Simply put, autoclaving is the most effective sterilization method because it uses high-pressure steam to achieve temperatures that are impossible for microorganisms to survive. This combination of moist heat and pressure rapidly denatures the essential proteins and lipids that make up microbial cells, including their highly resistant spores, ensuring a level of sterility that dry heat or chemical disinfectants cannot reliably match.
The core principle is that pressurized steam is a far more efficient agent for heat transfer than dry air. It penetrates materials and rapidly delivers lethal temperatures to every surface, ensuring the complete destruction of even the most resilient life forms known to science.

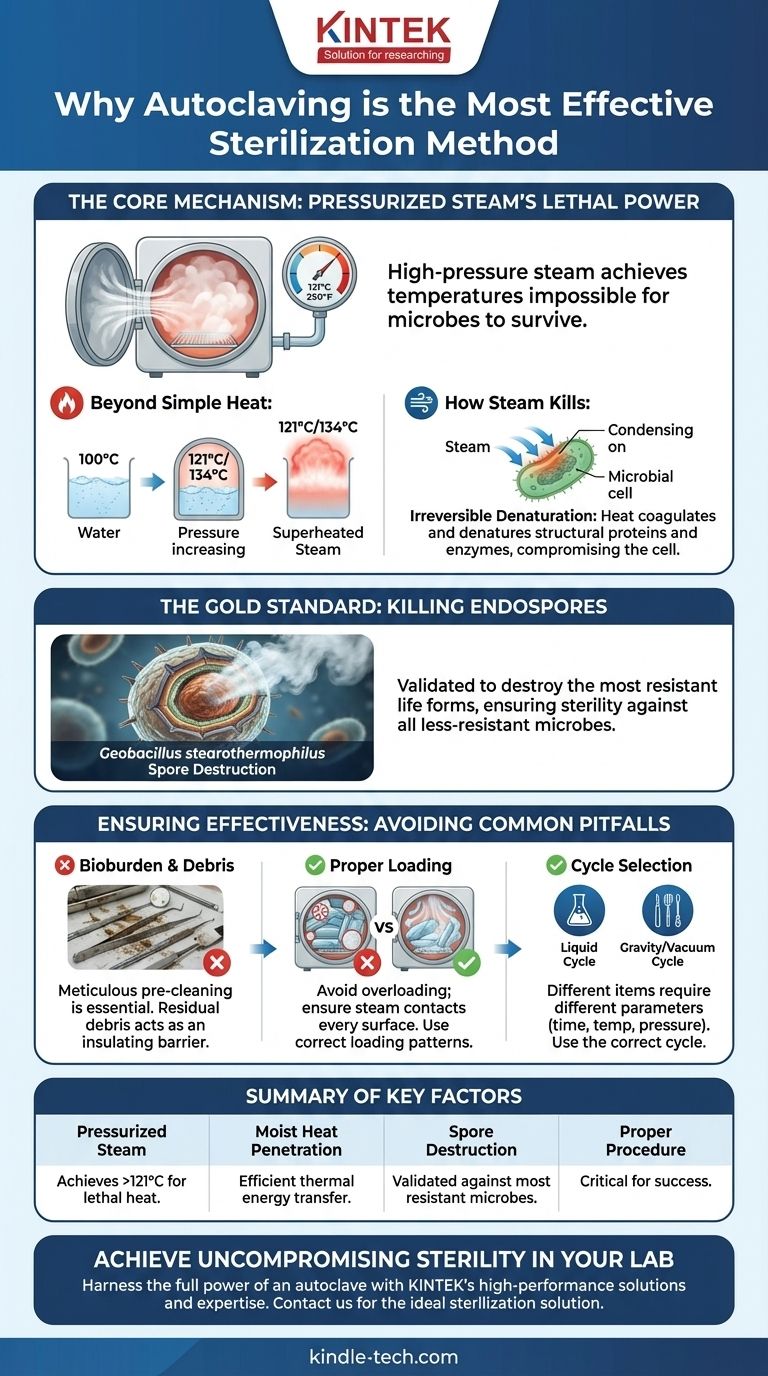
The Core Mechanism: Pressurized Steam's Lethal Power
To understand why autoclaving is the gold standard, you must look beyond just heat. The true effectiveness comes from the physics of pressurized, saturated steam.
Beyond Simple Heat: The Role of Pressure
Under normal atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). By increasing the pressure inside a sealed chamber, an autoclave forces water to remain a liquid at higher temperatures, only turning to steam at temperatures like 121°C or 134°C.
This superheated steam contains significantly more thermal energy than boiling water or dry hot air, making it a powerful sterilization agent.
How Steam Kills: Irreversible Denaturation
When this high-energy steam contacts cooler items in the chamber, it condenses back into water, rapidly transferring its heat to the surfaces of those items.
This intense heat transfer irreversibly coagulates and denatures the structural proteins and essential enzymes within any microorganism. The cell's internal machinery is effectively cooked, its membrane is compromised, and it dies.
The Gold Standard: Killing Endospores
The ultimate test of any sterilization process is its ability to kill bacterial endospores. These are dormant, highly protected structures produced by certain bacteria, like Geobacillus stearothermophilus, which are incredibly resistant to heat, chemicals, and radiation.
Autoclaves are specifically designed and validated to destroy these spores. If a process can kill the toughest known spores, it is considered effective for sterilizing against all other less-resistant microbes.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When Effectiveness Fails
While the principle is robust, the effectiveness of an autoclave in practice depends entirely on correct procedure. Operator error or improper preparation can easily compromise a sterilization cycle.
The Enemy of Steam: Bioburden and Debris
Steam must physically touch every surface to sterilize it. If instruments are not thoroughly cleaned before being placed in the autoclave, residual debris like proteins, salts, or organic matter can act as an insulating barrier.
This "bioburden" can shield the underlying microorganisms from the steam's lethal heat, leading to sterilization failure.
The Importance of Contact: Proper Loading
Overloading the autoclave or packing items too densely prevents proper steam circulation. Air can become trapped in pockets within the load, creating cold spots that do not reach the required sterilization temperature.
Items must be arranged to allow steam to flow freely around and inside them. Waste bags should be left partially open, and jars or containers should be placed on their sides.
Choosing the Right Cycle
A common mistake is using a single "standard" cycle for all materials. Different items require different cycle parameters (time, temperature, pressure).
For example, a "liquid" cycle uses a slower exhaust phase to prevent media from boiling over, while a "gravity" or "vacuum" cycle is designed for instruments or porous goods. Using the wrong cycle can either damage the item or fail to sterilize it completely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these principles transforms the autoclave from a simple machine into a reliable and verifiable process. Success hinges on ensuring that the lethal power of steam can do its job without obstruction.
- If your primary focus is routine instrument sterilization: Your priority must be meticulous pre-cleaning to remove all bioburden and loading the chamber correctly to ensure steam contacts every surface.
- If your primary focus is preparing sterile liquids or media: Your priority is selecting the correct liquid cycle and ensuring you do not overfill containers, which guarantees the entire volume reaches the target temperature without boiling over.
- If your primary focus is validating your process for compliance: Your priority is the correct use of biological indicators containing G. stearothermophilus spores to prove your specific loading patterns and cycles achieve a complete kill.
By controlling these critical factors, you can reliably harness the power of pressurized steam to achieve absolute sterility.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Why It Matters for Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Pressurized Steam | Achieves temperatures above boiling point (e.g., 121°C) for lethal heat transfer. |
| Moist Heat Penetration | Steam rapidly condenses on surfaces, efficiently transferring thermal energy to microbes. |
| Spore Destruction | Validated to kill the most resistant bacterial endospores, ensuring complete sterility. |
| Proper Procedure | Correct loading, cycle selection, and pre-cleaning are critical to avoid failure. |
Achieve Uncompromising Sterility in Your Lab
Harnessing the full power of an autoclave requires the right equipment and knowledge. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab autoclaves and consumables designed for reliability and compliance.
Our experts can help you select the perfect autoclave for your specific needs—whether for sterilizing instruments, preparing media, or validating processes—ensuring you achieve absolute sterility every time.
Contact KINTEK today to find the ideal sterilization solution for your laboratory and ensure your processes are both effective and compliant.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- What types of items and materials can be processed in a laboratory autoclave? Essential Guide for Lab Safety
- What is the normal temperature of an autoclave? Achieve Sterile Confidence with Precise Control



















