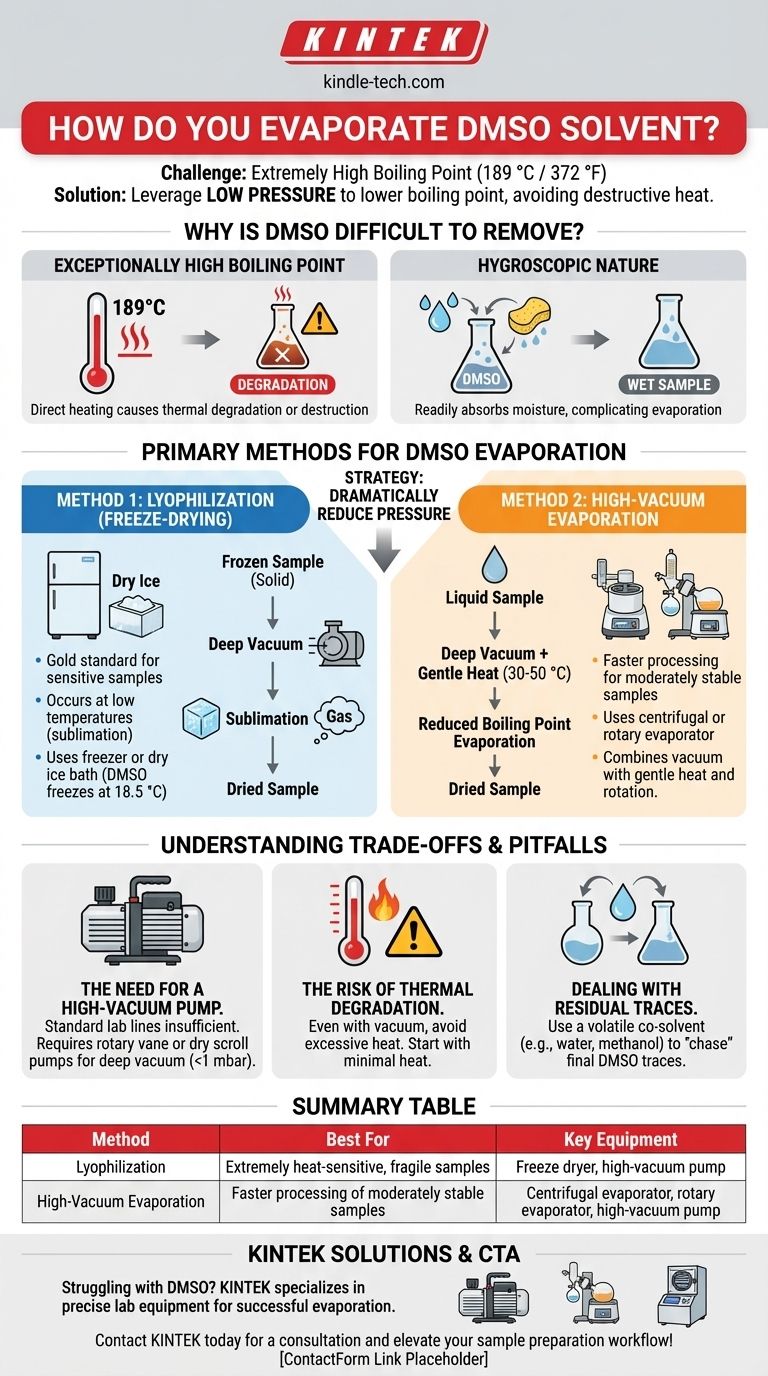
To evaporate DMSO effectively, you must use methods that lower its boiling point, as heating it directly is often destructive to the sample. The two primary techniques are lyophilization (freeze-drying) and high-vacuum evaporation, both of which leverage low pressure to remove the solvent at a much safer, lower temperature.
The core challenge in removing DMSO is its extremely high boiling point (189 °C / 372 °F). The solution is not to apply extreme heat, but to use a deep vacuum to force evaporation at a temperature that won't degrade your compound of interest.

Why Is DMSO So Difficult to Remove?
Understanding the properties of Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) is the first step to removing it successfully. Two key characteristics create this challenge.
Its Exceptionally High Boiling Point
At standard atmospheric pressure, DMSO boils at 189 °C (372 °F). This temperature is high enough to cause thermal degradation or complete destruction of many organic molecules and biological samples.
Simply heating your sample on a hot plate to boil off the DMSO is almost never a viable option.
Its Hygroscopic Nature
DMSO is highly hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere. This absorbed water can complicate the evaporation process and leave you with a wet sample even after the DMSO appears to be gone.
Primary Methods for DMSO Evaporation
The strategy for both primary methods is the same: reduce the pressure dramatically. Lowering the pressure reduces the solvent's boiling point, allowing for rapid removal without damaging heat.
Method 1: Lyophilization (Freeze-Drying)
Lyophilization removes a solvent by freezing the sample and then applying a deep vacuum, causing the frozen solvent to turn directly from a solid to a gas (sublimation).
This is often the gold standard for sensitive samples. Because DMSO has a convenient freezing point of 18.5 °C (65.3 °F), samples can often be frozen in a standard lab freezer or with a dry ice bath. The process is extremely gentle as it occurs at low temperatures.
Method 2: High-Vacuum Evaporation
This technique uses a strong vacuum pump to lower the boiling point of DMSO while it's in a liquid state. This is typically done with specialized equipment.
Common tools include a centrifugal evaporator (like a GeneVac or SpeedVac) or a rotary evaporator (rotovap). These systems combine a deep vacuum with gentle heat (typically 30-50 °C) and, in the case of a rotovap, rotation to increase the surface area and speed up the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Successfully removing DMSO requires more than just the right equipment; it requires avoiding common mistakes that can ruin your sample.
The Need for a High-Vacuum Pump
Standard laboratory vacuum lines (water aspirators) are often insufficient to significantly lower DMSO's boiling point.
To be effective, you need a high-vacuum pump, such as a rotary vane oil pump or a dry scroll pump, capable of pulling a very deep vacuum (well below 1 mbar).
The Risk of Thermal Degradation
Even with a vacuum, applying too much heat can still damage your sample. The goal is to find the lowest possible temperature that allows for efficient evaporation under your vacuum conditions. Start with minimal heat and only increase it slightly if the process is too slow.
Dealing with Residual Traces
Due to its high boiling point, it can be difficult to remove the final traces of DMSO. A common technique is to add a small amount of a more volatile co-solvent, such as water or methanol, and re-evaporate. This process can help "chase" the last bit of DMSO from the sample.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Sample
Your choice depends entirely on the nature of your compound and the equipment you have available.
- If your primary focus is preserving a fragile or heat-sensitive compound: Lyophilization (freeze-drying) is the safest and most gentle method available.
- If your primary focus is speed and you have a moderately stable compound: High-vacuum evaporation using a centrifugal evaporator or rotovap is a highly effective and common choice.
- If you are struggling to remove the final, stubborn traces of DMSO: Employ a co-solvent like water, evaporate, and repeat the cycle a few times to achieve a completely dry sample.
Ultimately, successfully removing DMSO is a matter of controlling temperature by controlling pressure.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Principle | Best For | Key Equipment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lyophilization (Freeze-Drying) | Sublimation under deep vacuum | Extremely heat-sensitive, fragile samples | Freeze dryer, high-vacuum pump |
| High-Vacuum Evaporation | Boiling point reduction under vacuum | Faster processing of moderately stable samples | Centrifugal evaporator, rotary evaporator, high-vacuum pump |
Struggling to remove DMSO without damaging your valuable samples? KINTEK specializes in the precise lab equipment you need for successful solvent evaporation. Our high-vacuum pumps, centrifugal evaporators, and freeze dryers are designed to handle challenging solvents like DMSO, ensuring the integrity of your most sensitive compounds. Let our experts help you select the ideal solution for your laboratory's specific needs.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and elevate your sample preparation workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a freeze dryer in the ice-templating process? Preserving Aligned Pore Scaffolds for LAGP
- What role does a laboratory freeze dryer play in the synthesis of graphene-based electrocatalysts? Preserve 3D Structures
- What is the purpose of an evaporator? The Key Component That Creates Cooling
- Why is a laboratory vacuum freeze dryer essential for plant extracts? Preserve Bioactivity & Structure
- What are the advantages of using freeze drying for phase change materials with biopolymer shells? Optimize Stability



















