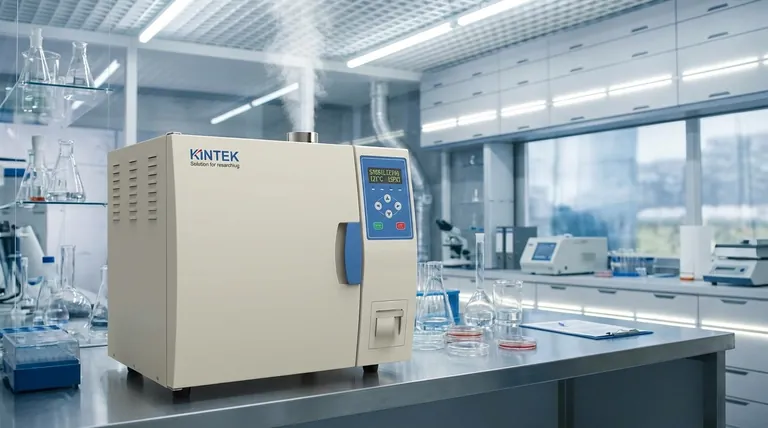
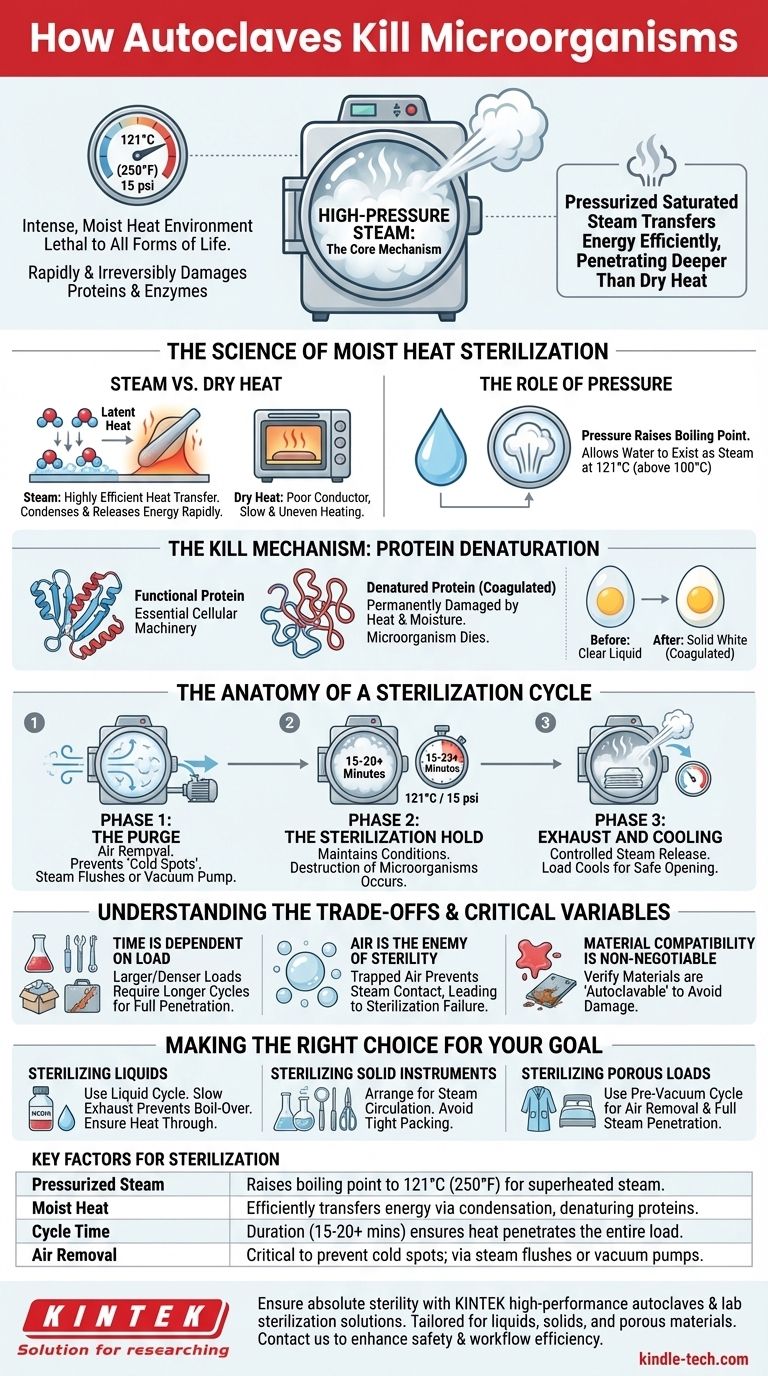
At its core, an autoclave kills microorganisms by using high-pressure steam. This process creates an environment of intense, moist heat, typically reaching 121°C (250°F), that is lethal to all forms of life. This combination of heat and moisture rapidly and irreversibly damages the essential proteins and enzymes within bacteria, viruses, and even highly resistant bacterial spores, ensuring complete sterilization.
The key to the autoclave's effectiveness is not just high temperature, but the use of pressurized saturated steam. This moist heat transfers energy far more efficiently than dry air, allowing it to penetrate and destroy microorganisms on a structural level where simple heat cannot.

The Science of Moist Heat Sterilization
To understand the autoclave, you must first understand why steam is the critical ingredient. The process is a precise application of physics and microbiology to achieve a state of absolute sterility.
Why Steam is More Effective Than Dry Heat
Dry heat, like in an oven, is a poor conductor of thermal energy. Steam, on the other hand, is a highly efficient vehicle for heat transfer.
When saturated steam makes contact with a cooler item, it immediately condenses into water, releasing a large amount of energy known as latent heat directly onto that surface. This allows for rapid and uniform heating of the entire load in a way that dry air cannot match.
The Role of Pressure
The primary purpose of pressure inside an autoclave is to allow water to exist as steam at temperatures far above its normal boiling point of 100°C.
At standard atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C. By increasing the pressure inside the chamber to approximately 15 pounds per square inch (psi) above atmospheric pressure, the boiling point is raised to 121°C. This superheated steam is the agent of sterilization.
The Kill Mechanism: Protein Denaturation
The combination of high temperature and moisture from the steam works to coagulate and denature essential proteins and enzymes within microorganisms.
Think of it like cooking an egg. The heat and moisture irreversibly change the structure of the egg white's proteins, turning them from a clear liquid into a solid white. In the same way, an autoclave permanently damages the cellular machinery that microorganisms need to live and reproduce, effectively killing them.
The Anatomy of a Sterilization Cycle
A typical autoclave cycle is a carefully controlled, automated process with distinct phases designed to ensure complete sterility.
Phase 1: The Purge
Before sterilization can begin, all air must be removed from the chamber. Air acts as an insulator and creates "cold spots" that steam cannot penetrate, which would lead to sterilization failure. Most autoclaves achieve this through steam flushes or a vacuum pump.
Phase 2: The Sterilization Hold
Once all air is purged and the chamber is filled with saturated steam, the autoclave reaches its set temperature and pressure (e.g., 121°C and 15 psi). It holds these conditions for a specific duration, typically a minimum of 15-20 minutes. This is the period when the actual destruction of microorganisms occurs.
Phase 3: Exhaust and Cooling
After the hold time is complete, the chamber's steam is released in a controlled manner, and the pressure returns to ambient levels. The load is then allowed to cool before the door can be safely opened.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Variables
Achieving successful sterilization is not as simple as pushing a button. Understanding the variables is critical to avoiding failure.
Time is Dependent on the Load
The standard "15-20 minutes at 121°C" is a guideline for small, non-complex loads. Larger, denser, or liquid-filled loads require significantly longer cycle times. The heat must have enough time to fully penetrate to the center of the most challenging item in the load.
Air is the Enemy of Sterility
Trapped air is the most common cause of sterilization failure. If items are packed too tightly or wrapped improperly, air pockets can prevent steam from making contact with all surfaces. Even if the autoclave's gauges show the correct temperature and pressure, items within these air pockets will not be sterile.
Material Compatibility is Non-Negotiable
Not all materials can withstand the high heat, pressure, and moisture of an autoclave. Heat-sensitive plastics can melt, sharp instruments can become dulled, and certain chemicals can be degraded. Always verify that your materials are rated as "autoclavable."
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge effectively, your approach must be tailored to the nature of your load.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing liquids (e.g., media): Use a dedicated liquid cycle with a slow, controlled exhaust to prevent the liquid from boiling over and ensure the volume has sufficient time to heat through completely.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing solid instruments or glassware: Arrange items to allow for maximum steam circulation, ensuring they are not packed too tightly, which can create insulating air pockets.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing porous loads (e.g., surgical gowns or animal bedding): You must use an autoclave with a pre-vacuum cycle that actively removes air from within the material itself to guarantee full steam penetration.
Understanding these core principles is what transforms an autoclave from a simple machine into a reliable and indispensable scientific tool for ensuring safety and sterility.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Sterilization |
|---|---|
| Pressurized Steam | Raises water's boiling point to 121°C (250°F) for superheated steam. |
| Moist Heat | Transfers energy efficiently via condensation, denaturing microbial proteins. |
| Cycle Time | Duration (typically 15-20+ minutes) ensures heat penetrates the entire load. |
| Air Removal | Critical to prevent cold spots; achieved via steam flushes or vacuum pumps. |
Ensure absolute sterility in your lab with the right equipment.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance autoclaves and lab sterilization solutions. Whether you need to sterilize liquids, solid instruments, or porous materials, our expertise ensures you get a reliable, efficient system tailored to your specific laboratory needs.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your sterilization requirements and discover how our lab equipment can enhance your safety and workflow efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
People Also Ask
- How long does an autoclave work? Understand Cycle Times for Effective Sterilization
- Is a UV sterilizer as good as an autoclave? The Critical Difference Between Sterilization and Disinfection
- What is an example of autoclave in laboratory? Essential Sterilization for Reliable Science
- What is the use of autoclave in microbiology? Ensuring Sterile Conditions for Reliable Results
- What are the settings for autoclave sterilization? Ensure Reliable Sterility with Proper Parameters



















