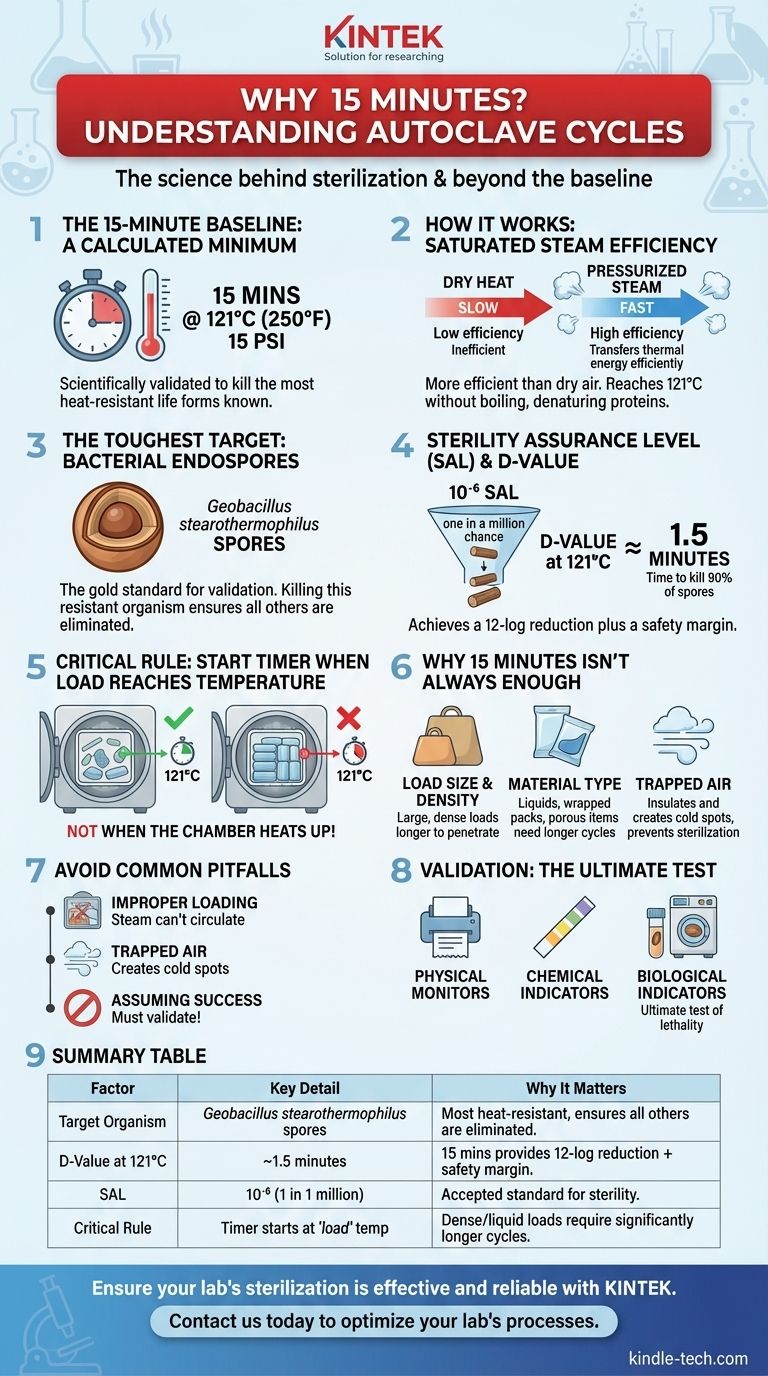
In short, the standard 15-minute autoclave cycle is the minimum time scientifically validated to kill the most heat-resistant life forms known to science—bacterial endospores—under specific conditions. This duration is not arbitrary; it is calculated to ensure a high probability of complete sterilization for typical laboratory loads.
The 15-minute cycle at 121°C (250°F) and 15 psi is a widely adopted benchmark, but it's crucial to understand it as a minimum baseline. True sterilization depends on an inseparable relationship between time, temperature, and—most importantly—the effective penetration of pressurized steam into the specific items being sterilized.
How Autoclaves Achieve Sterilization
An autoclave is more than just a hot oven. Its effectiveness comes from using high-pressure steam, which is a far more efficient method of heat transfer than dry air.
It's Not Just Heat, It's Saturated Steam
Dry heat is slow and inefficient. Imagine reaching into a hot oven (with a mitt) versus being exposed to steam at the same temperature; the steam would cause a severe burn almost instantly.
This is because pressurized steam transfers thermal energy with extreme efficiency. The pressure inside an autoclave allows water to reach 121°C without boiling away, creating a "saturated steam" environment that forcibly penetrates materials and denatures the essential proteins within microorganisms.
The True Target: The Toughest Spores
Sterilization procedures are not designed to kill common, fragile bacteria. They are designed to eliminate the most resilient microbial structures known: bacterial endospores.
The gold standard for validation is the spore of Geobacillus stearothermophilus. This organism is not a common pathogen, but its spores are exceptionally resistant to heat. The principle is simple: if your process kills G. stearothermophilus spores, it is assumed to have killed all other, less-resistant microorganisms.
The Goal: A Sterility Assurance Level (SAL)
"Sterile" is not an absolute state but a statistical probability. The accepted standard for medical and research applications is a Sterility Assurance Level (SAL) of 10⁻⁶.
This means the process is designed to leave no more than a one-in-a-million chance of a single viable microorganism surviving on an item.
Where the 15-Minute Rule Originates
To achieve this high level of assurance, scientists use a concept called the D-value, or "decimal reduction time." The D-value is the time required at a specific temperature to kill 90% (or one "log") of a microbial population.
At 121°C, the D-value for G. stearothermophilus spores is approximately 1.5 minutes. To achieve the required 12-log reduction for a high initial bioburden (from 1,000,000 spores down to a 1 in 1,000,000 probability of survival), you need multiple D-value cycles. The 15-minute timeframe provides a sufficient number of these cycles, plus a crucial safety margin.
Why 15 Minutes Isn't Always the Answer
Relying blindly on the 15-minute rule is a common and dangerous mistake. The timer should only start once the material inside the load has reached the target temperature, not when the chamber itself gets hot.
The Impact of Load Size and Density
A small load of loose metal instruments will heat up very quickly. In contrast, a large, dense bag of biological waste or a large flask of liquid can take a long time for steam to penetrate and heat the center. For these loads, the actual sterilization time required might be 30, 45, or even 60 minutes.
The Type of Material Being Sterilized
Liquids require longer "liquid" cycles, not just for heat penetration but also to allow for a slow, controlled depressurization to prevent them from boiling over.
Wrapped instrument packs require more time for steam to penetrate the porous wrapper. This is why many modern autoclaves use pre-vacuum cycles to actively remove air and ensure steam reaches every surface.
Porous materials like animal bedding or lab gowns are challenging because air can become trapped within them, creating "cold spots" that steam cannot reach.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Effective sterilization can fail for several reasons beyond just incorrect timing. Understanding these is critical for safety and a successful outcome.
Pitfall 1: Improper Loading
Overpacking an autoclave is the most frequent cause of cycle failure. If items are packed too tightly, steam cannot circulate freely. This prevents steam from reaching all surfaces, leading to incomplete sterilization. Always leave space between items.
Pitfall 2: Trapped Air
Air is the enemy of steam sterilization. It acts as an insulator, preventing steam from making direct contact with item surfaces. If air is not properly purged from the chamber and the load, a "cold spot" can form where the temperature never reaches 121°C, even if the autoclave's sensors read correctly.
Pitfall 3: Assuming the Cycle Worked
Never assume a cycle was successful without verification. Modern practices require three forms of validation:
- Physical monitors: The autoclave's own printout of time, temperature, and pressure.
- Chemical indicators: Strips or tapes that change color when exposed to the correct temperature, indicating steam has reached that spot.
- Biological indicators: Vials containing G. stearothermophilus spores. After a cycle, these are incubated to prove that the spores were actually killed. This is the ultimate test of lethality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The standard 15-minute cycle is a powerful tool, but it must be applied correctly. Use the following as a guide.
- If your primary focus is routine sterilization of unwrapped glassware or metal tools: The standard 15-minute cycle at 121°C is generally reliable, provided the autoclave is not overloaded.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing liquids, media, or biohazard bags: You must increase the cycle time to account for slow heat penetration. Start with 30 minutes and validate with indicators, increasing time as needed based on volume.
- If your primary focus is critical medical or pharmaceutical applications: You must never rely on a standard time. Your specific cycle must be rigorously validated for your specific load using biological indicators to prove it achieves the required Sterility Assurance Level.
Ultimately, the 15-minute rule is a foundational guideline, not an unbreakable law; true sterility is achieved by understanding and controlling time, temperature, and steam penetration for every unique load.

Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Detail | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Target Organism | Geobacillus stearothermophilus spores | The most heat-resistant life form; killing it ensures all others are eliminated. |
| D-Value at 121°C | ~1.5 minutes | Time to kill 90% of spores; 15 minutes provides a 12-log reduction plus safety margin. |
| Sterility Assurance Level (SAL) | 10⁻⁶ | The accepted standard, meaning a 1 in 1 million chance of a surviving organism. |
| Critical Rule | Timer starts when the load reaches 121°C | Not when the chamber heats up; dense or liquid loads require significantly longer cycles. |
Ensure your lab's sterilization is effective and reliable. The standard 15-minute cycle is a baseline, but proper validation is key to safety. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality autoclaves and consumables tailored to your laboratory's specific needs. Our experts can help you select the right equipment and validate your cycles for complete peace of mind.
Contact us today to discuss your sterilization requirements and optimize your lab's processes with KINTEK's trusted solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What should be autoclaved in a lab? A Guide to Safe and Effective Sterilization
- What is autoclave in laboratory? Achieve Total Sterility for Your Lab
- What are the uses of autoclave in laboratory equipment? Ensure Sterile Conditions for Your Research
- What is the life expectancy of an autoclave machine? Maximize Your Investment with Proper Care
- What is the 121 cycle of autoclave? A Guide to Guaranteed Sterilization



















