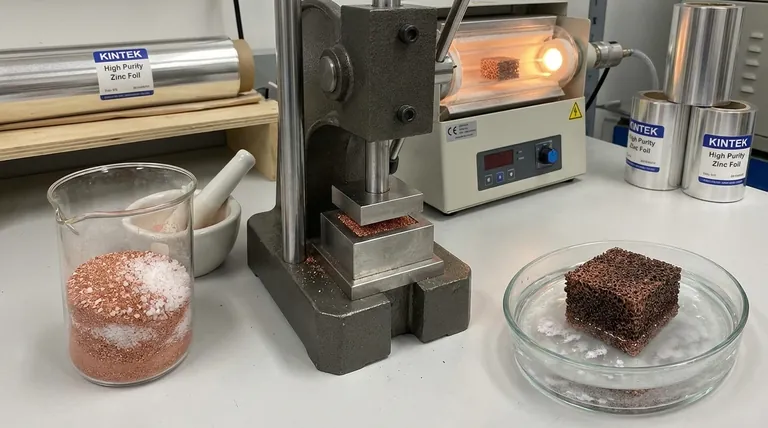
At its core, making copper foam is a process of creating a temporary scaffold and then building a copper structure around it. The most common and accessible method, known as the space-holder technique, involves mixing fine copper powder with a removable placeholder material like sugar or salt particles. This mixture is compacted, the placeholder is dissolved away, and the remaining porous copper framework is heated until the particles fuse together in a process called sintering.
The essential principle is not creating the copper structure directly, but rather creating the empty space within it. By precisely controlling the size and amount of the placeholder material, you gain direct control over the porosity, density, and performance of the final copper foam.

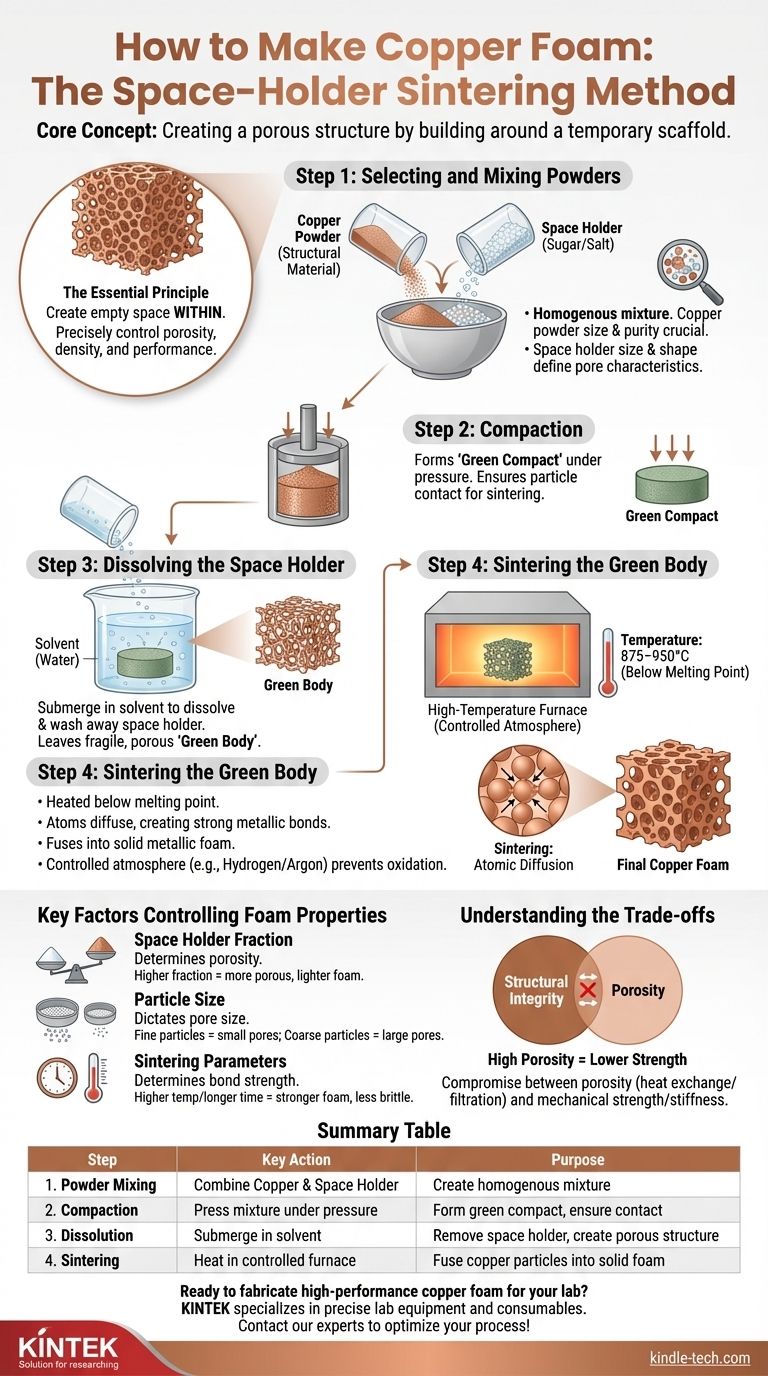
The Space Holder Sintering Method: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
This powder metallurgy approach is valued for its control and versatility. It can be broken down into four critical stages, each influencing the final properties of the foam.
Step 1: Selecting and Mixing the Powders
The process begins by creating a homogenous mixture of two key components: the structural material and the space holder.
The copper powder forms the final metallic structure. Its particle size and purity are crucial for successful sintering and final strength.
The space holder is a temporary filler that creates the eventual pores. Common choices are sugar or salt because they are inexpensive, non-reactive with copper, and easily dissolved in a simple solvent like water. The size and shape of these particles will directly define the size and shape of the pores in the finished foam.
Step 2: Compaction
The powder mixture is poured into a mold and compacted under pressure. This step creates what is known as a "green compact."
Compaction serves two purposes: it forms the mixture into the desired net shape and, more importantly, it presses the copper particles into close contact with one another, which is essential for the final sintering stage.
Step 3: Dissolving the Space Holder
The green compact is submerged in a solvent, typically water, to dissolve and wash away the space holder particles (the sugar or salt).
This leaves behind a fragile, interconnected network of copper particles that retains the shape of the compacted part. This fragile object is often called the "green body."
Step 4: Sintering the Green Body
This is the final and most critical step. The porous green body is placed in a high-temperature furnace with a controlled atmosphere.
It is heated to a temperature below the melting point of copper (e.g., around 875–950°C, while copper melts at 1085°C). At this temperature, the copper particles don't melt, but atoms diffuse across the boundaries between particles, creating strong metallic bonds. This process, sintering, fuses the powder into a single, solid piece of metallic foam.
A controlled atmosphere, such as hydrogen or an inert gas like argon, is essential during sintering to prevent the copper from oxidizing, which would compromise the foam's structural integrity and conductivity.
Key Factors Controlling Foam Properties
The genius of this method is the high degree of control it offers. By adjusting a few key variables in the process, you can engineer the foam's final characteristics.
The Role of the Space Holder Fraction
The ratio of the space holder to copper powder is the single most important factor determining the foam's porosity.
A higher weight fraction of sugar will result in a more porous, lighter foam with larger voids. A lower fraction will produce a denser, stronger foam.
The Impact of Particle Size
The size of the space holder particles directly dictates the pore size of the final foam. Using fine salt will create a foam with small pores, while using coarse sugar crystals will create one with large, open cells.
The size of the copper particles also matters, influencing how efficiently the structure sinters and its final mechanical strength.
The Influence of Sintering Parameters
The sintering temperature and duration determine the strength of the bonds between copper particles.
Higher temperatures or longer times lead to more complete bonding, resulting in a stronger, less brittle foam. However, excessive sintering can also cause the foam to shrink and densify, reducing its overall porosity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, this fabrication method involves inherent compromises that are critical to understand for any practical application.
Structural Integrity vs. Porosity
This is the fundamental trade-off. The primary goal of a foam is often high porosity for applications like heat exchange or filtration. However, as porosity increases, the mechanical strength, stiffness, and toughness of the material decrease significantly.
Process Complexity and Scalability
The space holder technique offers excellent control for laboratory and bespoke applications. However, the multi-step process—especially the dissolution and controlled-atmosphere sintering—can be complex and costly to scale for high-volume industrial production.
The Risk of Oxidation
Copper is highly susceptible to oxidation at the elevated temperatures required for sintering. A failure to maintain a pure, oxygen-free furnace atmosphere will result in a brittle, useless part composed of copper oxides instead of a strong metallic foam. This requirement adds significant cost and technical challenge to the process.
Applying This Knowledge to Your Goal
Understanding this fabrication process allows you to tailor the material to a specific application by manipulating the key variables.
- If your primary focus is maximizing heat transfer: You will want to use a high fraction of larger space-holder particles to create a highly porous foam with large, interconnected pores for fluid flow.
- If your primary focus is structural support with weight reduction: You should use a lower fraction of the space holder and optimize sintering time and temperature to achieve a stronger, denser foam.
- If your primary focus is filtration or wicking: The key is to use uniformly sized space-holder particles to create a consistent and predictable pore size throughout the material.
Ultimately, mastering copper foam fabrication lies in controlling the "nothing"—the empty space—to define the final product's performance.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Powder Mixing | Combine copper powder with space holder (e.g., sugar/salt) | Create homogenous mixture for pore formation |
| 2. Compaction | Press mixture in a mold under pressure | Form green compact and ensure particle contact |
| 3. Dissolution | Submerge compact in solvent (e.g., water) | Remove space holder to create porous structure |
| 4. Sintering | Heat in controlled atmosphere furnace (875–950°C) | Fuse copper particles into solid metallic foam |
Ready to fabricate high-performance copper foam for your lab? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables—like high-purity metal powders and controlled-atmosphere furnaces—essential for successful sintering. Our expertise ensures you achieve the exact porosity, strength, and conductivity your application demands. Contact our experts today to discuss your copper foam project and optimize your process with KINTEK’s reliable solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PPF and coating? Armor vs. Slick Shell for Your Car
- Does nanomaterials have potential hazards to human health? Understanding the Risks and Safe Handling
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic coating? A Guide to Sacrificial vs. Barrier Protection
- What are the disadvantages of using metal? Understanding Corrosion, Weight, and Cost Challenges


















