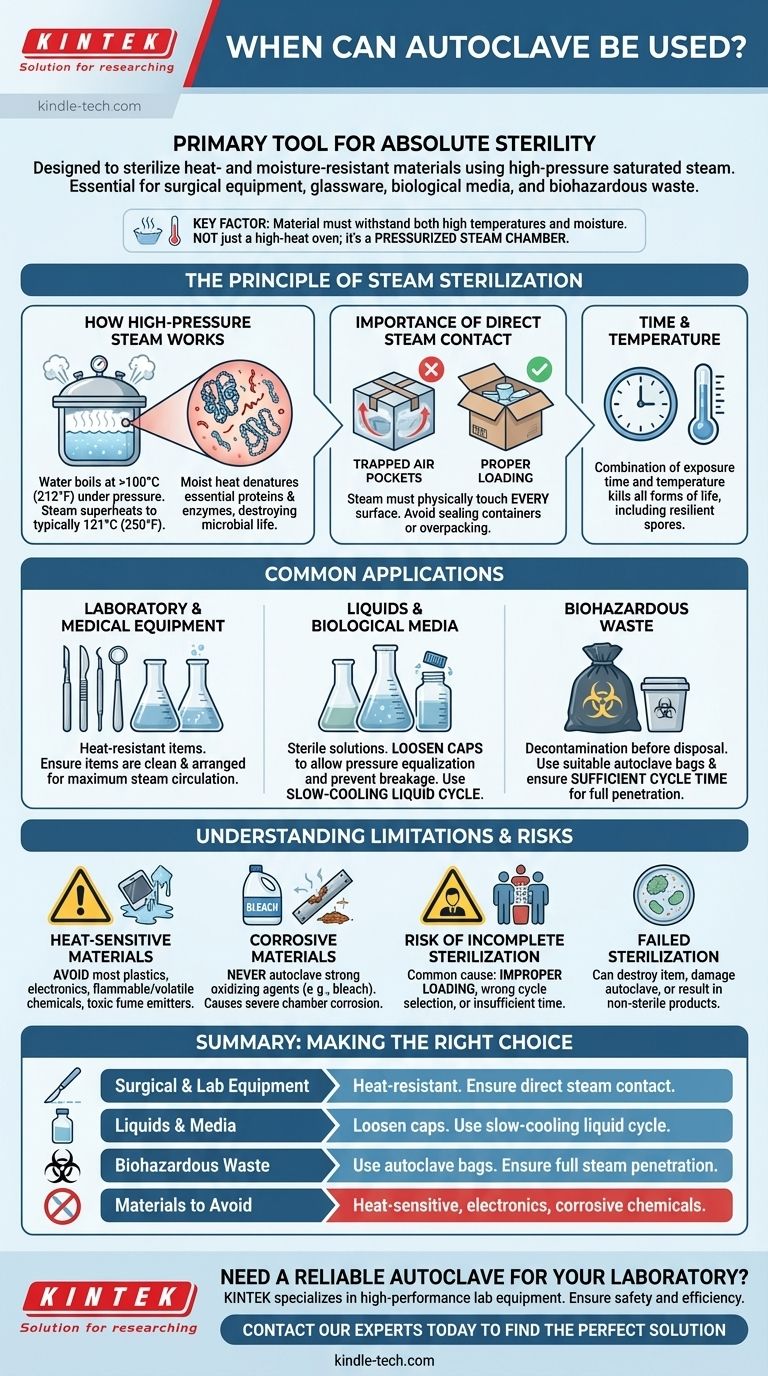
In any setting requiring absolute sterility, an autoclave is the primary tool used. It is designed to sterilize a wide range of materials by subjecting them to high-pressure, saturated steam at elevated temperatures. This process is essential for sterilizing surgical equipment, laboratory glassware, biological media and solutions, and decontaminating biohazardous waste before disposal.
An autoclave is not merely a high-heat oven; it is a pressurized steam chamber. Its effectiveness hinges on steam's ability to make direct contact with every surface, meaning its use is defined by one critical factor: whether the material can withstand both high temperatures and moisture.

The Principle of Steam Sterilization
Understanding how an autoclave works is key to using it correctly. The process relies on a combination of time, temperature, and direct steam contact to kill all forms of microbial life, including resilient bacterial spores.
How High-Pressure Steam Works
An autoclave creates an environment where water boils at a temperature higher than its normal 100°C (212°F). By increasing the pressure inside the chamber, the steam becomes superheated, typically to 121°C (250°F) or higher.
This moist heat is exceptionally effective at denaturing the essential proteins and enzymes within microorganisms, leading to their destruction far more efficiently than dry heat alone.
The Importance of Direct Steam Contact
For sterilization to be successful, steam must physically touch every surface of the items being processed. Trapped air is the enemy of autoclaving.
This is why proper loading is critical. You must never seal containers completely or overpack the chamber, as this creates air pockets that prevent steam from penetrating and sterilizing those areas.
Common Applications for an Autoclave
An autoclave is a versatile instrument found in microbiology, medical, veterinary, and dental fields. It is capable of sterilizing a variety of solid, liquid, and hollow items.
Laboratory and Medical Equipment
The most common use is for heat-resistant items. This includes stainless steel surgical instruments, forceps, glassware (like flasks and beakers), and certain types of heat-stable plastics (e.g., polypropylene).
Liquids and Biological Media
Autoclaves are essential for preparing sterile liquid solutions and nutrient media for microbiological cultures.
When autoclaving liquids, bottle caps must be loosened to allow for pressure equalization during the heating and cooling cycles. A tight seal can cause the container to shatter.
Biohazardous Waste
Before disposal, potentially infectious materials such as used petri dishes, cultures, and contaminated lab supplies must be decontaminated.
Placing this waste in a suitable autoclave bag and running a sterilization cycle renders it non-hazardous and safe for standard disposal.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, an autoclave is not a universal solution. Using it on the wrong materials can destroy the item, damage the autoclave, or lead to failed sterilization.
Heat-Sensitive Materials to Avoid
Any material that can be damaged by high temperatures or moisture must not be autoclaved.
This includes most plastics (like polyethylene), flammable or volatile chemicals, items containing electronics, and any substance that may emit toxic fumes when heated.
Corrosive Materials
Strong oxidizing agents, such as bleach, should never be placed in an autoclave. The high heat and pressure will cause them to vaporize and severely corrode the stainless steel chamber, leading to permanent damage.
Risk of Incomplete Sterilization
User error is the most common cause of sterilization failure. This often results from improper loading (packing items too densely), selecting the wrong cycle for the material, or not allowing enough time for steam to penetrate the entire load.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure safety and effectiveness, match your procedure to the material you are sterilizing.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing solid equipment or glassware: Ensure items are clean and arranged to allow for maximum steam circulation between them.
- If your primary focus is preparing liquids or media: Always loosen caps and select a dedicated "liquid" cycle, which cools down slowly to prevent boil-over and vessel breakage.
- If your primary focus is decontaminating biohazardous waste: Use a vented autoclave bag within a secondary heat-resistant container and ensure the cycle time is sufficient to penetrate the entire mass of waste.
Properly understanding an autoclave's function transforms it from a simple machine into a reliable pillar of your safety and research protocols.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Surgical & Lab Equipment | Must be heat-resistant (e.g., stainless steel, glass). Arrange for direct steam contact. |
| Liquids & Media | Loosen caps; use a slow-cooling liquid cycle to prevent boil-over. |
| Biohazardous Waste | Use autoclave bags in secondary containers; ensure full steam penetration. |
| Materials to Avoid | Heat-sensitive plastics, electronics, corrosive chemicals (e.g., bleach). |
Need a reliable autoclave for your laboratory? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including autoclaves designed for precise sterilization of instruments, media, and waste. Ensure your lab meets the highest standards of safety and efficiency—contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
People Also Ask
- Why is it important to use the autoclave to sterilize laboratory tools? Ensure Complete Sterility for Reliable Results
- What is the function of autoclave in tissue culture laboratory? Ensure Absolute Sterility for Successful Cell Growth
- What is the 121 cycle of autoclave? A Guide to Guaranteed Sterilization
- What is the purpose of autoclaving in the laboratory? Ensure Sterile Safety & Integrity
- What are the specifications of a laboratory autoclave? A Guide to Key Features for Safe Sterilization



















