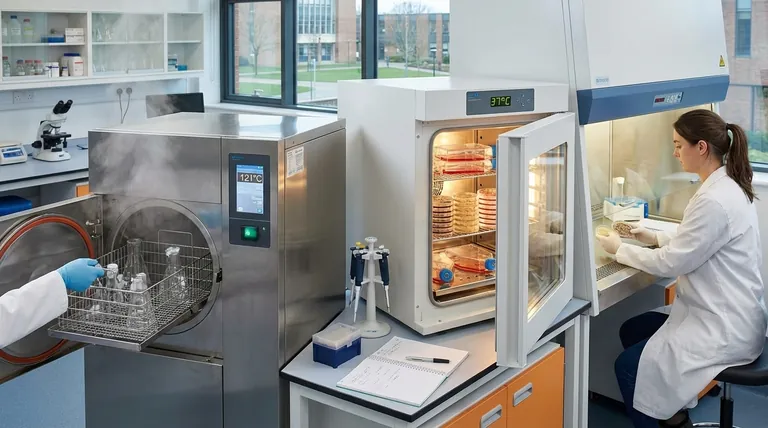
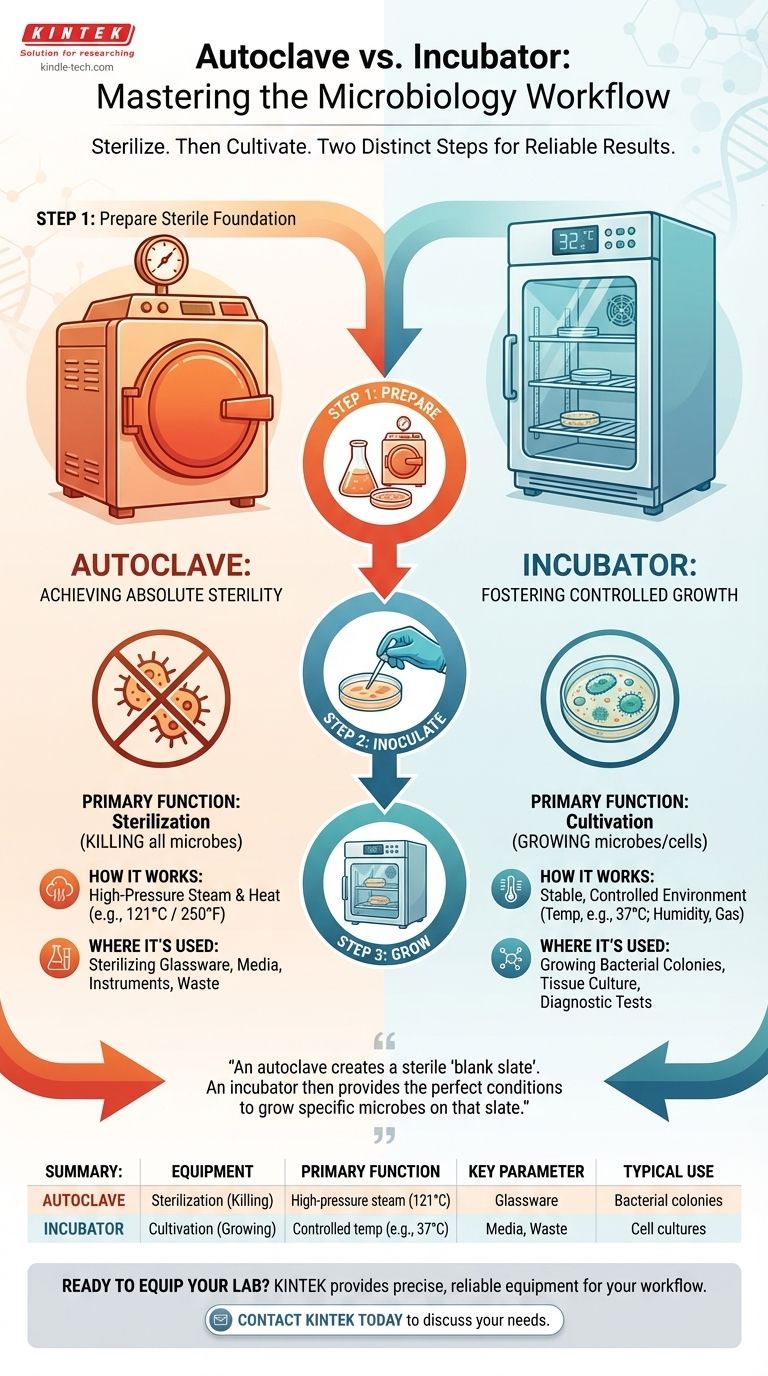
The term "autoclave incubator" is a point of confusion as it combines two pieces of laboratory equipment with opposite functions. An autoclave is a machine designed to kill all microbial life through high-pressure steam sterilization. In contrast, an incubator is a device that provides a controlled, stable environment to nurture and grow microorganisms or cell cultures.
An autoclave creates a sterile, "blank slate" by destroying all microbes. An incubator then provides the perfect conditions to grow specific, desired microbes on that sterile slate. They are two separate, sequential steps in a single scientific workflow.

The Role of the Autoclave: Achieving Absolute Sterility
The primary purpose of an autoclave is to achieve sterilization, which is the complete elimination of all forms of microbial life. This includes resilient bacteria, viruses, fungi, and even highly resistant bacterial spores.
How It Works: Steam, Pressure, and Heat
An autoclave functions like a sophisticated pressure cooker. It uses high-pressure steam at temperatures above boiling (typically 121°C or 250°F) to denature the essential proteins and enzymes that microbes need to survive.
The combination of moist heat and high pressure is far more effective at penetrating and killing microorganisms than dry heat alone.
Where It's Used
Autoclaves are essential for preparing a sterile environment. Common uses include sterilizing:
- Laboratory glassware and plasticware
- Surgical instruments
- Culture media (like agar and broth) before it is used for an experiment
- Biohazardous waste before disposal
The Role of the Incubator: Fostering Controlled Growth
The purpose of an incubator is the exact opposite of an autoclave: it is designed to nurture and cultivate life under highly specific and controlled conditions.
How It Works: A Stable Environment
An incubator is an insulated box that maintains a constant and optimal environment for growth. This typically involves precise control over temperature, but can also include humidity and gas levels like CO₂ and oxygen.
For example, many bacteria relevant to human health are grown at 37°C (98.6°F), which mimics the temperature of the human body.
Where It's Used
Incubators are used whenever you need to grow, maintain, or count microorganisms or cells. Common uses include:
- Growing bacterial colonies on a petri dish for study
- Cultivating tissue and cell lines for research
- Performing diagnostic tests that rely on the growth of a specific pathogen
The Critical Workflow: Why You Need Both
Understanding the relationship between these two devices is fundamental to microbiology. They are used in a sequence to ensure that experimental results are accurate and free from contamination.
Step 1: Prepare with the Autoclave
First, you prepare your materials. You would place your culture media (e.g., agar in a flask) and glassware (e.g., empty petri dishes) inside the autoclave. This sterilizes them, creating a perfectly clean, microbe-free foundation for your experiment.
Step 2: Inoculate with Your Sample
After the sterile media has cooled, you introduce (or inoculate) the specific microbe you wish to study. This is done carefully to avoid introducing any unwanted contaminants from the air or other surfaces.
Step 3: Grow with the Incubator
Finally, you place the inoculated petri dish into the incubator. The incubator provides the ideal temperature and conditions for only your desired microbe to grow into visible colonies, as all competing organisms were eliminated in the autoclave.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To avoid confusion, always consider the verb: are you trying to kill or to grow?
- If your primary focus is to eliminate all microorganisms: You need an autoclave to sterilize equipment, media, or waste.
- If your primary focus is to grow a specific microorganism or cell line: You need an incubator to provide a stable, nurturing environment.
- If your primary focus is running a standard microbiology experiment: You will use the autoclave first to prepare sterile materials and then the incubator to cultivate your specific organism.
Mastering the distinct roles of sterilization and incubation is the bedrock of producing reliable and repeatable scientific results.
Summary Table:
| Equipment | Primary Function | Key Parameter | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autoclave | Sterilization (Killing microbes) | High-pressure steam (121°C / 250°F) | Sterilizing glassware, media, instruments, and waste |
| Incubator | Cultivation (Growing microbes/cells) | Controlled temperature (e.g., 37°C) and atmosphere | Growing bacterial colonies, cell cultures, and diagnostic tests |
Ready to equip your lab for success?
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise, reliable equipment your laboratory needs. Whether you require a robust autoclave for guaranteed sterilization or a precisely controlled incubator for cultivating sensitive cultures, our solutions are designed to ensure the integrity and repeatability of your work.
Let our experts help you select the right tools for your specific workflow. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your lab's equipment needs and enhance your research capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What are the different sterilization methods for a microbiology lab? Ensure Reliable and Safe Experiments
- What is cryogenic grinding of cardamom? Preserve Flavor, Aroma & Color with Extreme Cold
- Why are conventional preservation methods less suitable for biological products? The Critical Risk to Efficacy and Safety
- What process advantages are offered by integrating a cryogenic cooling device during HPT? Achieve Ultimate Grain Refinement
- How are the shelves inside an Ultra Freezer designed to maintain temperature uniformity? Ensuring Sample Integrity with Compartmentalized Shelves













