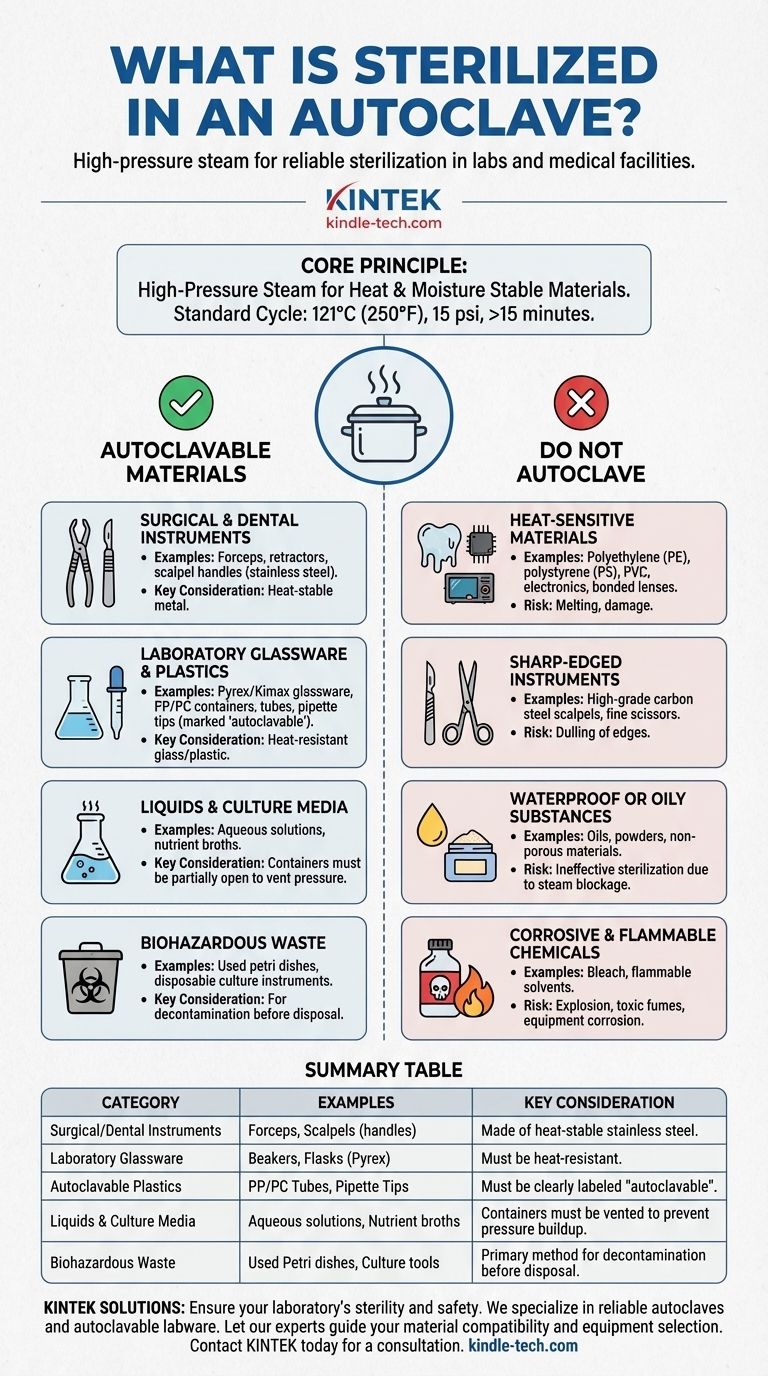
To be clear, an autoclave is designed to sterilize surgical instruments, laboratory glassware, autoclavable plastics (like certain tubes and pipette tips), culture media, aqueous solutions, and biohazardous waste. The core principle is its use of high-pressure steam, making it suitable for any material that can withstand high temperatures and moisture.
The decision to autoclave an instrument hinges on a single factor: its ability to withstand high temperatures (typically 121°C) and pressurized steam. If a material is heat-stable and allows for steam penetration, it is a candidate for autoclaving; if not, an alternative sterilization method is required.

The Principle of Autoclave Sterilization
An autoclave does not simply use dry heat. Its effectiveness comes from using steam under pressure to achieve temperatures high enough to kill all microorganisms, including resilient bacterial spores.
The Role of Pressurized Steam
The process involves heating water in a sealed pressure vessel to create steam. As this steam is forced into the chamber, it displaces air and raises both the temperature and pressure significantly.
This pressurized steam efficiently transfers heat to the items inside, denaturing the proteins of any microorganisms present and ensuring complete sterilization.
The Standard Sterilization Cycle
A typical autoclave cycle runs at 121°C (250°F) under 15 psi (pounds per square inch) of pressure for at least 15 minutes. This duration can be extended for larger loads to ensure the steam fully penetrates all items.
Autoclavable Materials: A Detailed Breakdown
Understanding which categories of materials are safe for autoclaving prevents damage to equipment and ensures the sterilization process is effective.
Surgical and Dental Instruments
Most metal surgical instruments, such as forceps, scalpels (handles, not always blades), and retractors, are made of stainless steel and are designed for autoclaving.
Laboratory Glassware and Plastics
Heat-resistant glassware, such as Pyrex or Kimax beakers and flasks, is ideal for autoclaving. Certain plastics, clearly marked as "autoclavable," like polypropylene (PP) and polycarbonate (PC) containers, tubes, and pipette tips, are also safe.
Liquids and Culture Media
Aqueous solutions, water, and nutrient media for microbiology are commonly sterilized in an autoclave. It is critical that containers for liquids are left partially open to prevent pressure buildup and potential explosion.
Biohazardous Waste
The autoclave is a primary method for decontaminating and sterilizing biohazardous waste, such as used petri dishes and disposable culture instruments, before disposal.
Understanding the Limitations: What to Never Autoclave
Attempting to autoclave unsuitable materials can result in melted equipment, ineffective sterilization, release of toxic fumes, or damage to the autoclave itself.
Heat-Sensitive Materials
Standard plastics like polyethylene (PE), polystyrene (PS), and PVC will melt under the high heat. Many electronic devices and instruments with bonded lenses or sensitive components are also unsuitable.
Sharp-Edged Instruments
While many surgical tools are autoclavable, very fine or sharp implements like high-grade carbon steel scalpels and scissors can become dull. The high temperature can degrade the integrity of the finely machined cutting edge.
Waterproof or Oily Substances
Oils, powders, and other waterproof substances are not effectively sterilized by autoclaving. Steam cannot penetrate these materials, leaving the sterilization process incomplete.
Corrosive and Flammable Chemicals
Never place flammable, reactive, corrosive, or toxic materials inside an autoclave. This includes common chemicals like household bleach, which can vaporize and corrode the stainless steel chamber.
Making the Right Sterilization Choice
Your choice of sterilization method must align with the material composition of your instruments and your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is routine surgical instruments and glassware: The autoclave is your most reliable and effective tool.
- If you are sterilizing delicate or sharp-edged instruments: Consider alternative methods like chemical sterilization or dry heat at a lower temperature to preserve the instrument's integrity.
- If your task is handling liquids or culture media: Autoclaving is the standard procedure, but ensure you follow proper venting protocols to prevent accidents.
- If you are decontaminating biohazardous waste: The autoclave is the correct choice for rendering biological materials safe for disposal.
Ultimately, always verify an item's material compatibility before placing it in an autoclave to ensure safety and sterility.
Summary Table:
| Category | Examples | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Surgical/Dental Instruments | Forceps, Scalpels (handles) | Made of heat-stable stainless steel. |
| Laboratory Glassware | Beakers, Flasks (Pyrex) | Must be heat-resistant. |
| Autoclavable Plastics | PP/PC Tubes, Pipette Tips | Must be clearly labeled "autoclavable". |
| Liquids & Culture Media | Aqueous solutions, Nutrient broths | Containers must be vented to prevent pressure buildup. |
| Biohazardous Waste | Used Petri dishes, Culture tools | Primary method for decontamination before disposal. |
Ensure your laboratory's sterility and safety with the right equipment.
Choosing the correct sterilization method is critical for both the integrity of your instruments and the validity of your research. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory equipment and consumables, including autoclaves and autoclavable labware, to meet your specific needs.
Let our experts help you select the perfect sterilization solution for your lab. We can guide you on material compatibility, cycle parameters, and equipment selection to ensure effective and safe sterilization every time.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and let us support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the size of the autoclave? Choose the Right Capacity for Your Lab
- Why is a PTFE-lined autoclave necessary for Na-Ce-modified-SBA-15 catalyst aging? Ensuring Structural Integrity
- What is the difference between dry-heat and steam sterilization? A Guide to Choosing the Right Method
- What is the most commonly used autoclave? Discover the Industry Standard for Sterilization
- Why is a high-pressure circulating autoclave necessary for PWR corrosion testing? Replicating Nuclear Environments
- What are the 3 most common machines used in sterilization? Choose the Right Method for Your Materials
- What are the common sterilization methods in a laboratory? A Guide to Choosing the Right Technique
- Why is a PTFE-lined stainless steel autoclave required for Ag@N-TiO2? Ensure Purity and Performance in Synthesis



















