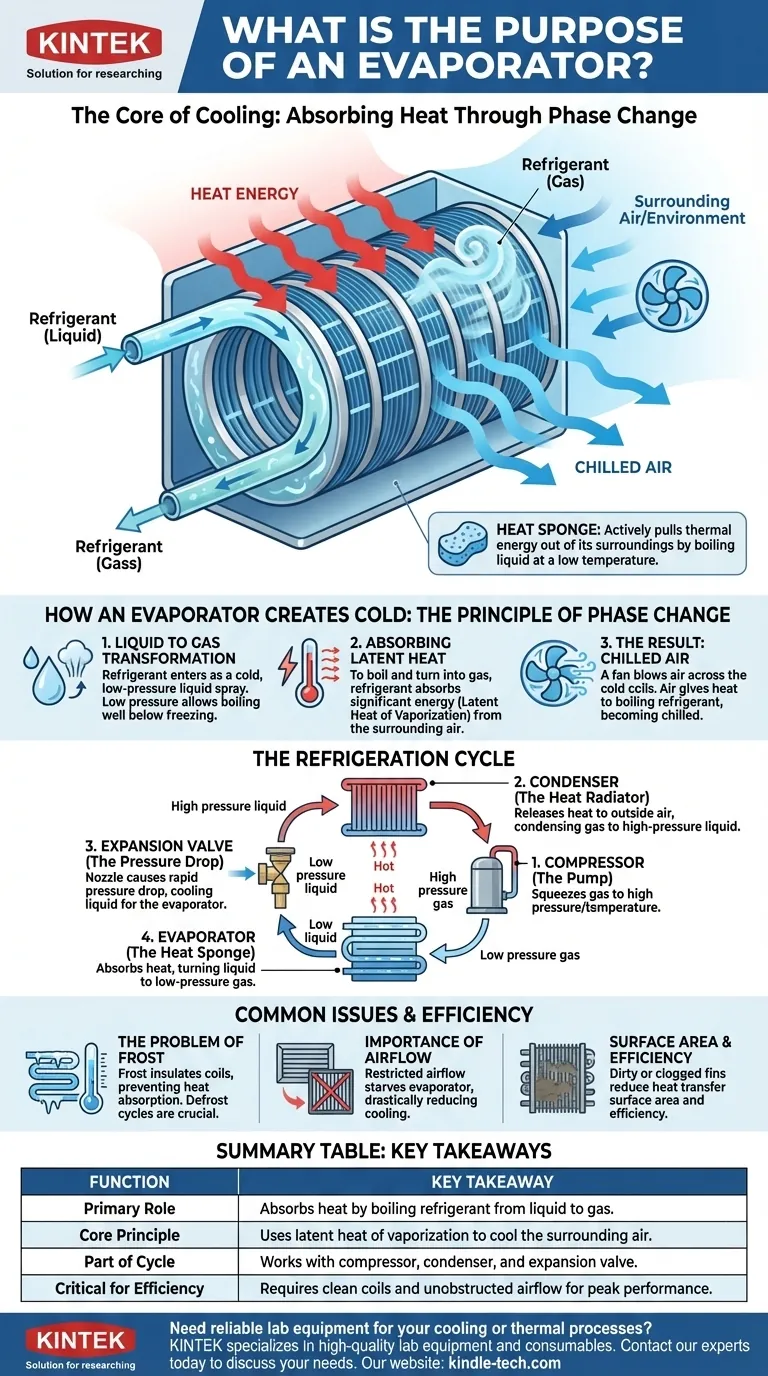
At its core, an evaporator's purpose is to absorb heat from an environment by turning a specialized liquid, called a refrigerant, into a gas. This phase-change process is what produces the cooling effect inside an air conditioner, refrigerator, or freezer. The evaporator is the specific component in the system that actually becomes cold and removes heat from the space you want to cool.
The evaporator isn't just a part of the cooling system; it is the source of the cooling. By forcing a liquid to boil and turn into a gas at a very low temperature, it functions as a "heat sponge," actively pulling thermal energy out of its surroundings.
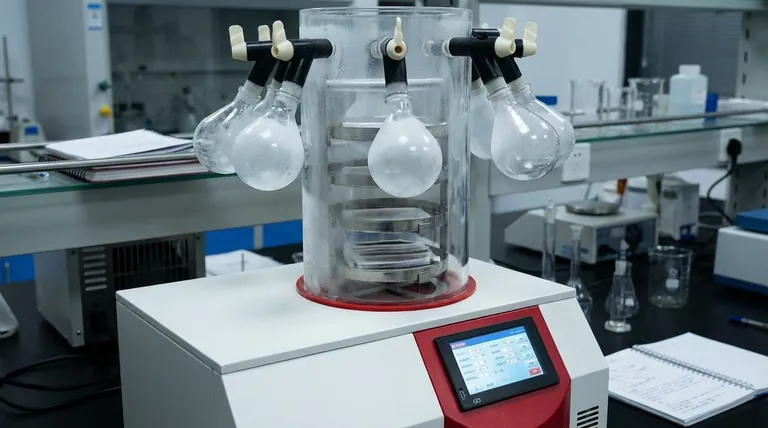

How an Evaporator Creates Cold: The Principle of Phase Change
The function of an evaporator is rooted in a fundamental law of thermodynamics: changing a substance from a liquid to a gas requires a significant amount of energy. The evaporator is designed to make this happen in a controlled way to absorb heat.
The Role of Refrigerant
Evaporators work as part of a closed loop containing a refrigerant. This fluid is engineered to have a very low boiling point, especially when it is at a low pressure.
Liquid to Gas Transformation
The refrigerant enters the evaporator as a very cold, low-pressure liquid spray. As it flows through the evaporator's coils, its pressure is low enough that it begins to boil, even at temperatures well below freezing.
Absorbing "Latent Heat"
To boil and turn into a gas, the liquid refrigerant must absorb energy. This energy is called latent heat of vaporization. The evaporator is designed to pull this heat energy directly from the air (in an AC unit) or the insulated box (in a refrigerator) that surrounds its coils.
The Result: Chilled Air
A fan blows air across the outside of the cold evaporator coils. The air gives up its heat to the boiling refrigerant inside the coils, and the now-chilled air is circulated back into the room or refrigerator, lowering the overall temperature.
The Evaporator's Place in the Refrigeration Cycle
The evaporator is one of four critical components in a standard refrigeration cycle. Understanding how it works with the others reveals the complete picture of how heat is moved from one place to another.
1. The Compressor (The Pump)
After leaving the evaporator as a low-pressure gas, the refrigerant flows to the compressor. The compressor squeezes this gas, raising its pressure and temperature significantly.
2. The Condenser (The Heat Radiator)
This hot, high-pressure gas then moves to the condenser coils (typically located on the outside of the unit). Here, the heat is released into the outside air, causing the refrigerant to cool down and condense back into a high-pressure liquid.
3. The Expansion Valve (The Pressure Drop)
The high-pressure liquid flows through an expansion valve, which acts as a tiny nozzle. This causes a rapid drop in pressure, making the refrigerant intensely cold as it prepares to enter the evaporator again.
4. The Evaporator (The Heat Sponge)
The cold, low-pressure liquid refrigerant enters the evaporator, absorbs heat from the indoor space, boils into a gas, and flows back to the compressor to repeat the cycle endlessly.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Issues
The design and condition of an evaporator are critical to the efficiency of the entire system. Ignoring them leads to poor performance and potential damage.
The Problem of Frost
Because the evaporator's surface is very cold, moisture from the air can freeze onto it. A thick layer of frost acts as an insulator, preventing the coils from absorbing heat from the air effectively. This is why freezers have defrost cycles.
The Importance of Airflow
An evaporator cannot absorb heat if air isn't moving across it. A dirty filter, a blocked vent, or a failing fan motor will starve the evaporator of the warm air it needs to function, drastically reducing cooling performance.
Surface Area and Efficiency
Evaporators are designed with thin metal fins to maximize surface area. This allows for the most efficient transfer of heat from the air to the refrigerant. Any dirt or debris that clogs these fins will reduce the system's efficiency.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Understanding the evaporator's role is key to both maintaining and troubleshooting any cooling system.
- If your primary focus is system efficiency: Ensure the evaporator coils are clean and that airflow is unobstructed by dirty filters or blocked vents.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting a cooling problem: A warm evaporator or one that isn't "sweating" during operation often points to a lack of refrigerant or a problem earlier in the cycle.
- If your primary focus is the core principle: Remember that the evaporator cools by boiling a liquid at a very low temperature, using the surrounding air's heat as the fuel for that process.
By grasping the evaporator's function, you transform the concept of "making cold" from an abstraction into a clear and logical process of moving heat.
Summary Table:
| Evaporator Function | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Role | Absorbs heat by boiling refrigerant from liquid to gas. |
| Core Principle | Uses latent heat of vaporization to cool the surrounding air. |
| Part of Cycle | Works with compressor, condenser, and expansion valve. |
| Critical for Efficiency | Requires clean coils and unobstructed airflow for peak performance. |
Need reliable lab equipment for your cooling or thermal processes?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to meet the precise demands of laboratory environments. Whether you're working on temperature-controlled experiments, material testing, or any process requiring efficient heat management, our solutions are designed for accuracy, durability, and peak performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your specific laboratory needs and help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is the function of Freeze-thaw Equipment in Au-(PNiPAAm/PVA) hydrogel? Achieve High-Speed Photothermal Actuation
- What role does a laboratory freeze dryer play in the synthesis of graphene-based electrocatalysts? Preserve 3D Structures
- What is the function of a freeze dryer in the ice-templating process? Preserving Aligned Pore Scaffolds for LAGP
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred over thermal drying for Fe-ZTA cermets? Ensure Pure, Homogeneous Slurry Processing
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred for reduced graphene oxide (Hh-RGO) powders? Preserve Nano-Structure and Performance



















