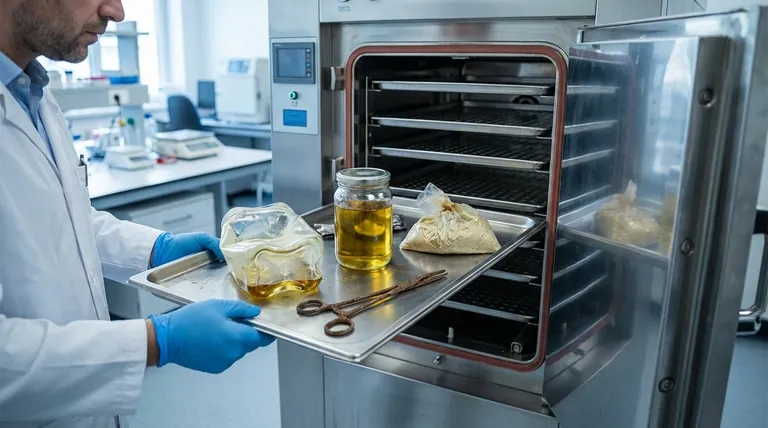
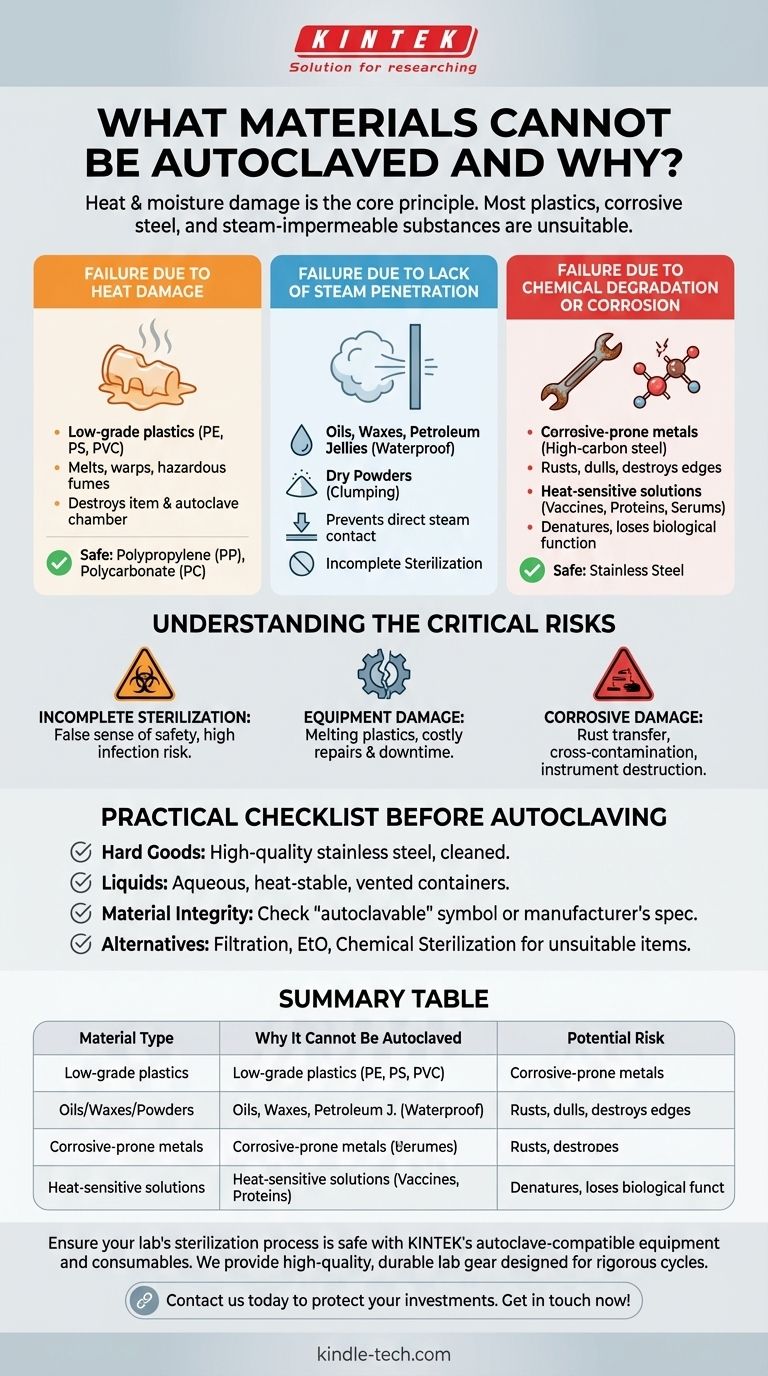
In short, any material that can be damaged by heat or moisture cannot be autoclaved. This includes most plastics, as they will melt or warp, certain types of steel that will corrode and dull, and any substance that is not permeable to steam, such as oils, waxes, or powders. Additionally, sensitive biological or chemical compounds that are degraded by high heat, like some proteins and vaccines, are unsuitable for steam sterilization.
The effectiveness of an autoclave relies on its ability to use superheated, high-pressure steam to kill microorganisms. If a material melts, corrodes, prevents steam penetration, or is chemically altered by this process, autoclaving will either destroy the item or, more dangerously, fail to sterilize it.

The Core Principles: Why Autoclaving Fails
An autoclave is not simply a hot oven; it is a highly specific environment. Understanding why certain materials fail is key to using it safely and effectively. The primary failure points are damage from heat, lack of steam penetration, and chemical degradation.
Failure Due to Heat Damage
The most common reason for exclusion is a material's low melting point. Autoclaves typically operate at 121°C (250°F) or higher, which is beyond the tolerance of many common materials.
Low-grade plastics like polyethylene (PE), polystyrene (PS), and PVC will melt, warp, or release hazardous fumes. This not only destroys the item but can also damage the autoclave chamber. Only plastics specifically rated for autoclaving, such as polypropylene (PP) and polycarbonate (PC), can withstand the process.
Failure Due to Lack of Steam Penetration
Steam must make direct contact with every surface to sterilize it. Any substance that repels or blocks water will render the process ineffective.
Oils, waxes, and petroleum jellies are waterproof. Steam will simply slide over their surfaces, leaving the bulk of the material and any microbes within it completely unsterilized.
Similarly, dry powders are not suitable for steam sterilization. The steam can cause the powder to clump, preventing penetration into the center of the material.
Failure Due to Chemical Degradation or Corrosion
The combination of heat and moisture can be highly reactive, either destroying the chemical function of a substance or physically damaging an item.
Corrosive-prone metals, such as high-carbon steel, will rust and become dull when autoclaved. This is why high-quality scalpel blades or scissors are often single-use or sterilized by other means—autoclaving would quickly ruin their sharp edge. Stainless steel, by contrast, is specifically designed to resist this type of corrosion.
Heat-sensitive solutions like certain vaccines, serums, and proteins will be denatured by the intense heat. This is a form of chemical degradation where the molecules change shape, destroying their biological function.
Understanding the Critical Risks
Attempting to autoclave an unsuitable item is not a neutral act. The consequences range from damaged equipment to a dangerous and false sense of sterility.
The Risk of Incomplete Sterilization
This is the most significant danger. If you autoclave an instrument coated in a thin layer of oil, it will emerge hot but not sterile. Using this instrument creates a high risk of infection, as you are operating under the false assumption that it is safe.
The Risk of Equipment Damage
Melting plastics can create a significant mess inside an autoclave, requiring intensive cleaning and potentially causing permanent damage to drains, valves, and sensors. This leads to costly downtime and repairs.
The Risk of Corrosive Damage
Repeatedly autoclaving non-stainless steel instruments will not only destroy the instruments themselves but can also cause rust particles to transfer to the inside of the autoclave chamber and to other instruments in the same load.
A Practical Checklist Before Autoclaving
Before placing any item in an autoclave, evaluate your goal and the material's properties.
- If your primary focus is sterility of hard goods: Ensure instruments are made of high-quality stainless steel and have been thoroughly cleaned of all organic debris and oils before sterilization.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing liquids: Confirm the liquid is aqueous (water-based) and that its chemical components are heat-stable. Never seal the container completely.
- If your primary focus is preserving material integrity: Check for an "autoclavable" symbol or manufacturer's specification, especially on plastics. For anything heat-sensitive, corrosive, or non-aqueous, you must use an alternative method like filtration, ethylene oxide (EtO), or chemical sterilization.
Ultimately, successful sterilization depends on understanding the limitations of your tools.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Why It Cannot Be Autoclaved | Potential Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Low-grade plastics (PE, PS, PVC) | Melts or warps at high temperatures | Equipment damage, release of hazardous fumes |
| Oils, waxes, powders | Repels steam, preventing penetration | Incomplete sterilization, false sense of safety |
| Corrosive-prone metals (high-carbon steel) | Rusts and dulls from heat/moisture | Instrument degradation, cross-contamination |
| Heat-sensitive solutions (vaccines, proteins) | Denatures and loses function | Destruction of biological activity |
Ensure your lab's sterilization process is safe and effective with KINTEK's autoclave-compatible equipment and consumables.
We provide high-quality, durable lab gear designed to withstand rigorous sterilization cycles, including autoclavable polypropylene and stainless steel instruments. Our experts can help you select the right products to avoid equipment damage and ensure complete sterility.
Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs and protect your investments. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- Why is the prevention of air entrapment critical for the autoclave sterilization process? Ensure 100% Sterility Today
- What is the necessity of using a steam autoclave for dental alloys? Ensure Pure Bacterial Adhesion Data
- How does an autoclave ensure the reliability of experimental results? Achieving a Sterile Baseline for Lab Research
- Why is a 24-hour hydrothermal treatment in an autoclave necessary for BMO nanosheets? Unlock Superior Photocatalysis



















