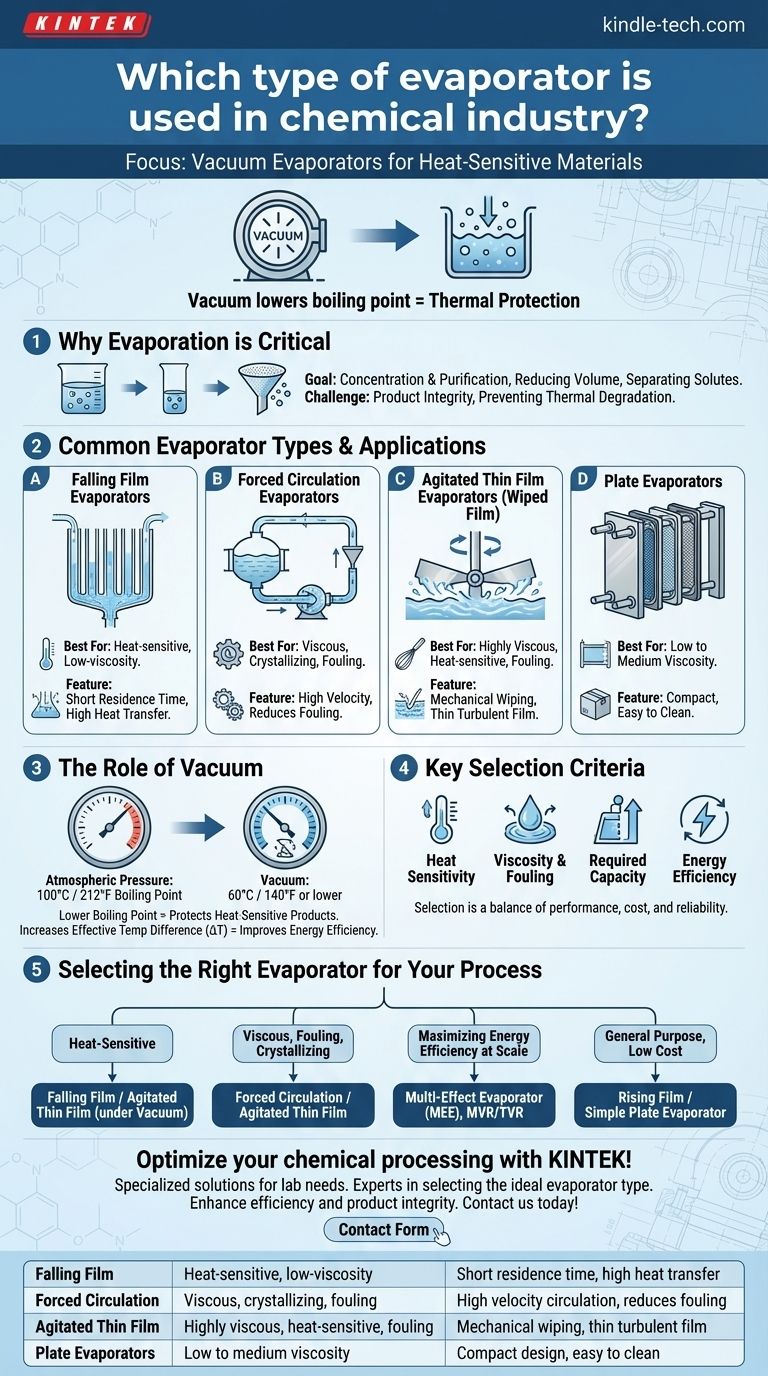
While many designs are used, the chemical industry frequently relies on vacuum evaporators to concentrate or separate liquid solutions. This technology is particularly critical when dealing with heat-sensitive materials, as it allows for boiling at a much lower temperature, preventing the thermal degradation of valuable chemical compounds.
The selection of an evaporator is not about finding a single "best" type. Instead, it is a critical engineering decision that involves matching the evaporator's design characteristics to the specific physical properties of the chemical product and the economic goals of the process.

Why Evaporation is Critical in Chemical Processing
Evaporation is a fundamental unit operation in the chemical industry, used to increase the concentration of a solution by removing a solvent, which is typically water.
The Goal: Concentration and Purification
The primary goal is often to concentrate a product, reducing its volume for storage or transport, or to prepare it for a subsequent process like crystallization. It also serves as a powerful purification method, separating non-volatile solutes from a volatile solvent.
The Challenge: Product Integrity
Many chemicals, especially in the pharmaceutical and specialty chemical sectors, are thermally sensitive. Exposing them to high temperatures for extended periods can cause decomposition, loss of activity, or the creation of unwanted byproducts, destroying the value of the product.
Common Evaporator Types and Their Applications
The chemical industry uses a diverse range of evaporators, each suited for different conditions. The choice depends largely on the liquid's viscosity, heat sensitivity, and tendency to foul or form crystals.
Falling Film Evaporators
In this design, liquid is fed to the top of vertical tubes and flows down the inner walls as a thin film. This provides a high rate of heat transfer with a very short residence time, making it ideal for concentrating large volumes of heat-sensitive, low-viscosity liquids.
Forced Circulation Evaporators
These are the workhorses for difficult applications. A pump circulates the liquid at high velocity through a heat exchanger, preventing solids from settling and reducing fouling on heat transfer surfaces. They are extremely effective for processing viscous, crystallizing, or fouling liquids.
Agitated Thin Film Evaporators (Wiped Film)
For the most challenging materials, an agitated thin film evaporator is used. Mechanical blades or rollers physically spread the liquid into an extremely thin, turbulent film on the heated surface. This design excels at handling highly viscous, heat-sensitive, or fouling materials that are impossible to process in other systems.
Plate Evaporators
Similar in concept to a plate heat exchanger, these units use a series of gasketed plates to create a large surface area in a compact volume. They are efficient and easy to clean, making them suitable for low to medium viscosity liquids in applications where space is a concern.
The Role of Vacuum in Evaporation
Applying a vacuum to the evaporator system is a powerful technique that fundamentally changes the process conditions, which is why it is so widely used.
Lowering the Boiling Point
The most significant advantage of vacuum is that it lowers the liquid's boiling point. Water that boils at 100°C (212°F) at atmospheric pressure can be made to boil at 60°C (140°F) or even lower under vacuum. This protects heat-sensitive products from damage.
Increasing the Effective Temperature Difference
By lowering the boiling point, you can use a lower-temperature heating medium (like low-pressure steam or hot water) while still maintaining an effective temperature difference (ΔT) for efficient heat transfer. This improves energy efficiency and plant safety.
Understanding the Key Selection Criteria
Choosing the right evaporator involves balancing performance, cost, and operational reliability. Several factors dictate the final decision.
Heat Sensitivity of the Product
This is often the primary driver. If a product degrades with heat, the choice immediately narrows to short-residence-time designs like falling film or agitated thin film, almost always operating under vacuum.
Viscosity and Fouling Tendency
As a product becomes more concentrated, its viscosity typically increases, and its tendency to foul heat transfer surfaces grows. For low-viscosity, clean liquids, a simple falling film evaporator may suffice. For highly viscous or fouling materials, a forced circulation or agitated thin film design is necessary.
Required Capacity and Throughput
The scale of the operation matters. Large-scale, continuous bulk chemical production often uses highly efficient multi-effect evaporators (MEE), where the vapor from one stage is used to heat the next, dramatically reducing energy consumption.
Energy Efficiency and Operating Costs
Energy is a major operating cost. Advanced configurations like MEE or systems using Thermal Vapor Recompression (TVR) or Mechanical Vapor Recompression (MVR) are more capital-intensive but offer significant long-term savings on steam consumption.
Selecting the Right Evaporator for Your Process
Making the correct choice requires a clear understanding of your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is processing heat-sensitive liquids: Choose a falling film or agitated thin film evaporator operating under vacuum to minimize thermal stress.
- If your primary focus is handling viscous, fouling, or crystallizing solutions: Choose a forced circulation or agitated thin film evaporator to ensure operational reliability.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy efficiency at scale: Specify a multi-effect evaporator (MEE) design, potentially enhanced with vapor recompression (MVR/TVR).
- If your primary focus is a general-purpose, low-cost solution for non-sensitive liquids: A rising film or simple plate evaporator can provide a cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, the optimal evaporator is the one that reliably achieves your process goals while protecting the integrity of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Evaporator Type | Best For | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Falling Film | Heat-sensitive, low-viscosity liquids | Short residence time, high heat transfer |
| Forced Circulation | Viscous, crystallizing, or fouling liquids | High velocity circulation, reduces fouling |
| Agitated Thin Film | Highly viscous, heat-sensitive, or fouling materials | Mechanical wiping, thin turbulent film |
| Plate Evaporators | Low to medium viscosity liquids | Compact design, easy to clean |
Optimize your chemical processing with the right evaporator solution from KINTEK!
Choosing the correct evaporator is critical for protecting heat-sensitive materials, improving energy efficiency, and ensuring reliable operation. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the ideal evaporator type—whether falling film, forced circulation, or agitated thin film—to match your product's viscosity, heat sensitivity, and fouling tendency.
Let KINTEK enhance your process efficiency and product integrity. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how our solutions can benefit your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- CVD Diamond Wire Drawing Die Blanks for Precision Applications
People Also Ask
- How does potassium bromide affect humans? A Look at Its Risks and Obsolete Medical Use
- What type of evaporation is used for removing flammable solvents? Safely Remove Flammable Solvents with Explosion-Proof Rotary Evaporators
- What role does a benchtop incubator shaker play during antimicrobial activity assessment? Ensure Precise Results
- What is the purpose of spark plasma sintering? Achieve Full Densification at Lower Temperatures
- Why pre sintering is required for some metals? The Key to Defect-Free Powder Metal Parts
- Why is it necessary to dry or calcine catalysts? Ensure Reactor Safety and Peak Performance
- What are the pros and cons of biomass? Weighing Renewable Energy Against Environmental Impact
- What transfer is sputtering based on? Momentum Transfer for Superior Thin Film Deposition



















