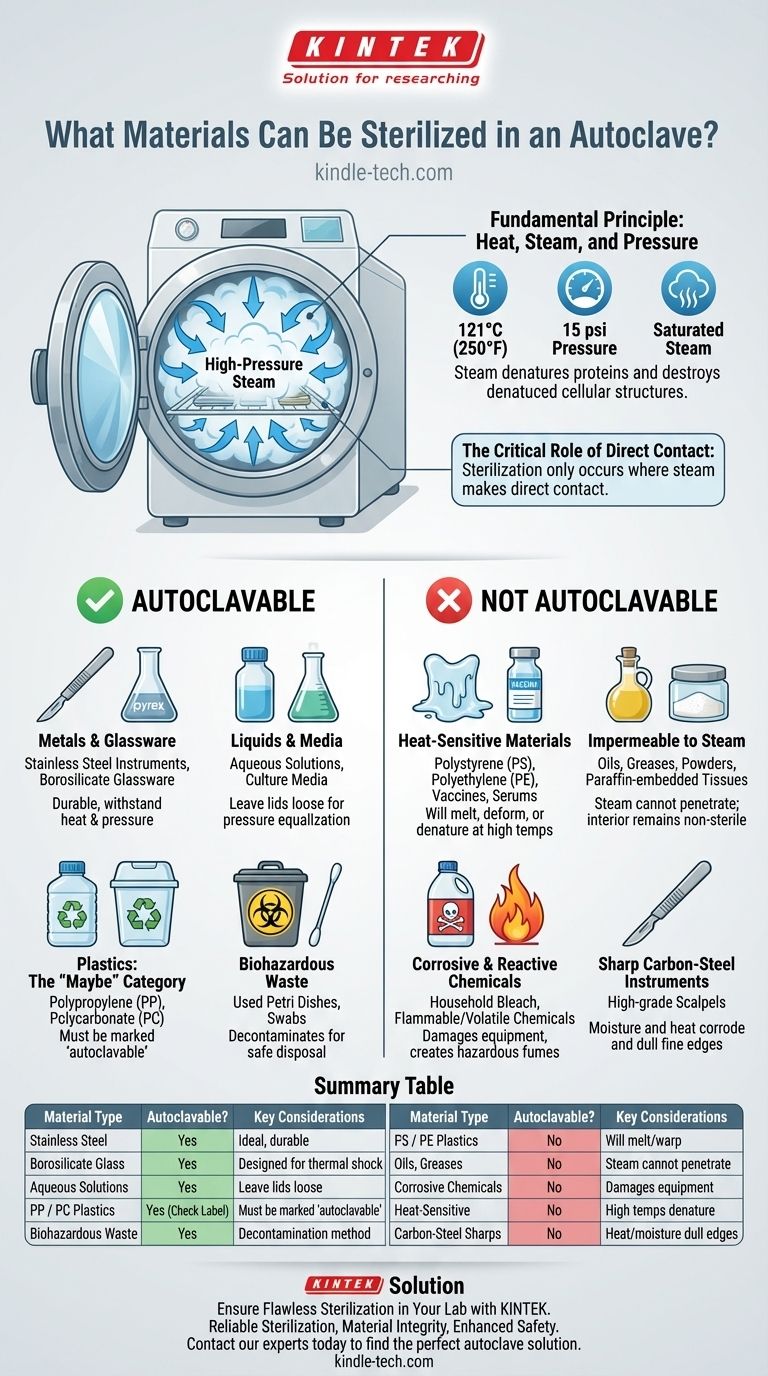
At its core, an autoclave is designed to sterilize materials that are both heat-stable and permeable to steam. This includes most surgical instruments, specific types of autoclavable plastics and pipette tips, heat-resistant glassware like Pyrex, aqueous solutions, culture media, and biohazardous waste. The process relies on high-pressure saturated steam to achieve temperatures that are lethal to microorganisms.
The suitability of a material for autoclave sterilization depends on two fundamental properties: its ability to withstand high temperatures (typically 121°C or higher) and its permeability to saturated steam. If a material will melt, degrade, or block steam penetration, it is not a candidate for autoclaving.

The Fundamental Principle: Heat, Steam, and Pressure
How Saturated Steam Achieves Sterilization
An autoclave is not simply a pressure cooker; it's a precision instrument. By increasing the pressure inside its chamber, it raises the boiling point of water far beyond 100°C.
The industry standard for sterilization is typically 121°C (250°F) at 15 psi of pressure for at least 15 minutes. This superheated steam effectively denatures proteins and destroys the cellular structures of bacteria, viruses, and spores.
The Critical Role of Direct Contact
Sterilization only occurs where steam makes direct contact with a surface. This is the single most important principle governing what can and cannot be autoclaved.
If an item is wrapped too tightly, placed in a sealed container, or is inherently waterproof (like oil), the steam cannot penetrate. Without direct contact, the item will get hot, but it will not become sterile.
Autoclavable Materials: A Detailed Breakdown
Metals and Glassware
Most laboratory and surgical instruments made of stainless steel are ideal for autoclaving. They are durable and easily withstand the required temperatures and pressures.
Likewise, borosilicate glassware (e.g., Pyrex, Kimax) is designed for thermal shock and is perfectly safe. Standard soda-lime glass, like jars or bottles, is not recommended as it may crack.
Liquids and Media
The autoclave is the gold standard for sterilizing aqueous solutions, including water, saline, and microbiological culture media. The steam environment prevents liquids from boiling away while ensuring sterility.
It is crucial to leave container lids slightly loose to allow for pressure equalization and prevent bottles from shattering during the cycle.
Plastics: The "Maybe" Category
This is where careful attention is required. Not all plastics are created equal.
- Autoclavable Plastics: Materials like polypropylene (PP) and polycarbonate (PC) are generally safe for autoclaving and are often marked with "autoclavable" or a recycling symbol with "PP" or "PC".
- Non-Autoclavable Plastics: Materials like polystyrene (PS), polyethylene (PE), and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) will melt, deform, or warp under autoclave conditions.
Biohazardous Waste
Autoclaving is a primary method for decontaminating solid biohazardous waste, such as used petri dishes, swabs, and disposable culture tubes. This renders the waste non-infectious and safe for disposal.
Critical Exclusions: What to Never Autoclave
Understanding what to keep out of an autoclave is just as important as knowing what to put in. Incorrectly autoclaving materials can damage the equipment, ruin your items, or create a significant safety hazard.
Heat-Sensitive Materials
Any material that cannot withstand 121°C should be excluded. This includes most common plastics, which will melt into a solid, unrecoverable mass.
It also includes heat-labile solutions like vaccines, serums, or certain proteins (e.g., urea), which will be denatured and rendered useless by the high temperatures.
Materials Impermeable to Steam
You cannot sterilize items that are waterproof or water-resistant. This includes oils, greases, powders, and paraffin-embedded tissues. The steam cannot penetrate these substances, leaving the interior non-sterile.
Corrosive and Reactive Chemicals
Never autoclave flammable, volatile, or corrosive chemicals. Materials like household bleach (sodium hypochlorite) will vaporize and release corrosive chlorine gas, which can severely damage the autoclave's stainless steel chamber.
Radioactive, toxic, or other hazardous chemicals should also never be autoclaved, as this can create dangerous, aerosolized compounds.
Sharp Carbon-Steel Instruments
While stainless steel is fine, high-grade carbon steel instruments, such as certain scalpels or scissors, should not be autoclaved. The combination of high heat and moisture will corrode and dull the fine cutting edge, compromising the instrument's function.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure success, match the material to the sterilization method.
- If your primary focus is routine lab work (media, glassware): The autoclave is your standard and most reliable method for sterilizing heat-stable equipment and aqueous solutions.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive plastics or solutions: You must verify the material is marked as "autoclavable" or consider alternatives like sterile filtration or chemical sterilization.
- If your primary focus is delicate, sharp instruments: Investigate dry heat or chemical sterilants to preserve the integrity of the carbon-steel cutting edges.
- If your primary focus is safety and waste disposal: The autoclave is essential for decontaminating biohazards, but never use it for volatile or corrosive chemical waste.
By understanding these core principles of heat and steam penetration, you can ensure the integrity of your materials and the absolute success of every sterilization cycle.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Autoclavable? | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel Instruments | Yes | Ideal; durable and withstands heat/pressure. |
| Borosilicate Glassware (Pyrex) | Yes | Designed for thermal shock; safe. |
| Aqueous Solutions & Media | Yes | Leave lids loose to prevent breakage. |
| Polypropylene (PP) / Polycarbonate (PC) | Yes (Check Label) | Must be marked "autoclavable". |
| Biohazardous Waste | Yes | Primary method for decontamination. |
| Polystyrene (PS) / Polyethylene (PE) | No | Will melt, deform, or warp. |
| Oils, Greases, Powders | No | Steam cannot penetrate; interior won't sterilize. |
| Corrosive Chemicals (e.g., Bleach) | No | Can damage the autoclave and create hazardous fumes. |
| Heat-Sensitive Solutions (Vaccines) | No | High temperatures will denature and ruin them. |
| Carbon-Steel Sharp Instruments | No | Moisture and heat will corrode and dull the edges. |
Ensure Flawless Sterilization in Your Lab
Choosing the right equipment is critical for effective and safe sterilization cycles. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality autoclaves and reliable lab consumables designed for the demanding needs of modern laboratories.
We help you achieve:
- Reliable Sterilization: Our autoclaves ensure consistent, precise steam sterilization for your heat-stable materials.
- Material Integrity: Use the right equipment to protect your valuable instruments, glassware, and media.
- Enhanced Safety: Properly decontaminate biohazardous waste and avoid damaging non-autoclavable items.
Let's discuss your lab's specific sterilization requirements. Contact our experts today to find the perfect autoclave solution and consumables for your research or clinical needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How long does autoclaving take? Mastering Sterilization Times for Your Lab
- What are the 3 most common machines used in sterilization? Choose the Right Method for Your Materials
- Why is an autoclave required for treating biomass hydrolysate? Ensure Sterile Fermentation for High Yields
- Where are autoclaves used? Ensuring Sterility from Hospitals to High-Tech Labs
- How long is the sterilization cycle in an autoclave? It's More Than Just 15 Minutes
- What is autoclave features and uses? A Guide to Sterilization and Safety
- What is the function of a circulating loop system with a Hastelloy autoclave? Enhance PWR Corrosion Research Accuracy
- What conditions does an autoclave simulate for 316L SCC testing? Replicating PWR Primary Circuit Environments



















