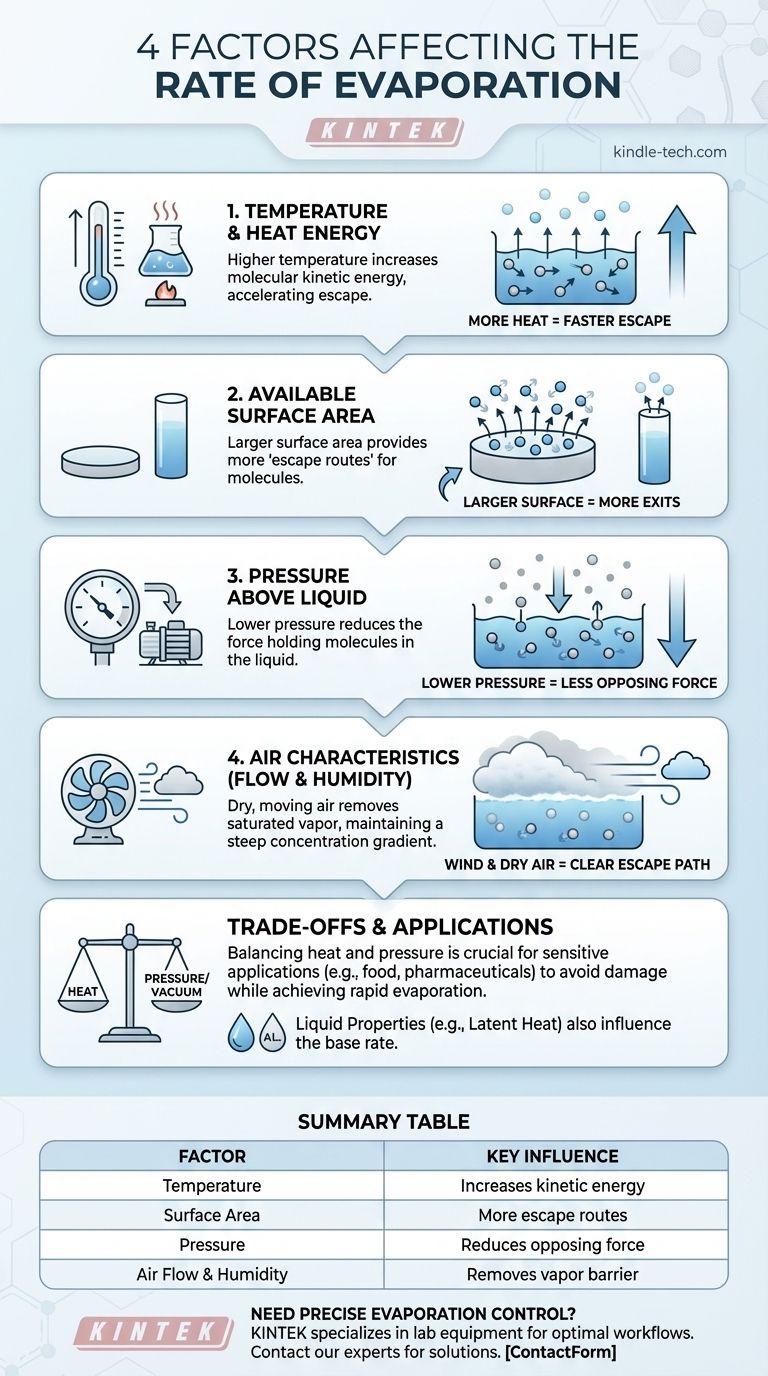
The four primary factors that affect the rate of evaporation are temperature, the surface area of the liquid, the pressure of the surrounding environment, and the characteristics of the air above the liquid, such as its flow and humidity. While other properties like the liquid's specific heat capacity play a role, these four variables are the most critical external levers for controlling how quickly a liquid turns into a gas.
Evaporation is fundamentally a process of molecules escaping from a liquid's surface. The rate of this escape is determined by the energy pushing the molecules out versus the environmental forces pushing them back in. To increase evaporation, you either increase the molecules' energy or decrease the forces holding them back.

Factor 1: Temperature and Heat Energy
The rate of evaporation is directly linked to the amount of heat energy available. Supplying more heat accelerates the process significantly.
The Role of Kinetic Energy
Heat is a form of energy. When a liquid is heated, its molecules absorb this energy and begin to move faster, increasing their kinetic energy.
Molecules with enough kinetic energy can overcome the intermolecular forces holding them within the liquid and escape from the surface as a gas. More heat means more molecules reach this escape velocity per second.
The Heat Transfer Rate
The speed at which heat can be transferred into the liquid is a critical bottleneck. A more efficient heat source or a liquid with better thermal conductivity will allow for a faster evaporation rate, as energy is supplied more quickly to the molecules at the surface.
Factor 2: Available Surface Area
The physical space where evaporation can occur is a major limiting factor. Evaporation only happens at the surface of a liquid.
The Escape Route
Think of the liquid's surface as the only exit from a crowded room. A larger surface area is like having more exit doors—it allows more molecules to escape simultaneously.
Spreading a liquid out into a thin film dramatically increases its surface area, which is why a puddle on the pavement evaporates much faster than the same amount of water in a deep bucket.
Factor 3: Pressure Above the Liquid
The pressure exerted on the liquid's surface, typically by the atmosphere, acts as a physical barrier against escaping molecules.
The Weight of the Air
Atmospheric pressure constantly pushes down on the surface of a liquid. This force makes it more difficult for molecules to break free and enter the gaseous phase.
How Lower Pressure Accelerates Evaporation
When you reduce the pressure above a liquid—for example, by creating a vacuum or moving to a higher altitude—you remove some of this opposing force.
With less pressure holding them back, molecules can escape more easily and at a much lower temperature. This is the principle behind vacuum evaporators used in the food industry to concentrate liquids without damaging them with high heat.
Factor 4: Air Characteristics (Flow and Humidity)
The state of the air directly above the liquid's surface plays a crucial role in either helping or hindering evaporation.
The Concept of Saturation
The air can only hold a certain amount of vapor, a state known as saturation. If the air directly above the liquid is already saturated with vapor (i.e., at 100% humidity), evaporation will effectively stop because there is no room for more molecules to escape into.
How Wind and Air Flow Help
Wind or any form of air flow is extremely effective at increasing evaporation. It works by blowing away the layer of humid, saturated air at the surface and replacing it with drier air.
This maintains a steep concentration gradient between the liquid and the air, ensuring the "escape route" for molecules remains clear and encouraging a continuous high rate of evaporation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
These factors do not operate in isolation; they interact with each other and with the intrinsic properties of the liquid itself.
Heat vs. Pressure
In many industrial applications, applying massive amounts of heat is either inefficient or would damage the product (like food or pharmaceuticals).
By significantly lowering the pressure, operators can achieve rapid evaporation at much lower temperatures, preserving the quality of the final product. This is a direct trade-off between the two factors.
The Liquid's Own Properties
Some liquids inherently evaporate faster than others. This is due to factors like the latent heat of vaporization—the amount of energy required to convert a unit of the liquid into a gas.
Water has a high latent heat, requiring a lot of energy to evaporate. In contrast, liquids like alcohol have weaker intermolecular forces and lower latent heat, allowing them to evaporate much more quickly under the same conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to managing evaporation depends entirely on your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is to speed up evaporation (e.g., drying clothes): Increase temperature (sunlight), maximize surface area (spread them out), and ensure good air flow (a breezy day or a fan).
- If your primary focus is to slow down evaporation (e.g., preserving a water supply): Reduce surface area (use a deep, narrow tank), cover it to stop air flow, and keep it cool and shaded.
- If your primary focus is efficient industrial processing (e.g., concentrating juice): Lowering the pressure is the most effective method for rapid evaporation without using damagingly high temperatures.
By understanding these core physical principles, you can effectively control the rate of evaporation for any application.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Influence on Evaporation Rate |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Higher temperature increases molecular kinetic energy, accelerating escape. |
| Surface Area | Larger surface area provides more 'escape routes' for molecules. |
| Pressure | Lower pressure reduces the force holding molecules in the liquid. |
| Air Flow & Humidity | Dry, moving air removes saturated vapor, maintaining a steep concentration gradient. |
Need precise control over evaporation in your lab? Whether you're concentrating samples, drying materials, or developing new processes, understanding these factors is just the first step. KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment that puts this knowledge into practice—from precise heating mantles and hot plates to efficient vacuum evaporators. Let our experts help you select the right equipment to optimize your workflow. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Laboratory Vertical Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What factors affect evaporation and condensation? Master the Science of Water's Phase Changes
- What temperature does evaporation occur? Unlock the Secrets to Controlling the Rate of Evaporation
- How long does it take for THC to evaporate? The Real Science Behind Potency Loss



