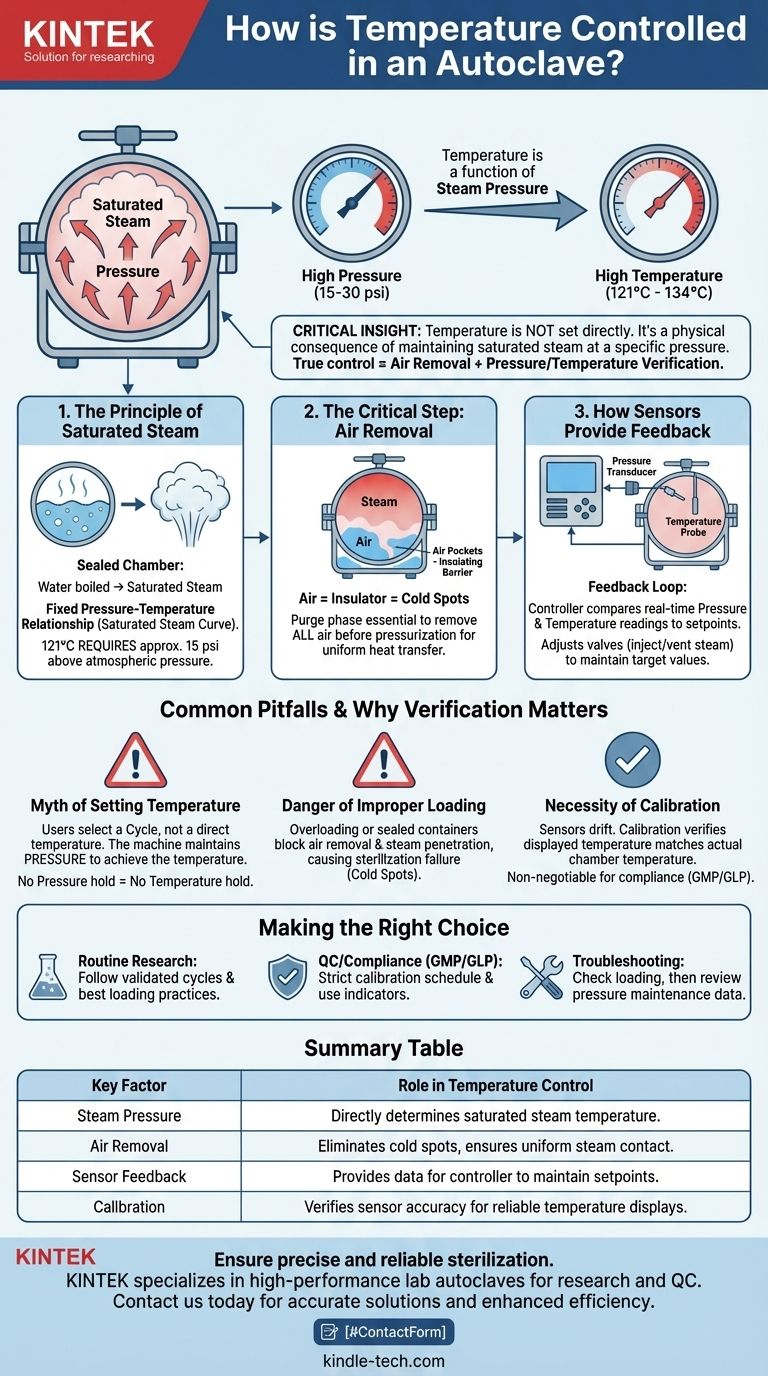
At its core, temperature in an autoclave is controlled by precisely managing steam pressure. Because the sterilization chamber is a sealed environment, the temperature of the saturated steam inside is directly proportional to its pressure. The autoclave's control system doesn't directly "dial up" a temperature; instead, it manipulates valves to inject or vent steam, holding a specific pressure that corresponds to the desired sterilization temperature, typically 121°C or 134°C.
The critical insight is that autoclave temperature is not an independent variable you can set directly. It is a physical consequence of achieving and maintaining saturated steam at a specific pressure. True control, therefore, involves ensuring all air is removed and verifying the pressure-to-temperature relationship through regular calibration.

The Physics of Autoclave Temperature Control
To trust an autoclave, you must first understand the fundamental physical principle it relies on. The entire process is built on the predictable properties of water and steam.
The Principle of Saturated Steam
In a sealed chamber, water boiled to create steam behaves according to a fixed pressure-temperature relationship. This is known as the saturated steam curve.
For sterilization to be effective, the steam must be saturated, meaning it holds the maximum possible amount of water vapor at that temperature. To reach 121°C (250°F), the autoclave's control system must raise and hold the internal pressure to approximately 15 psi (or 1 bar) above atmospheric pressure.
The Critical Step: Air Removal
The single biggest obstacle to achieving uniform temperature is residual air. Air pockets act as an insulating barrier, preventing steam from making direct contact with the items being sterilized.
This creates cold spots where the temperature never reaches the required level, even if the autoclave's main sensor reads 121°C. Therefore, the initial phase of any sterilization cycle, known as the purge or conditioning phase, is dedicated to removing all air from the chamber.
How Sensors Provide Feedback
Modern autoclaves use a feedback loop. A pressure transducer measures the chamber pressure, while one or more temperature probes (thermocouples) measure the temperature, typically near the chamber drain where air is most likely to be trapped.
The autoclave's controller constantly compares these readings to the cycle's setpoints. It then automatically opens and closes valves to adjust the steam level, ensuring the target pressure and corresponding temperature are held steady for the required duration.
Common Pitfalls and Why Verification Matters
An autoclave is a precision instrument, but operational errors or mechanical drift can lead to sterilization failure. Understanding these failure points is essential for ensuring safety and compliance.
The Myth of Setting the Temperature
Users select a temperature like "121°C" on the interface, but they are actually selecting a pre-programmed cycle. This program tells the controller to execute a series of steps, with the primary goal being to maintain the pressure that yields 121°C. If the machine cannot hold this pressure, it cannot hold the temperature.
The Danger of Improper Loading
Overloading the autoclave or using sealed containers prevents proper air removal and steam penetration. This is the most common cause of cycle failure. Even if the autoclave itself functions perfectly, a poorly packed load will contain cold spots and will not be sterile.
The Necessity of Calibration
The internal sensors that measure pressure and temperature can drift over time, becoming inaccurate. Calibration is the process of checking the autoclave's displayed temperature against an independent, certified temperature measurement device.
This verification is non-negotiable in regulated environments (like medical or pharmaceutical labs) to prove that 121°C on the screen means it is truly 121°C inside the chamber. Without it, you are placing blind trust in an unverified system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ensuring effective temperature control is about both proper operation and consistent verification. Your approach should depend on your specific needs and risk tolerance.
- If your primary focus is routine research use: Rely on the manufacturer's validated, pre-set cycles and ensure your lab follows best practices for loading the autoclave.
- If your primary focus is quality control or compliance (GMP/GLP): Implement a strict, documented calibration schedule and use chemical or biological indicators in every load to provide auditable proof of sterilization.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting a failed cycle: First, investigate the load for improper packing, then review the cycle data to confirm the chamber reached and maintained the correct pressure for the entire sterilization phase.
By understanding that temperature control is a function of pressure and verification, you can operate your autoclave with confidence and ensure the integrity of your results.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Temperature Control |
|---|---|
| Steam Pressure | Directly determines the temperature of saturated steam in the sealed chamber. |
| Air Removal | Critical for eliminating cold spots and ensuring uniform steam contact and heat transfer. |
| Sensor Feedback | Pressure transducers and temperature probes provide data for the control system to maintain setpoints. |
| Calibration | Verifies the accuracy of internal sensors to ensure the displayed temperature matches the actual chamber temperature. |
Ensure precise and reliable sterilization in your lab.
Understanding the principles of autoclave temperature control is the first step. Implementing them with the right equipment is what guarantees consistent, compliant results.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab autoclaves and consumables, designed for accuracy and ease of use. Our equipment helps laboratories in research, pharmaceutical, and quality control settings achieve perfect sterilization cycles, time after time.
Contact us today to find the perfect autoclave solution for your specific needs and let our experts help you enhance your lab's safety and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- What is the life expectancy of an autoclave machine? Maximize Your Investment with Proper Care



















