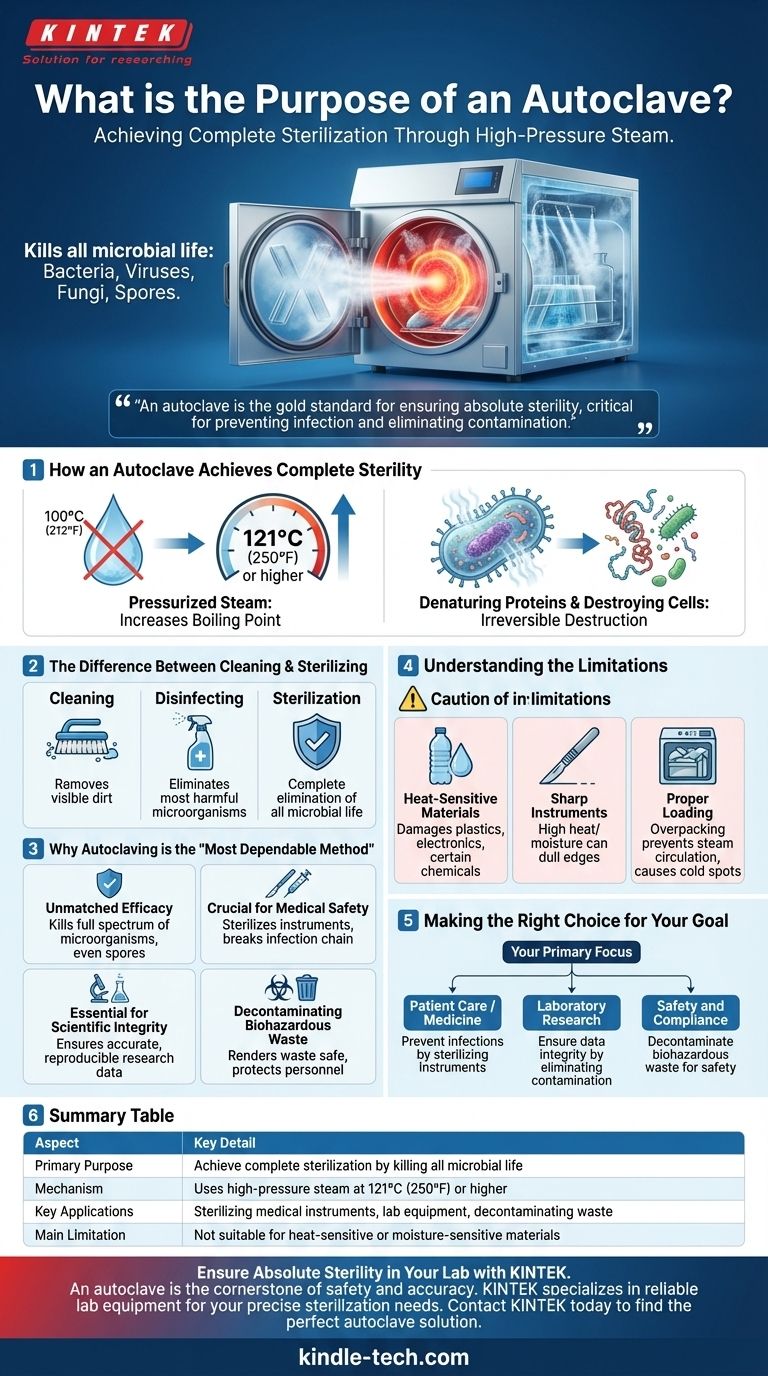
At its core, the purpose of an autoclave is to achieve complete sterilization. It is a machine that uses high-pressure steam to kill all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and even highly resistant bacterial spores, on equipment, liquids, and waste materials.
An autoclave is not merely a high-tech dishwasher; it is the gold standard for ensuring absolute sterility. Its function is critical for preventing infection in medicine and eliminating contamination in scientific research.

How an Autoclave Achieves Complete Sterility
An autoclave's effectiveness comes from a powerful combination of heat and pressure, creating conditions that are lethal to all microorganisms.
The Power of Pressurized Steam
Simply boiling water at 100°C (212°F) is not sufficient to kill all microbes, particularly bacterial spores.
By increasing the pressure inside its chamber, an autoclave raises the boiling point of water. This allows it to generate steam at much higher temperatures, typically 121°C (250°F) or higher.
Denaturing Proteins and Destroying Cells
This superheated, high-pressure steam effectively penetrates materials and transfers heat to any microorganisms present.
The intense heat and moisture rapidly denature essential proteins and enzymes within the microbial cells, causing them to coagulate and die. This process is irreversible and ensures the microbe is not just inhibited, but destroyed.
The Difference Between Cleaning and Sterilizing
It is critical to distinguish between cleaning, disinfecting, and sterilizing.
Cleaning removes visible dirt. Disinfecting eliminates most harmful microorganisms but not all of them. Sterilization, which is what an autoclave does, is the complete elimination of all microbial life.
Why Autoclaving is the "Most Dependable Method"
While other sterilization methods exist, steam autoclaving is widely considered the most reliable and effective for most applications.
Unmatched Efficacy
The combination of moist heat and high pressure is exceptionally effective at killing the full spectrum of microorganisms, from common bacteria to the toughest spores. This makes it the benchmark against which other methods are measured.
Crucial for Medical Safety
In hospitals and clinics, autoclaves sterilize surgical instruments and other medical devices. This breaks the chain of infection, protecting patients from dangerous pathogens that could be transmitted during medical procedures.
Essential for Scientific Integrity
In a laboratory, an unwanted microbe can ruin an experiment, leading to invalid data. Autoclaves are used to sterilize glassware, growth media, and other equipment to ensure that research results are accurate and reproducible.
Decontaminating Biohazardous Waste
Before disposal, materials contaminated with infectious agents (like used petri dishes or lab specimens) must be rendered safe. Autoclaving is the primary method for decontaminating this biohazardous waste, protecting lab personnel and the public.
Understanding the Limitations
While highly effective, autoclaving is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
Not Suitable for Heat-Sensitive Materials
The high temperatures will damage or destroy materials that are sensitive to heat and moisture. This includes many plastics, electronics, and certain chemicals.
Sharp Instruments Can Be Dulled
The combination of high heat and moisture can dull the edges of very sharp surgical instruments over repeated cycles. Other sterilization methods may be preferred for these items.
Proper Loading is Critical
If an autoclave is packed too tightly, the steam cannot penetrate and circulate effectively. This can create cool spots where microorganisms may survive, resulting in a failed sterilization cycle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the core purpose of an autoclave helps contextualize its role in different fields.
- If your primary focus is patient care or medicine: The autoclave is your most important tool for preventing healthcare-associated infections by sterilizing surgical and medical instruments.
- If your primary focus is laboratory research: The autoclave is essential for ensuring data integrity by eliminating microbial contamination from your experiments and media.
- If your primary focus is safety and compliance: The autoclave is the standard for decontaminating biohazardous waste, protecting personnel and the environment from infectious agents.
Ultimately, the autoclave's purpose is to provide an absolute guarantee of sterility, a function foundational to modern medicine and science.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Achieve complete sterilization by killing all microbial life. |
| Mechanism | Uses high-pressure steam at temperatures of 121°C (250°F) or higher. |
| Key Applications | Sterilizing medical instruments, lab equipment, and decontaminating biohazardous waste. |
| Main Limitation | Not suitable for heat-sensitive or moisture-sensitive materials. |
Ensure Absolute Sterility in Your Lab with KINTEK
An autoclave is the cornerstone of safety and accuracy in any laboratory. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables to meet your precise sterilization needs. Whether you are in medical research, pharmaceuticals, or any field requiring uncontaminated results, our expertise ensures you have the right tools for guaranteed sterility.
Let us help you protect your patients, your research, and your team. Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect autoclave solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What is the life expectancy of an autoclave machine? Maximize Your Investment with Proper Care



















