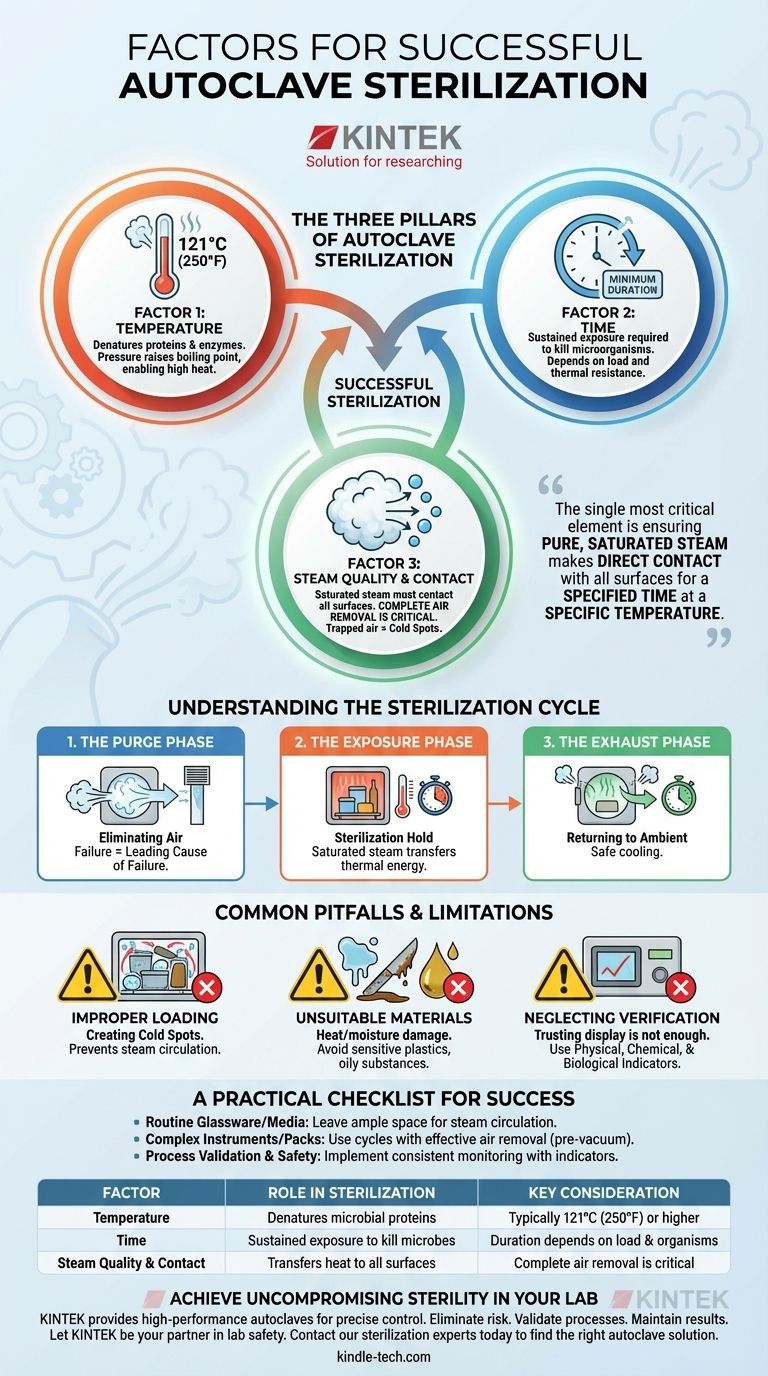
At its core, successful autoclave sterilization depends on three interdependent factors: time, temperature, and direct contact with high-quality saturated steam. It is not the pressure that sterilizes, but the high temperature that pressure makes possible. Achieving this requires the complete removal of air from the chamber so that steam can penetrate and make contact with every surface of the items being sterilized.
The single most critical element for successful sterilization is ensuring that pure, saturated steam makes direct contact with all surfaces of an object for a specified amount of time at a specific temperature. The primary point of failure is almost always trapped air, which acts as an insulating barrier and prevents effective heat transfer.
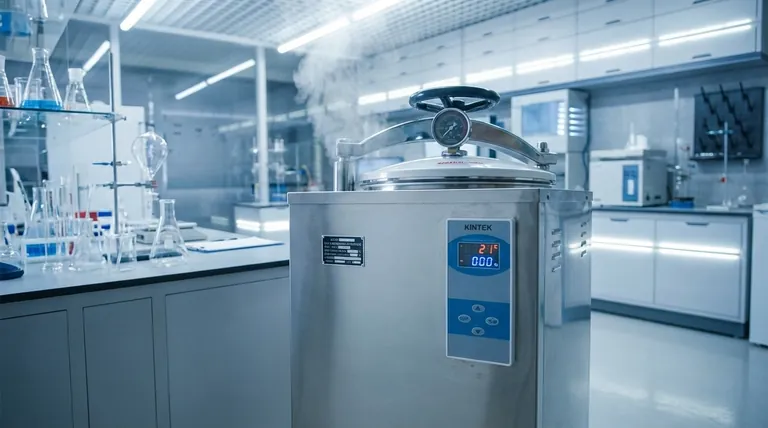

The Three Pillars of Autoclave Sterilization
To achieve sterile results, you must master the relationship between temperature, time, and steam. These are not independent settings but a unified system.
Factor 1: Temperature
The high temperatures achieved inside an autoclave—typically 121°C (250°F) or higher—are what denature the essential proteins and enzymes of microorganisms, leading to their death.
Pressure is merely the tool used to raise the boiling point of water above 100°C. Without pressure, you cannot achieve sterilizing temperatures with steam.
Factor 2: Time
Microorganisms do not die instantaneously. They must be exposed to the target temperature for a minimum duration to ensure they are all eliminated.
This required duration, or exposure time, depends on the nature of the items being sterilized and the thermal resistance of the microorganisms you aim to kill.
Factor 3: Steam Quality and Contact
This is arguably the most critical and often misunderstood factor. Sterilization requires saturated steam, which is pure water vapor at the temperature at which it is about to condense.
For steam to be effective, it must displace all the air within the sterilization chamber and within the items themselves. Air pockets create "cold spots" that prevent steam from reaching surfaces, rendering the process ineffective.
Understanding the Sterilization Cycle
A standard autoclave cycle is a precisely controlled three-phase process designed to manage these factors effectively.
The Purge Phase: Eliminating Air
The cycle begins by actively removing air from the chamber. Steam is injected, displacing the cooler, denser air and forcing it out through an exhaust vent.
Failure to completely purge all air is the leading cause of sterilization failure.
The Exposure Phase: The Sterilization Hold
Once air is removed, the exhaust valve closes. Steam continues to enter, raising the pressure and temperature to the desired setpoint for the programmed exposure time.
During this phase, the saturated steam transfers its thermal energy to the items, maintaining the lethal temperature needed for sterilization.
The Exhaust Phase: Returning to Ambient
After the exposure time is complete, the exhaust valve opens, releasing the steam and pressure from the chamber. This allows the chamber to slowly return to normal atmospheric pressure and the items to cool.
Common Pitfalls and Limitations
Understanding what can go wrong is as important as knowing the ideal process. Autoclaving is a powerful technique, but it has clear boundaries.
Improper Loading: Creating Cold Spots
Placing items too close together, using sealed containers, or packing materials too densely prevents steam from circulating and penetrating. This effectively creates insulating air pockets where sterilization cannot occur.
Unsuitable Materials: What Not to Autoclave
An autoclave is not a universal solution. The high heat and moisture will damage or destroy certain materials.
Avoid autoclaving heat-sensitive plastics that can melt, high-grade carbon steel instruments (like scalpel blades) that can become dull, and oily or waxy substances that do not mix with water. Many protein-based solutions, such as vaccines or serums, will also degrade and must be sterilized by other methods like filtration.
Neglecting Verification
Trusting the machine's display is not enough. Successful sterilization protocols require routine verification.
Use physical indicators, such as an alloy that melts only when the correct time and temperature are met, to provide a visual check for each load. Regular calibration and maintenance of the autoclave are also non-negotiable for reliable performance.
A Practical Checklist for Success
Apply these principles to ensure your sterilization process is both effective and repeatable.
- If your primary focus is routine sterilization of glassware and media: Emphasize proper loading by leaving ample space between items to ensure steam can circulate freely.
- If you are sterilizing complex instruments or wrapped packs: Ensure you are using an autoclave cycle with an effective air removal (purge) phase, such as a pre-vacuum cycle, to guarantee steam penetration.
- If your priority is process validation and safety: Implement a consistent monitoring program using physical, chemical, and biological indicators to confirm every cycle achieves true sterility.
Understanding these core principles transforms autoclaving from a simple machine operation into a controlled, scientific process that ensures safety and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Role in Sterilization | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Denatures microbial proteins | Typically 121°C (250°F) or higher |
| Time | Sustained exposure to kill microbes | Duration depends on load and organisms |
| Steam Quality & Contact | Transfers heat to all surfaces | Complete air removal is critical |
Achieve Uncompromising Sterility in Your Lab
Mastering autoclave use is fundamental to laboratory safety and integrity. KINTEK understands that reliable sterilization is non-negotiable for your research, diagnostics, and production workflows.
We provide high-performance autoclaves and consumables designed for precise control over time, temperature, and steam quality, helping you eliminate the risk of sterilization failure. Our expertise supports laboratories in validating their processes and maintaining consistent, verifiable results.
Let KINTEK be your partner in lab safety.
Contact our sterilization experts today to find the right autoclave solution for your specific needs and ensure every cycle achieves true sterility.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave equipped with a stirring device for molten salt testing? Dynamic Accuracy
- What is the primary function of a laboratory autoclave in the pre-treatment of medical plastic waste for liquid fuel?
- What is the function of laboratory autoclaves in SCWR research? Predict Material Compatibility and Corrosion Kinetics
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK



















