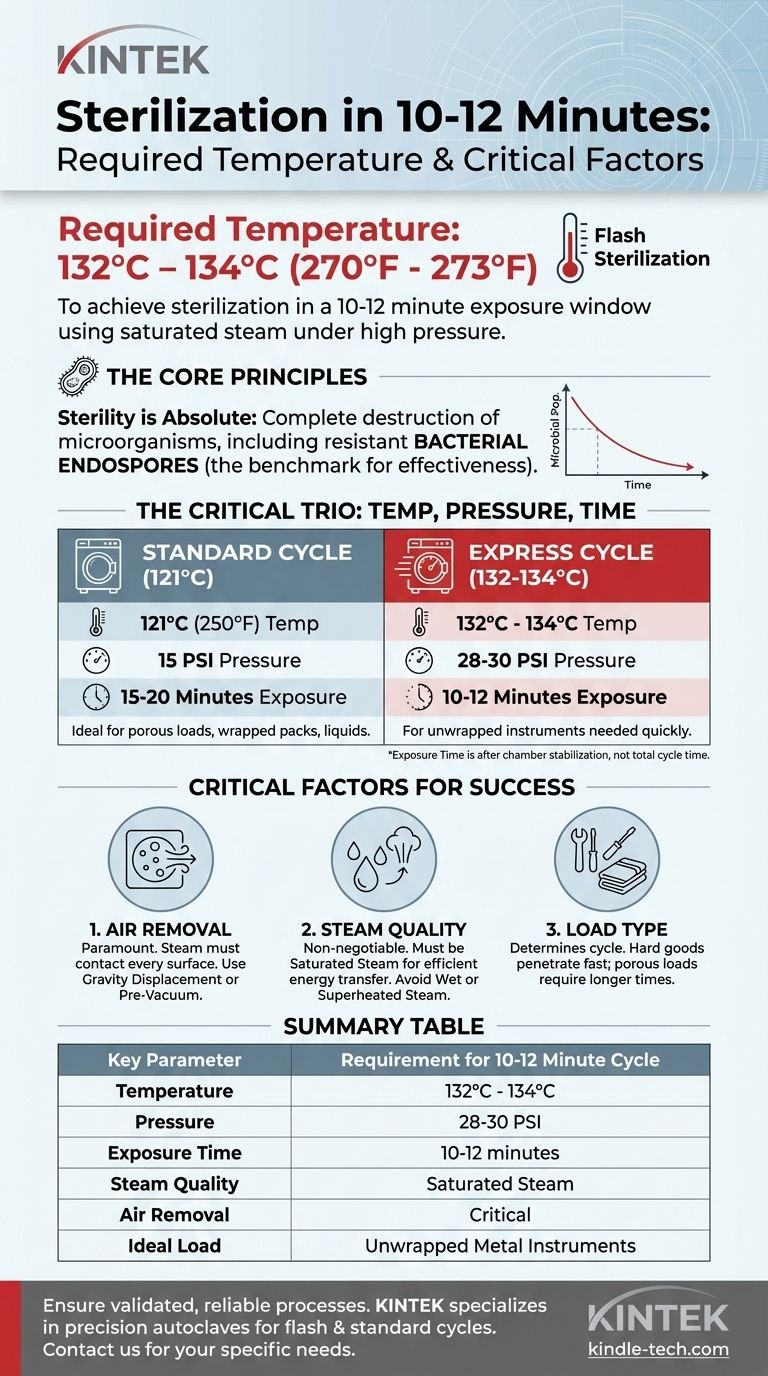
To achieve sterilization in a 10 to 12-minute exposure window, the required temperature is typically 132°C to 134°C (270°F to 273°F). This process, known as flash or express sterilization, relies on using saturated steam under high pressure inside a specialized device called an autoclave. Simply reaching this temperature is not enough; the method and conditions are just as critical for success.
The question of sterilization is not just about temperature and time. True sterility is achieved through a validated process where saturated steam, at the correct temperature and pressure, directly contacts all surfaces of an object for a specific duration, ensuring even the most resistant microorganisms are eliminated.

The Core Principles of Sterilization
Sterilization is an absolute term. An item is either sterile or it is not. It means the complete destruction of all viable microorganisms, including the highly resistant dormant forms known as bacterial endospores.
Why Spores are the Benchmark
Most bacteria are easily killed by boiling water (100°C). However, endospores from bacteria like Geobacillus stearothermophilus can survive these conditions. Effective sterilization methods are specifically designed and validated to prove they can kill these tough spores, ensuring that all lesser organisms have also been destroyed.
It's a Game of Probabilities
Sterilization is a logarithmic process. For a given temperature, a certain percentage of the microbial population is killed every minute. The goal is to run the process long enough to achieve a "sterility assurance level" (SAL), typically a one-in-a-million probability that a single viable microorganism remains.
The Critical Trio: Temperature, Pressure, and Time
For steam sterilization, these three factors are inseparable. Higher temperatures can achieve sterilization in shorter times, but only if the correct pressure and steam quality are present.
The Standard Cycle: 121°C (250°F)
The most common and historically validated sterilization cycle is 121°C (250°F), held for an exposure time of 15 to 20 minutes. This requires maintaining a pressure of approximately 15 PSI (pounds per square inch) above atmospheric pressure to keep the water as saturated steam instead of boiling off.
The Express Cycle: 132°C to 134°C (270°F to 273°F)
To reduce the cycle time to the 10-12 minute range you asked about, the temperature must be increased significantly. This higher temperature of 132°C to 134°C kills spores much more rapidly. This requires a correspondingly higher pressure of around 28 to 30 PSI. This is often used for unwrapped instruments needed quickly.
Exposure Time vs. Total Cycle Time
It is critical to understand that the "10-12 minutes" is the exposure time—the period after the chamber has fully reached the target temperature and pressure. The total cycle time will be much longer, as it includes the time needed to heat up, remove air, and then cool down and vent.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
Simply setting an autoclave to 134°C for 10 minutes does not guarantee sterility. The following factors are equally important and are common points of failure.
Factor 1: Air Removal is Paramount
Steam must directly contact every surface to transfer its energy. Any trapped air creates an insulating pocket, a "cold spot," where the temperature will not reach the target. Autoclaves use two main methods to solve this:
- Gravity Displacement: Steam is fed into the top, and because it is less dense than air, it pushes the colder air out of a drain at the bottom. This is a slower but simpler method.
- Pre-Vacuum (Pre-Vac): A vacuum pump actively removes air from the chamber before steam is introduced. This is faster and more effective, especially for complex or wrapped items.
Factor 2: Steam Quality is Non-Negotiable
The ideal medium is saturated steam. This is steam at the precise temperature where it is about to condense back into water. This condensation is what transfers immense thermal energy to the items being sterilized, rapidly denaturing microbial proteins.
- Wet Steam (too much water) doesn't hold as much energy and leaves loads wet.
- Superheated Steam (too dry) acts more like hot air, which is far less efficient at transferring heat and requires much longer exposure times.
Factor 3: The Load Determines the Cycle
You cannot sterilize all items with the same cycle. The nature of the load dictates the time required for steam to penetrate it fully.
- Hard, Non-Porous Goods (e.g., a single steel tool): Steam penetrates instantly. Short cycles are effective.
- Porous Loads (e.g., surgical gowns, wrapped packs): Steam must penetrate deep into the material. This requires longer exposure times, often using a pre-vacuum cycle.
- Liquids (e.g., growth media): Liquids heat slowly and require longer cycles at lower temperatures (like 121°C) to prevent boiling over.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct cycle depends entirely on what you are trying to sterilize and the equipment you have.
- If your primary focus is rapidly sterilizing simple, unwrapped metal instruments: A 132°C-134°C cycle with a 10-minute exposure time is an appropriate and common standard, provided you are using a modern, validated autoclave.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing porous loads, wrapped packs, or liquids: You must use a longer cycle to ensure full steam penetration, with 121°C for 15-20 minutes serving as a much safer and more reliable baseline.
- If you are operating in a critical environment (medical, pharmaceutical): You must never assume a cycle works. Use chemical indicators in every run and periodic biological indicators (spore tests) to formally validate that your process is achieving true sterility.
Ultimately, successful sterilization is not about hitting a number, but about executing a validated and controlled scientific process.
Summary Table:
| Key Parameter | Requirement for 10-12 Minute Cycle |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 132°C to 134°C (270°F to 273°F) |
| Pressure | 28-30 PSI |
| Exposure Time | 10-12 minutes (after chamber stabilization) |
| Steam Quality | Saturated steam (non-negotiable) |
| Air Removal | Critical (Gravity Displacement or Pre-Vacuum) |
| Ideal Load Type | Simple, unwrapped metal instruments |
Ensure your lab's sterilization process is validated and reliable. KINTEK specializes in precision laboratory autoclaves and sterilization equipment designed to meet the exacting demands of modern research and healthcare. Our autoclaves deliver consistent saturated steam, precise temperature control, and validated cycles for both flash sterilization (132°C) and standard porous loads (121°C).
Let our experts help you select the right equipment for your specific applications—from rapid instrument processing to complex porous load sterilization. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory's sterilization needs and achieve guaranteed sterility assurance levels.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tube Racks
People Also Ask
- Can autoclave sterilize liquid? Master Safe and Effective Liquid Sterilization
- What is the use of autoclave in medical? The Critical Role of Sterilization in Patient Safety
- How does the lab autoclave work? Achieve Complete Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What are the sizes of autoclaves? A Guide to Choosing the Right Capacity for Your Lab
- Why is it important to autoclave the prepared reagents before using? Ensure Sterility and Reliable Results



















