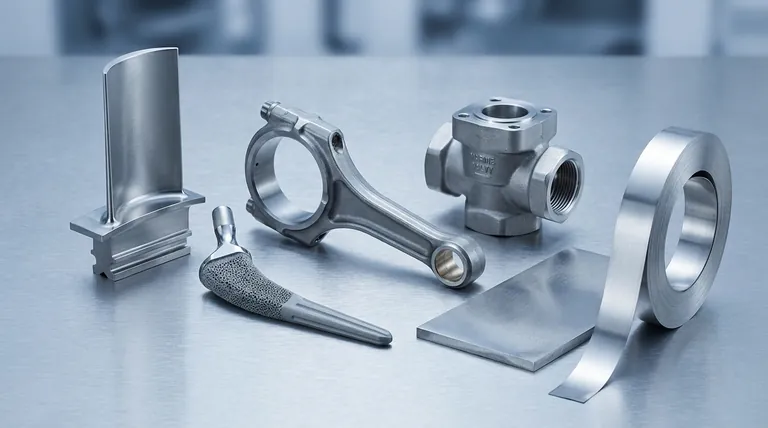
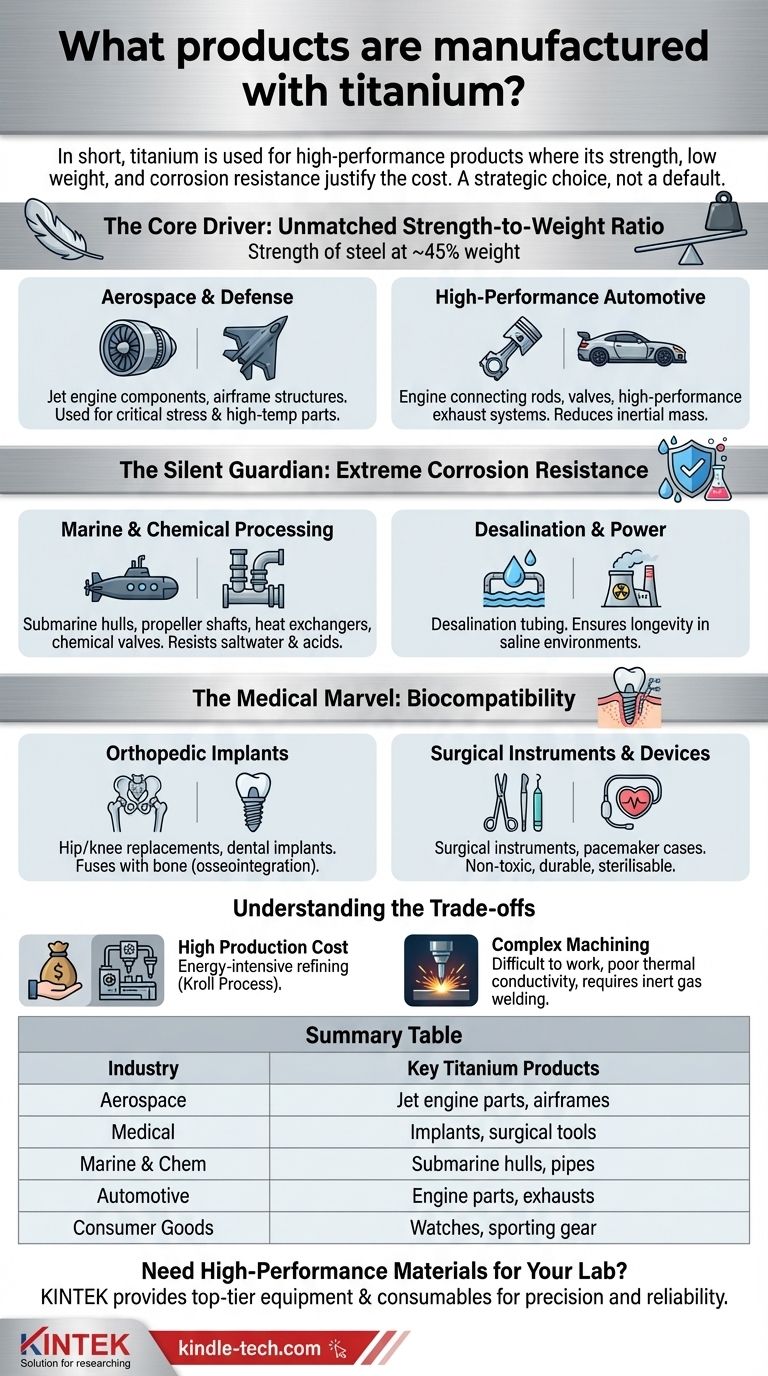
In short, titanium is used to manufacture high-performance products where its unique combination of strength, low weight, and corrosion resistance justifies its high cost. Key examples include jet engine components, aircraft frames, surgical implants, submarine hulls, chemical processing equipment, and premium consumer goods like high-end watches and sporting equipment.
The use of titanium is a strategic decision, not a default choice. It is reserved for applications where materials like steel or aluminum would fail or where the performance gains from its superior strength-to-weight ratio are mission-critical.

The Core Driver: An Unmatched Strength-to-Weight Ratio
The most celebrated property of titanium is its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. It provides the strength of many steels at only 45% of the weight, a characteristic that drives its use in industries where every gram matters.
Aerospace and Defense Applications
In aviation, reducing weight directly translates to increased payload capacity, longer range, and better fuel efficiency. Titanium is the material of choice for this.
It is used for critical airframe structures, landing gear, and, most importantly, jet engine components like fan blades, discs, and shafts that must withstand immense stress and high temperatures. Famously, the SR-71 Blackbird's airframe was largely constructed from titanium to endure the extreme heat of Mach 3+ flight.
High-Performance Automotive
In the world of racing and supercars, titanium is used to reduce inertial mass and overall vehicle weight.
You will find it in engine connecting rods, valves, and high-performance exhaust systems. These components allow engines to rev higher and faster while also improving the car's handling and power-to-weight ratio.
The Silent Guardian: Extreme Corrosion Resistance
Titanium exhibits a remarkable resistance to corrosion from saltwater, acids, and industrial chemicals. This is because it instantly forms a stable, tough, and protective oxide layer on its surface when exposed to air or moisture.
Marine and Chemical Processing
Steel and other metals degrade quickly in saltwater or harsh chemical environments. Titanium, however, thrives.
It is used to construct submarine hulls, propeller shafts, and heat exchangers for naval vessels. In the chemical industry, it is essential for pipes, reaction vessels, and valves that handle chlorides and other corrosive agents that would destroy lesser materials.
Desalination and Power Generation
Desalination plants, which turn seawater into fresh water, rely heavily on titanium tubing and components. Its ability to resist corrosion from highly saline water ensures the plant's longevity and operational reliability.
The Medical Marvel: Biocompatibility
Titanium is one of the most biocompatible metals, meaning it is non-toxic and not rejected by the human body. Furthermore, it possesses the unique ability of osseointegration, where bone tissue can grow and fuse directly onto its surface.
Orthopedic Implants
This biocompatibility makes titanium the gold standard for medical implants intended to last for decades.
It is the primary material for hip and knee replacements, bone screws and plates for fracture repair, and dental implants. Its strength ensures these devices can withstand the mechanical stresses of daily life.
Surgical Instruments and Devices
Because it is strong, lightweight, and can be repeatedly sterilized without degrading, titanium is also used for surgical instruments. It is also used to encase critical implantable devices like pacemakers, protecting the electronics from the body's internal environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Isn't Everything Titanium?
If titanium is so remarkable, the logical question is why it isn't used more broadly. The answer comes down to two significant challenges: cost and complexity.
The High Cost of Production
The process of refining titanium metal from its ore is significantly more complex and energy-intensive than for iron or aluminum. The primary method, the Kroll Process, is a multi-stage batch process that makes raw titanium sponge far more expensive than other common structural metals.
The Challenge of Machining and Welding
Working with titanium is notoriously difficult. It has poor thermal conductivity, which causes heat to build up at the cutting tool, and it has a tendency to gall (smear and stick to the tool). Welding it requires an inert gas shield to prevent contamination, adding further cost and complexity to manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use titanium is always a deliberate calculation of performance versus cost. It is chosen when its specific advantages provide a value that cannot be achieved with any other material.
- If your primary focus is extreme performance and weight savings (aerospace, racing): Titanium is the standard for critical structural and engine components where failure is not an option.
- If your primary focus is surviving harsh, corrosive environments (marine, chemical): Titanium's upfront cost is justified by its long-term reliability and prevention of costly failures.
- If your primary focus is compatibility with the human body (medical): Titanium's unique biocompatibility and ability to fuse with bone make it the default material for permanent implants.
- If your primary focus is creating premium consumer products (watches, electronics): Titanium offers a marketable combination of durability, low weight, and a high-end aesthetic that customers will pay more for.
Ultimately, understanding these properties reveals that titanium is not just a material, but a strategic solution for engineering's most demanding challenges.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Titanium Products | Primary Property Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Jet engine components, airframe structures | Strength-to-weight ratio |
| Medical | Hip/knee implants, dental implants, surgical instruments | Biocompatibility, osseointegration |
| Marine & Chemical | Submarine hulls, pipes, valves, heat exchangers | Extreme corrosion resistance |
| Automotive | Connecting rods, valves, exhaust systems | High-performance, weight reduction |
| Consumer Goods | High-end watches, sporting equipment | Premium durability and lightweight |
Need High-Performance Materials for Your Lab?
Titanium's unique properties make it ideal for demanding applications. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing top-tier lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're in research, chemical processing, or materials testing, our solutions ensure precision, durability, and reliability.
Contact us today to explore how we can support your laboratory's success with the right tools and expertise!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Ball Press Mold for Lab
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- XRF & KBR plastic ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
People Also Ask
- How does hardness change with temperature? Understand the Inverse Relationship to Prevent Failure
- What are the advantages disadvantages and uses of sheet metal? The Ultimate Guide to Material Selection
- What are two disadvantages of metal? Understanding Corrosion and Weight Limitations
- How can you improve corrosion resistance? Extend Equipment Life with Proven Strategies
- What is titanium used for in manufacturing? Leveraging High-Performance Properties for Critical Applications



















