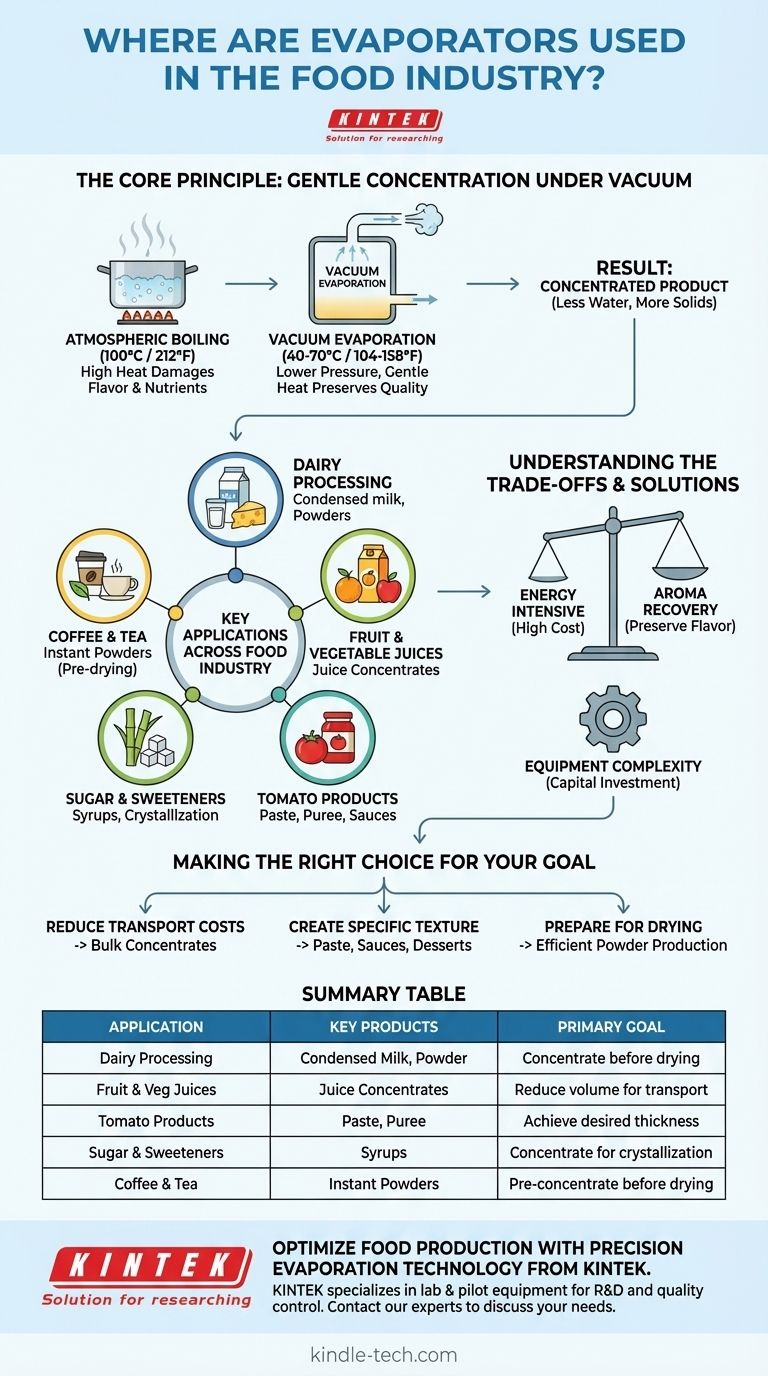
In the food industry, evaporators are primarily used to concentrate liquid foods by removing water. This process is fundamental in the production of staples like fruit juice concentrates, condensed milk, tomato paste, and instant coffee, where reducing volume and increasing solids content is critical.
The core purpose of evaporation in food processing is not simply to remove water, but to do so under controlled conditions—typically a vacuum—that lower the boiling point. This gentle approach preserves the food's flavor, color, and nutritional value, which would otherwise be damaged by high heat.

The Core Principle: Gentle Concentration Under Vacuum
Evaporation technology is essential for creating shelf-stable, cost-effective, and high-quality food products. The entire process is designed around one central challenge: removing water without "cooking" or degrading the food itself.
Why Not Just Boil It?
Simply boiling a liquid food product at atmospheric pressure often requires high temperatures (100°C / 212°F). This level of heat can scorch sugars, break down delicate flavor compounds, degrade vitamins, and alter the product's intended color and texture.
The Role of Vacuum
Evaporators solve this problem by applying a vacuum. By lowering the pressure inside the evaporation chamber, the boiling point of water is significantly reduced. This allows water to be rapidly boiled off at much lower temperatures (e.g., 40-70°C / 104-158°F).
This low-temperature process is crucial for protecting the sensitive organic compounds that give food its character.
The Result: A More Concentrated Product
As water vapor is removed, the remaining liquid becomes more concentrated in dissolved solids like sugars, minerals, proteins, and flavor molecules. This concentrated liquid is the desired end product or an intermediate for further processing, like drying.
Key Applications Across the Food Industry
Evaporation is a cornerstone process in numerous sectors of the food industry, valued for its ability to reduce shipping weight, increase shelf life, and intensify flavor.
Dairy Processing
In the dairy industry, evaporators are used to produce condensed milk and evaporated milk. They are also a critical first step in making milk powder, whey protein concentrate, and infant formula by concentrating the liquid before it enters a spray dryer.
Fruit and Vegetable Juices
The production of fruit juice concentrates relies heavily on evaporation. Removing water from fresh juice creates a stable, high-value syrup that is cheaper to transport and store, which can later be reconstituted into juice by adding water back.
Tomato Products
Evaporation is the key process for converting raw tomato juice into tomato paste, puree, and sauces. The level of concentration directly determines the thickness and richness of the final product.
Sugar and Sweeteners
In sugar refining, large-scale evaporators concentrate the thin, watery juice extracted from sugar cane or sugar beets. This creates a thick syrup from which sugar crystals can be formed and harvested.
Coffee and Tea
The manufacturing of instant coffee and tea involves brewing the product and then concentrating the resulting liquid using an evaporator. This concentrated liquid is then dried (typically by spray or freeze-drying) to create the final soluble powder.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While indispensable, evaporation technology presents clear operational challenges and trade-offs that food producers must manage.
Energy Consumption
Boiling off large volumes of water, even at low temperatures, is an extremely energy-intensive process. Energy costs are a major factor in the economic viability of evaporation, leading to complex multi-stage designs (Multiple-Effect Evaporators) to recover and reuse heat.
Potential for Flavor Loss
Some of the most delicate and volatile aroma compounds can be lost along with the water vapor during evaporation. Advanced systems often include aroma recovery units that capture these compounds from the vapor and add them back to the final concentrate to maintain a full flavor profile.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
Industrial evaporators are sophisticated, large-scale pieces of equipment. They represent a significant capital investment and require specialized knowledge for operation and maintenance to ensure efficiency and product safety.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The application of evaporation is always tied to a specific commercial or product objective.
- If your primary focus is reducing transport and storage costs: Evaporation is ideal for creating bulk concentrates, such as fruit juices or sugar syrups, that can be shipped globally and reconstituted later.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific product texture: Evaporation is used to achieve the desired thickness and solids content for products like tomato paste, dairy desserts, and sauces.
- If your primary focus is preparing for a drying process: Evaporation serves as an efficient pre-concentration step before spray drying, dramatically improving the efficiency of creating powders like milk or instant coffee.
Ultimately, evaporation is a foundational technology that transforms perishable liquid raw materials into stable, valuable, and globally transportable food products.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Products | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Dairy Processing | Condensed milk, milk powder, whey protein | Concentrate before drying; create shelf-stable products |
| Fruit & Vegetable Juices | Juice concentrates (e.g., orange, apple) | Reduce volume for cheaper transport and storage |
| Tomato Products | Tomato paste, puree, and sauces | Achieve desired thickness and richness |
| Sugar & Sweeteners | Sugar syrups | Concentrate raw juice for crystallization |
| Coffee & Tea | Instant coffee and tea powders | Pre-concentrate liquid before spray drying |
Optimize your food production with precision evaporation technology from KINTEK.
Whether you are developing a new concentrate, improving product quality, or scaling up production, the right evaporation system is critical for preserving flavor and controlling costs. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for food R&D and quality control, helping you perfect your processes before full-scale implementation.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory and pilot-scale evaporation needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What role do laboratory freeze dryers play in the food industry? Unlock Superior Food Preservation
- What is the main difference between freeze drying and vacuum drying? A Guide to Quality vs. Efficiency
- What are the different freeze drying methods? Choose the Right Lyophilization Path
- What is the function of Freeze-thaw Equipment in Au-(PNiPAAm/PVA) hydrogel? Achieve High-Speed Photothermal Actuation
- What types of biological materials are suitable for freeze drying? Preserve Stability and Activity



















