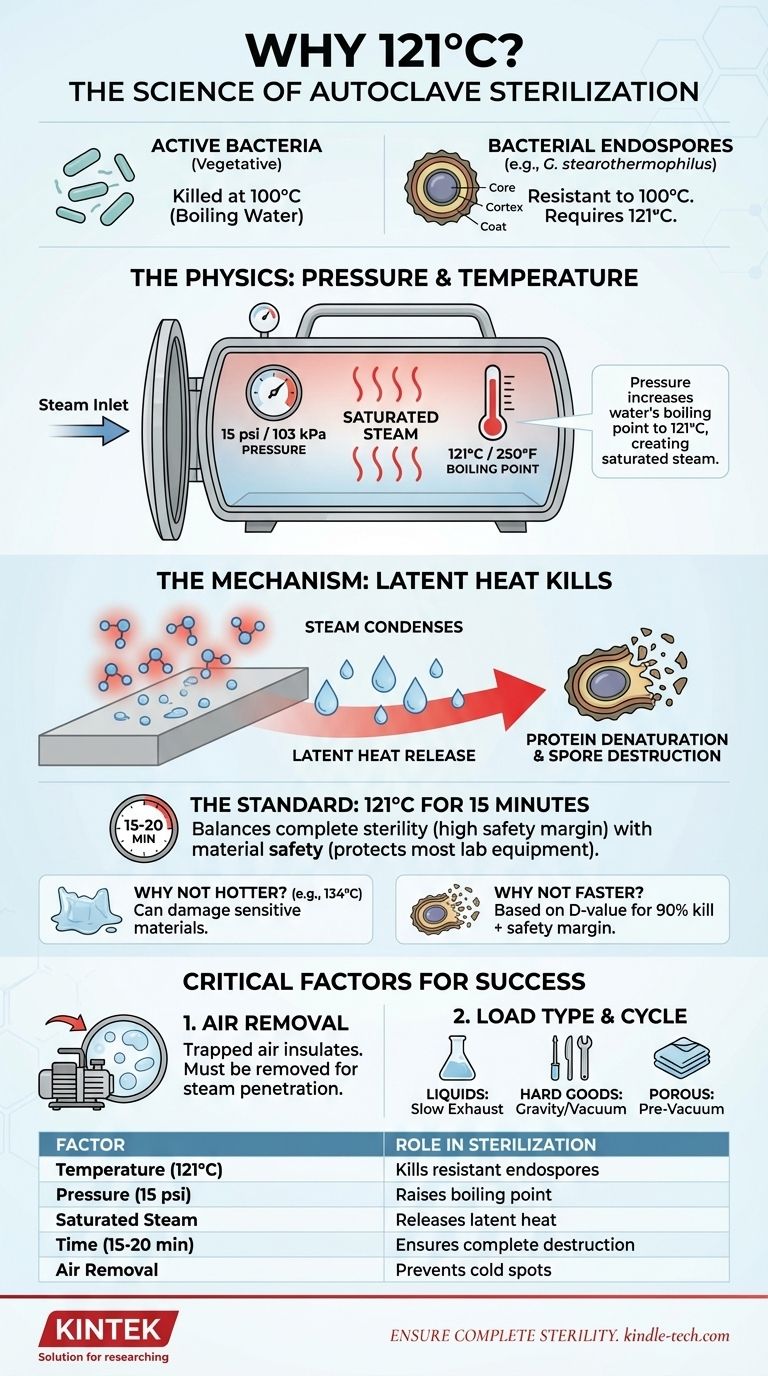
The selection of 121°C for autoclaving is a precise balance of physics and microbiology. This temperature is the established industry standard because it is the minimum required to reliably kill the most heat-resistant life forms known—bacterial endospores. At atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C, which is insufficient to destroy these spores. By increasing the pressure inside the autoclave to approximately 15 psi (103 kPa), the boiling point of water is raised to 121°C, creating saturated steam that can effectively achieve sterilization.
Autoclaving is designed to overcome the ultimate survivalist: the bacterial endospore. The 121°C standard provides a sufficient thermal kill-rate to achieve complete sterility within a practical timeframe (typically 15-20 minutes) without being overly destructive to the majority of laboratory and medical equipment.

The True Target: Why 100°C Isn't Enough
To understand the 121°C standard, we must first identify the actual target of the sterilization process. It isn't the common bacteria, but their nearly indestructible dormant forms.
The Benchmark for Sterility: Bacterial Spores
Most active, or vegetative, bacteria are easily killed by boiling water at 100°C. However, certain bacteria, such as Geobacillus stearothermophilus, produce endospores as a survival mechanism.
These spores are the toughest known life forms on Earth, capable of withstanding extreme heat, radiation, and chemical attack. True sterilization is only achieved when these spores are completely eliminated.
The Structure of a Spore
Spores are so resilient because of their unique structure. A dehydrated core containing the cell's DNA is protected by multiple thick layers, including a tough, keratin-like protein coat.
This structure makes them impervious to temperatures that would instantly kill a normal bacterium. To destroy them, you need a more powerful method than simply boiling.
The Physics of an Autoclave: Beyond Boiling
An autoclave is essentially a sophisticated pressure cooker that manipulates the laws of physics to create a superheated, sterilizing environment.
The Role of Pressure
The key principle is the direct relationship between pressure and the boiling point of water. In an open container at sea level, water boils at 100°C (212°F).
By sealing the chamber and pumping in steam, an autoclave increases the internal pressure. This forces the boiling point of water to rise.
Reaching 121°C with Saturated Steam
To reach the target temperature of 121°C (250°F), the pressure inside the chamber is raised to approximately 15 pounds per square inch (psi) above the normal atmospheric pressure.
This process doesn't just create hot air; it creates saturated steam—a state where the steam holds the maximum possible amount of water vapor.
Why Saturated Steam is the Real Killer
Saturated steam is a vastly more efficient agent for sterilization than dry heat.
When this 121°C steam makes contact with a cooler item (like a flask or surgical instrument), it immediately condenses into water. This condensation releases a massive amount of energy, known as latent heat, directly onto the surface.
This rapid heat transfer instantly and irreversibly denatures the essential proteins and enzymes within the spores, killing them.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While 121°C is the standard, it's crucial to understand the variables and why this specific temperature was chosen over others.
Why Not Go Hotter?
Higher temperatures can indeed sterilize faster. For example, many autoclaves have a 134°C cycle that can sterilize unwrapped metal instruments in as little as three minutes.
However, this intense heat can damage more sensitive materials like certain plastics, liquids, and rubber tubing. The 121°C for 15 minutes cycle is a robust, universal standard that effectively sterilizes while being compatible with the widest range of common materials.
The Importance of Time
Temperature alone is not enough. The standard 15-minute exposure time is based on the D-value—the time required at a given temperature to kill 90% of a specific microbial population.
A 15-minute cycle at 121°C provides a massive safety margin, ensuring it runs for many multiples of the D-value for the most resistant spores. This guarantees a high Sterility Assurance Level (SAL), typically a one-in-a-million probability of a single microbe surviving.
The Critical Role of Air Removal
Trapped air is the primary enemy of steam sterilization. Air pockets act as an insulator, preventing steam from making contact with surfaces and creating cold spots where sterilization will fail.
Proper loading techniques and, in more advanced autoclaves, pre-vacuum cycles are essential for removing all air and ensuring complete steam penetration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The standard 121°C/15 psi/15 min cycle is a starting point. Effective sterilization requires matching the cycle parameters to the specific load.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing biological media or liquids: Use a "liquid" or "slow exhaust" cycle to prevent the superheated liquid from boiling over violently during depressurization.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing hard, non-porous goods (e.g., glassware, metal instruments): Ensure items are arranged to allow for complete steam penetration and use a "gravity displacement" or "vacuum" cycle for efficient air removal.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing porous loads (e.g., surgical gowns, filters): A pre-vacuum cycle is non-negotiable to remove trapped air from within the materials, ensuring no cold spots remain.
Understanding the interplay of temperature, pressure, steam, and time is the key to moving from simply operating an autoclave to guaranteeing true sterility.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Sterilization |
|---|---|
| Temperature (121°C) | Minimum required to kill the most heat-resistant bacterial endospores |
| Pressure (15 psi) | Raises water's boiling point to 121°C, creating saturated steam |
| Saturated Steam | Condenses on surfaces, releasing latent heat to denature proteins |
| Time (15-20 min) | Provides safety margin to ensure complete spore destruction |
| Air Removal | Prevents cold spots and ensures steam penetrates all surfaces |
Ensure your lab achieves complete sterility with reliable autoclaves from KINTEK.
Whether you're sterilizing liquid media, surgical instruments, or porous materials, choosing the right autoclave cycle is critical for your research and safety. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, providing autoclaves designed for precise temperature control, efficient air removal, and consistent performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your laboratory's sterilization needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your workflow, protect your samples, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the steps to prepare instruments for autoclaving? Ensure Sterility and Protect Your Equipment
- What is the maintenance schedule for an autoclave? Ensure Sterilization Safety & Maximize Equipment Life
- How does temperature affect sterilization? Unlock the Science of Heat-Based Microbial Destruction
- How long should equipment be autoclaved? Ensure Proper Sterilization Time and Conditions
- What is autoclave features and uses? A Guide to Sterilization and Safety
- How long is the sterilization cycle in an autoclave? It's More Than Just 15 Minutes
- Why is a Nickel-based alloy typically selected for the high-pressure autoclave? Ensure Safety & Precision in S-CO2 Testing
- Why is a laboratory autoclave necessary for Postgate Medium B (PMB)? Ensure Pure SRB Cultures & Accurate MIC Research



















