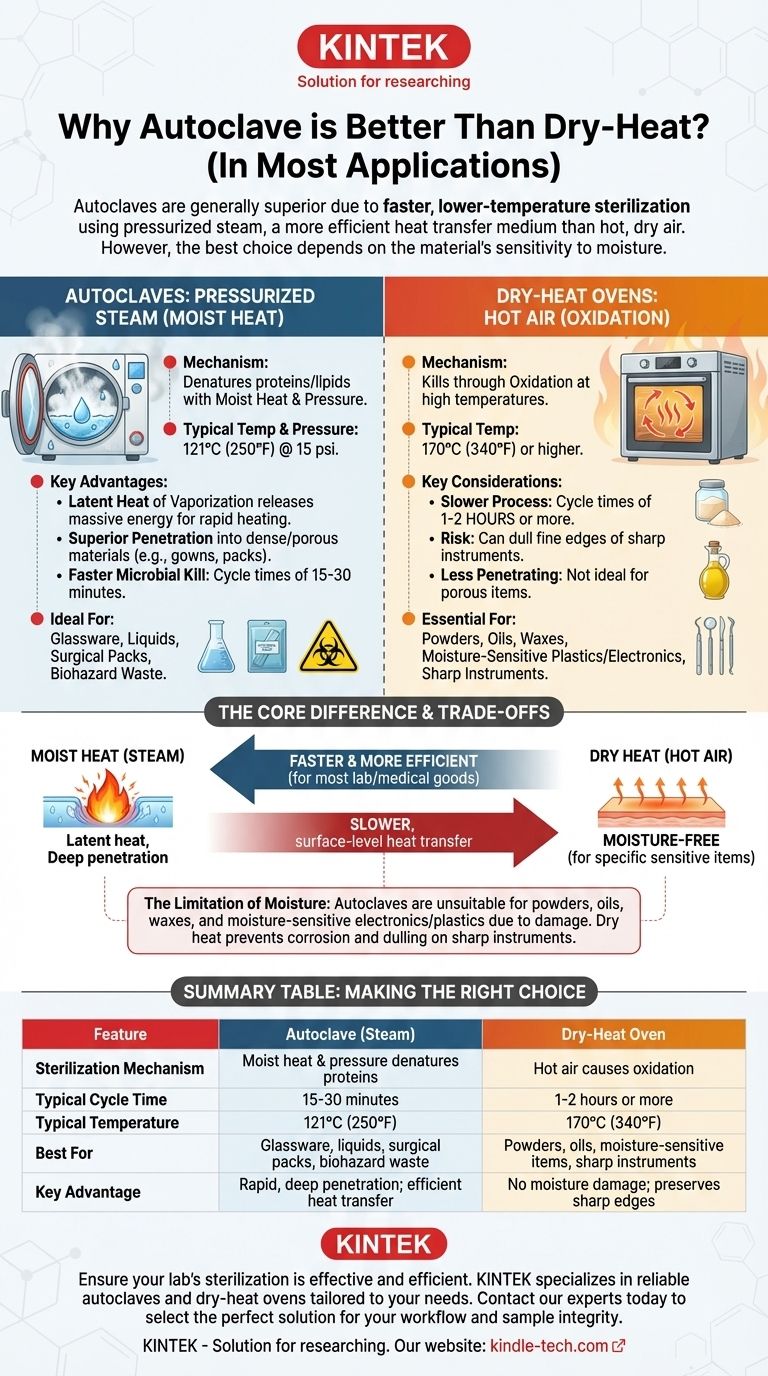
In most applications, an autoclave is considered superior to a dry-heat oven because it achieves sterilization more rapidly and at lower temperatures. The use of pressurized steam is a significantly more efficient medium for heat transfer and microbial destruction than the hot, dry air used in a dry-heat oven.
The choice between an autoclave and dry-heat sterilization is not about which is universally "better," but which is appropriate for the material you need to sterilize. Steam is faster and more effective for most items, but dry heat is essential for materials that would be damaged by moisture.

The Core Difference: How Heat Is Delivered
The fundamental distinction between these two methods lies in the medium used to transfer heat and kill microorganisms. Understanding this is key to choosing the right tool.
Autoclaves: Pressurized Steam
An autoclave is essentially a highly controlled pressure chamber. It works by replacing the air inside with saturated steam and holding it at a specific temperature and pressure (e.g., 121°C / 250°F at 15 psi).
This combination of moist heat and pressure is exceptionally effective at denaturing the essential proteins and lipids that make up microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, and spores.
Dry-Heat Ovens: Hot Air
A dry-heat oven is much simpler, functioning like a conventional oven that circulates hot, dry air. To achieve sterilization, it must reach significantly higher temperatures (e.g., 170°C / 340°F) and maintain them for much longer periods.
This method kills microbes through a process of oxidation, essentially baking them until their cellular components are destroyed.
Why Steam Sterilization Is More Efficient
Pressurized steam has several inherent physical properties that make it a more potent sterilizing agent than dry air.
The Power of Latent Heat
When steam makes contact with a cooler surface, it condenses back into water. This phase change releases a massive amount of energy, known as latent heat of vaporization.
This rapid and efficient energy transfer heats items far more quickly and deeply than dry air at the same temperature. A burn from steam is far more severe than a burn from dry air for this very reason.
Superior Penetration
Steam is better able to penetrate dense or porous materials, such as surgical gowns, wrapped instrument packs, and microbiological growth media. It ensures that all surfaces, including internal ones, reach the required sterilization temperature.
Dry air is less effective at penetrating these materials, creating a risk that items may not be fully sterilized in their core.
Faster Microbial Kill Times
The combination of moist heat and rapid energy transfer destroys microbial proteins and melts lipids much faster than the slow oxidation process of dry heat.
This means a standard autoclave cycle might last 15-30 minutes, whereas a typical dry-heat cycle can take 1-2 hours or more to achieve the same level of sterility.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When Dry Heat Is the Correct Choice
Despite the clear efficiency advantages of autoclaving, it is not a universally applicable solution. There are critical situations where dry-heat sterilization is not just an alternative, but a necessity.
The Limitation of Moisture
The primary advantage of an autoclave—steam—is also its primary limitation. It is completely unsuitable for materials that are sensitive to or degraded by moisture.
This includes powders, oils, waxes, and certain plastics or electronics. Attempting to autoclave these items would ruin them.
The Risk of Corrosion and Dulling
The moisture present in an autoclave can promote rust and corrosion on certain carbon steel instruments. More importantly for surgical or dental applications, it can dull the fine edges of sharp instruments.
For this reason, dry heat is often the preferred method for sterilizing delicate, sharp tools to preserve their integrity.
Equipment and Operational Costs
While the reference notes that autoclaving is economical—largely due to high throughput from short cycle times—dry-heat ovens are often simpler machines that can be less expensive to purchase initially. However, their long cycle times and high energy usage can lead to higher operational costs over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the decision rests on the nature of the items being sterilized. Use this guide to make a clear, defensible choice.
- If your primary focus is speed and efficiency for general lab and medical goods: The autoclave is your definitive choice for sterilizing glassware, stainless steel instruments, liquids, and biohazardous waste.
- If you are sterilizing moisture-sensitive materials: Dry-heat sterilization is the only suitable and correct method for items like oils, powders, glassware for anhydrous chemistry, or certain metal instruments prone to corrosion.
- If your priority is preserving the sharpness of fine-edged instruments: Dry-heat is often the preferred method to avoid the potential for moisture-induced dulling and corrosion.
By matching the sterilization method to the material's properties, you ensure both effective sterility and the preservation of your valuable equipment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Autoclave (Steam) | Dry-Heat Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Sterilization Mechanism | Moist heat & pressure denatures proteins | Hot air causes oxidation |
| Typical Cycle Time | 15-30 minutes | 1-2 hours or more |
| Typical Temperature | 121°C (250°F) | 170°C (340°F) |
| Best For | Glassware, liquids, surgical packs, biohazard waste | Powders, oils, moisture-sensitive items, sharp instruments |
| Key Advantage | Rapid, deep penetration; efficient heat transfer | No moisture damage; preserves sharp edges |
Ensure your lab's sterilization is both effective and efficient. Choosing the right equipment is critical for your workflow and sample integrity. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing reliable autoclaves and dry-heat ovens tailored to your specific laboratory needs. Whether you're processing liquids, glassware, or delicate instruments, our experts can help you select the perfect solution. Contact us today to discuss your sterilization requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your lab's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature and high-pressure autoclave? Testing Cr2AlC Coatings for Nuclear Safety
- Why is the hydrothermal environment provided by an autoclave necessary for synthesizing manganese oxide? Key Benefits
- What is the function of a stainless steel high-pressure autoclave with a PTFE liner? Enhance CoO Synthesis Purity
- What role does a PTFE-lined stainless steel autoclave play in the synthesis of BiOBr precursor nanosheets?
- What are autoclaves used in the chemical industry? High-Pressure Reactors for Synthesis & Curing
- How does a slow strain rate testing system integrated with an autoclave facilitate material research? | KINTEK
- What is the primary function of a laboratory autoclave in the pre-treatment of medical plastic waste for liquid fuel?
- What is autoclave in laboratory? Achieve Total Sterility for Your Lab



















