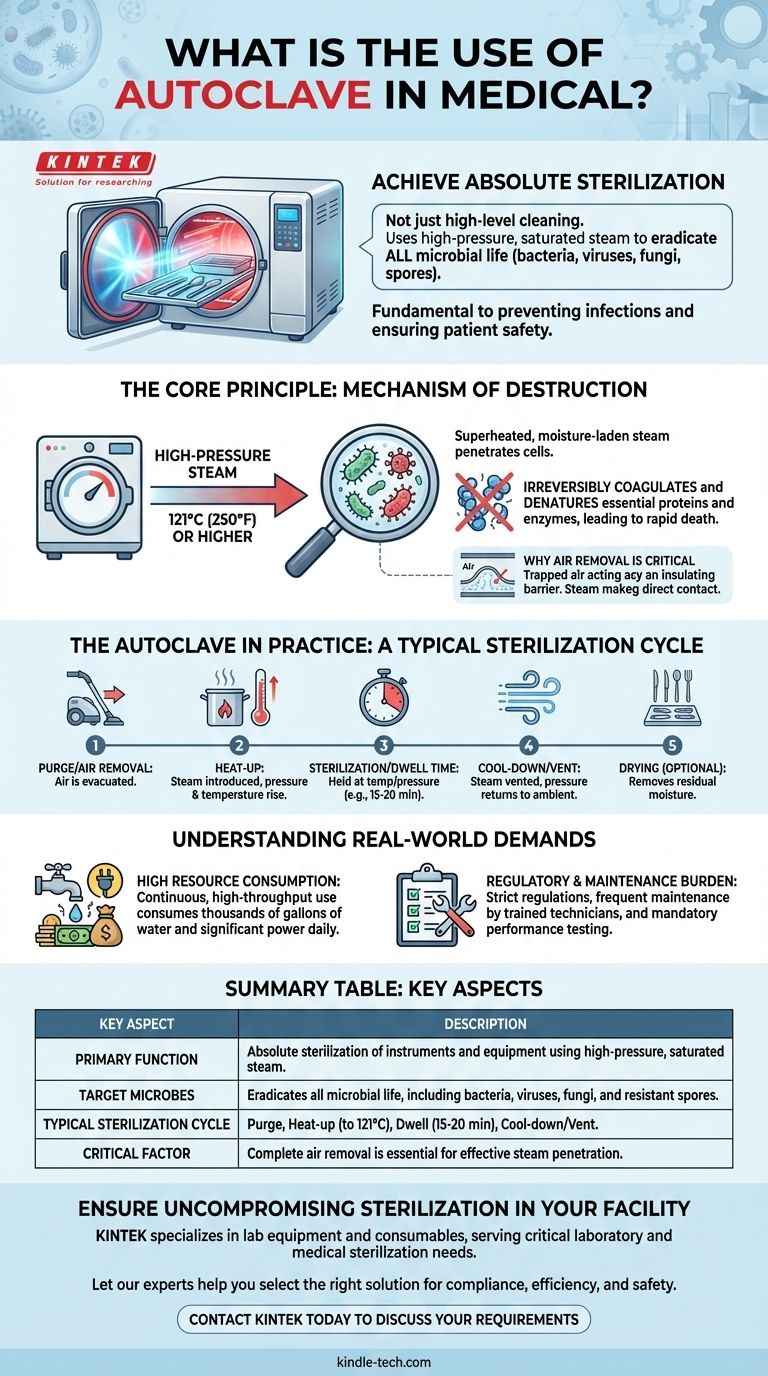
In any medical setting, the primary and non-negotiable use of an autoclave is to achieve absolute sterilization of instruments and equipment. It is not simply a high-level cleaning device; it is a specialized chamber that uses high-pressure, saturated steam to eradicate all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and even highly resistant spores. This process is fundamental to preventing infections and ensuring patient safety.
An autoclave's function goes far beyond simple cleaning. By leveraging the physical properties of steam under pressure, it achieves a level of microbial destruction that is impossible with detergents or boiling water alone, making it the cornerstone of modern infection control.

The Core Principle: How Autoclaves Achieve Sterilization
To understand the autoclave's role, you must first understand its mechanism. It is not merely the heat that sterilizes; it is the combination of heat, pressure, and moisture that creates an incredibly effective and lethal environment for microorganisms.
Harnessing High-Pressure Steam
An autoclave is essentially a pressure chamber. After items are loaded and the door is sealed, a vacuum may remove air from the chamber. Water is then heated to produce steam, which is pumped into the sealed chamber.
Because the chamber is pressurized, the boiling point of water increases. This allows the steam to reach temperatures far above the normal 100°C (212°F), typically achieving 121°C (250°F) or higher.
The Mechanism of Destruction
This superheated, moisture-laden steam is the key. The moist heat is highly effective at transferring thermal energy to every surface inside the chamber, penetrating microbial cells.
This intense heat irreversibly coagulates and denatures essential proteins and enzymes within the microorganisms. When these proteins are destroyed, the cell's metabolic and structural integrity collapses, leading to rapid death.
Why Air Removal is Critical
Removing air from the chamber before the steam cycle is crucial. Pockets of trapped air can act as an insulating barrier, preventing steam from making direct contact with the surfaces of the instruments. Incomplete steam penetration results in failed sterilization.
The Autoclave in Practice: A Typical Sterilization Cycle
While the principles are scientific, the daily operation is a standardized and often automated process designed for safety and repeatability.
Preparing the Load
Items for sterilization, such as surgical instruments, glassware, or other heat-stable medical supplies, are placed inside the autoclave. The way items are loaded is important to ensure steam can circulate freely.
Executing the Cycle
The operator selects a pre-programmed cycle using a control interface. A typical liquid cycle involves:
- Purge/Air Removal: Air is evacuated from the chamber.
- Heat-Up: Steam is introduced, and pressure and temperature rise to the set point (e.g., 121°C).
- Sterilization/Dwell Time: The temperature and pressure are held constant for a specified duration, usually 15-20 minutes, to ensure complete microbial kill.
- Cool-Down/Vent: The steam is vented, and the pressure returns to ambient levels.
- Drying (Optional): A drying phase may follow to remove residual moisture from wrapped instrument packs.
Customization and Control
Modern autoclaves allow for customization of these cycles. The duration of the sterilization phase can be adjusted based on the size and density of the load to ensure full steam penetration and effective sterilization every time.
Understanding the Real-World Demands
While essential, integrating medical-grade autoclaves into a healthcare facility comes with significant operational considerations. They are far more demanding than a simple laboratory benchtop unit.
High Resource Consumption
Hospital autoclaves are built for continuous, high-throughput use. This means they are major consumers of resources, often using thousands of gallons of water and significant electrical power each day to generate the necessary steam for back-to-back cycles.
Regulatory and Maintenance Burden
As critical medical devices, autoclaves are subject to strict regulations and quality standards. They require demanding and frequent maintenance by trained technicians to ensure they are functioning safely and effectively. Regular performance testing is mandatory to validate that sterilization conditions are being met.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the autoclave is about recognizing its place in the larger system of patient care. Its function is not just a technical process but a critical pillar of medical safety.
- If your primary focus is patient safety: Recognize that proper autoclaving is the definitive barrier against surgical site infections and the cross-contamination of reusable instruments.
- If your primary focus is operational procedure: Adhere strictly to the loading protocols and cycle parameters, as any deviation can compromise the entire sterilization process.
- If your primary focus is facility management: Factor in the significant and ongoing costs of water, energy, and specialized maintenance required to keep these critical devices online.
The autoclave is the unsung hero of the medical field, a device whose reliable function underpins the safety of countless procedures every single day.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Absolute sterilization of instruments and equipment using high-pressure, saturated steam. |
| Target Microbes | Eradicates all microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and resistant spores. |
| Typical Sterilization Cycle | Purge (air removal), Heat-up (to 121°C/250°F), Dwell (15-20 min), Cool-down/Vent. |
| Critical Factor | Complete air removal is essential for steam to penetrate and sterilize all surfaces effectively. |
Ensure Uncompromising Sterilization in Your Facility
Your commitment to patient safety depends on reliable, medical-grade sterilization equipment. The high-throughput demands and strict regulatory requirements of a healthcare setting require autoclaves you can trust.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving critical laboratory and medical sterilization needs. We understand the operational challenges you face. Let our experts help you select and maintain the right autoclave solution to ensure compliance, efficiency, and the highest standard of care.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific sterilization requirements and safeguard your patients.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How do you sterilize glassware by autoclave? Master the 3-Step Process for Reliable Sterility
- Do you need to autoclave glassware? A Guide to Sterilization vs. Cleaning
- What temperature must be reached for sterilization in 10-12 minutes? Achieve Rapid, Reliable Sterility with Flash Autoclaving
- Can autoclave sterilize liquid? Master Safe and Effective Liquid Sterilization
- Why is it important to autoclave the prepared reagents before using? Ensure Sterility and Reliable Results



















