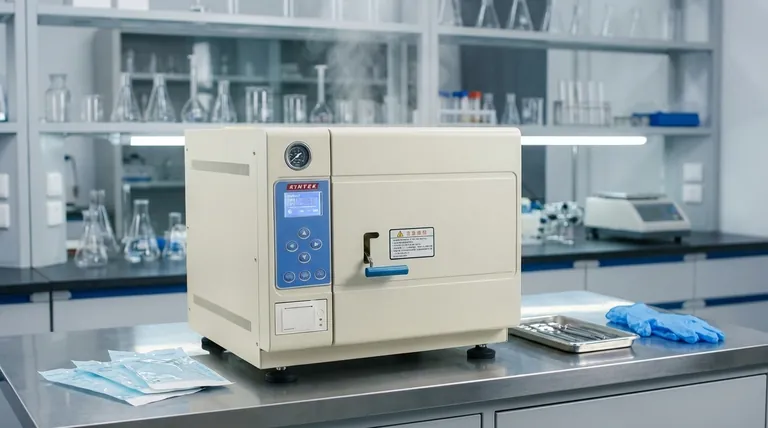
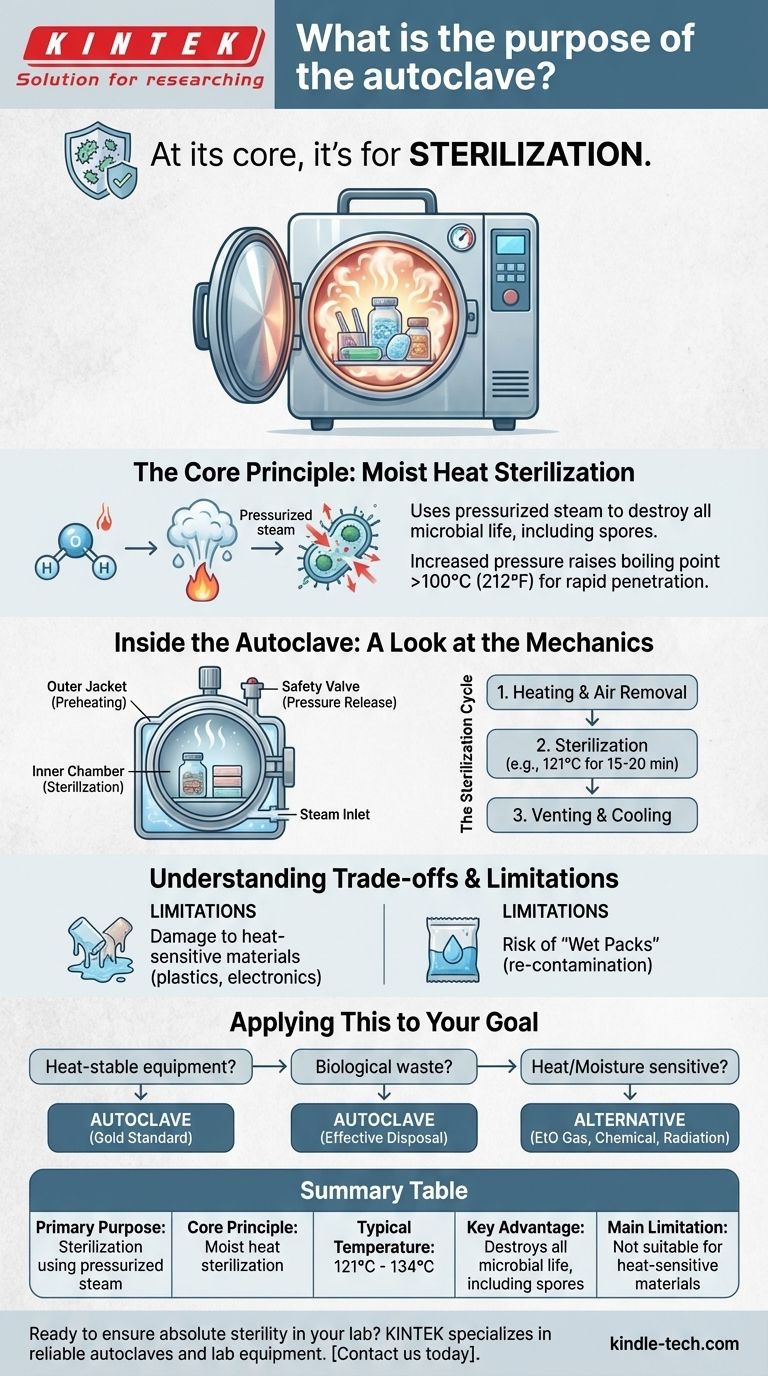
At its core, an autoclave is a high-pressure chamber designed for one primary purpose: sterilization. It uses pressurized steam to destroy all forms of microbial life—including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and even highly resistant bacterial spores—on equipment, liquids, and waste materials. This makes it an indispensable tool in any environment where absolute sterility is critical.
The true power of an autoclave lies not just in its heat, but in its use of pressurized steam. By increasing pressure, the autoclave raises the boiling point of water far beyond 100°C (212°F), creating superheated steam that can rapidly penetrate and kill microorganisms far more effectively than dry heat or simple boiling.

The Core Principle: Moist Heat Sterilization
The effectiveness of an autoclave is rooted in a process known as moist heat sterilization. This method is the gold standard because it is remarkably efficient at transferring lethal heat to microorganisms.
Why Pressure is the Key Ingredient
Water normally boils at 100°C (212°F) at standard atmospheric pressure. While this temperature can kill many microbes, it is not sufficient to destroy resilient bacterial spores.
By sealing the chamber and injecting steam, an autoclave increases the internal pressure. This elevated pressure forces the boiling point of water to rise—typically to 121°C (250°F) or even 134°C (273°F).
How Steam Ensures Complete Sterilization
This superheated steam is the active sterilizing agent. Unlike dry heat, steam can flow into and penetrate the deepest parts of complex instruments, porous materials, and liquids.
As the steam contacts a cooler surface, it condenses into water, releasing a massive amount of thermal energy directly onto the object. This rapid heat transfer denatures and coagulates the essential proteins within microorganisms, killing them completely.
Inside the Autoclave: A Look at the Mechanics
An autoclave is more than just a pressure cooker. Its components are engineered to ensure the sterilization process is reliable, efficient, and safe.
The Sterilization Cycle
A typical cycle involves several phases. First, the chamber is heated and steam is introduced, pushing out the cooler, less effective air. The chamber then reaches the target temperature and pressure, which is held for a specified duration—often 15 to 20 minutes—to ensure full sterilization. Finally, the steam is vented, and the items are allowed to cool.
The Role of the Chamber and Jacket
The main body of an autoclave is the vessel, which contains an inner chamber for the items and an outer jacket. This jacket is often filled with steam to preheat the chamber walls.
This design serves two critical functions: it reduces the total cycle time and minimizes the amount of condensation that forms inside the chamber, preventing items from coming out overly wet.
The Importance of the Safety Valve
Given the high pressures involved, safety is paramount. Every autoclave is equipped with a safety valve on its lid. If the internal pressure ever rises to a dangerous level, this valve automatically opens to release the excess steam, preventing a catastrophic failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, an autoclave is not a universal solution. Its high heat and pressure create specific limitations that are crucial to understand.
Damage to Heat-Sensitive Materials
The primary drawback is its reliance on high temperatures. An autoclave will melt many plastics, damage sensitive electronic components, and can dull the sharp edges of certain fine surgical instruments.
The Problem of "Wet Packs"
If operated incorrectly or if the load is packed too densely, items can emerge from the autoclave wet. These "wet packs" are considered unsterile because the moisture can create a pathway for microorganisms to re-contaminate the item's surface after the cycle is complete.
Applying This to Your Goal
Choosing the right sterilization method depends entirely on what you need to sterilize and the material it is made from.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-stable medical or laboratory equipment: The autoclave is the definitive gold standard for its reliability and effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is decontaminating biological waste: Autoclaving is the most effective and widely used method to render infectious waste completely safe for disposal.
- If your primary focus is processing items sensitive to heat or moisture: You must use an alternative, such as ethylene oxide (EtO) gas, chemical sterilization, or radiation.
Ultimately, the autoclave provides an unmatched level of sterile assurance, making modern medicine, research, and manufacturing possible.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Sterilization using pressurized steam |
| Core Principle | Moist heat sterilization |
| Typical Temperature | 121°C (250°F) to 134°C (273°F) |
| Key Advantage | Destroys all microbial life, including spores |
| Main Limitation | Not suitable for heat-sensitive materials |
Ready to ensure absolute sterility in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in providing reliable autoclaves and lab equipment designed to meet the rigorous sterilization demands of medical, research, and manufacturing facilities. Our solutions help you achieve complete decontamination, protect your workflows, and maintain compliance with safety standards.
Contact us today to find the perfect sterilization system for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
People Also Ask
- What is the use of autoclave in microbiology? Ensuring Sterile Conditions for Reliable Results
- What is the minimum temperature and time for autoclave? Achieve Guaranteed Sterilization Every Time
- What is the pressure of autoclave at 121 C? The Key to Effective Steam Sterilization
- What are the considerations for autoclave? Ensure Sterilization Success and Safety
- What are the settings of autoclave in microbiology? Achieve Guaranteed Sterility for Your Lab



















