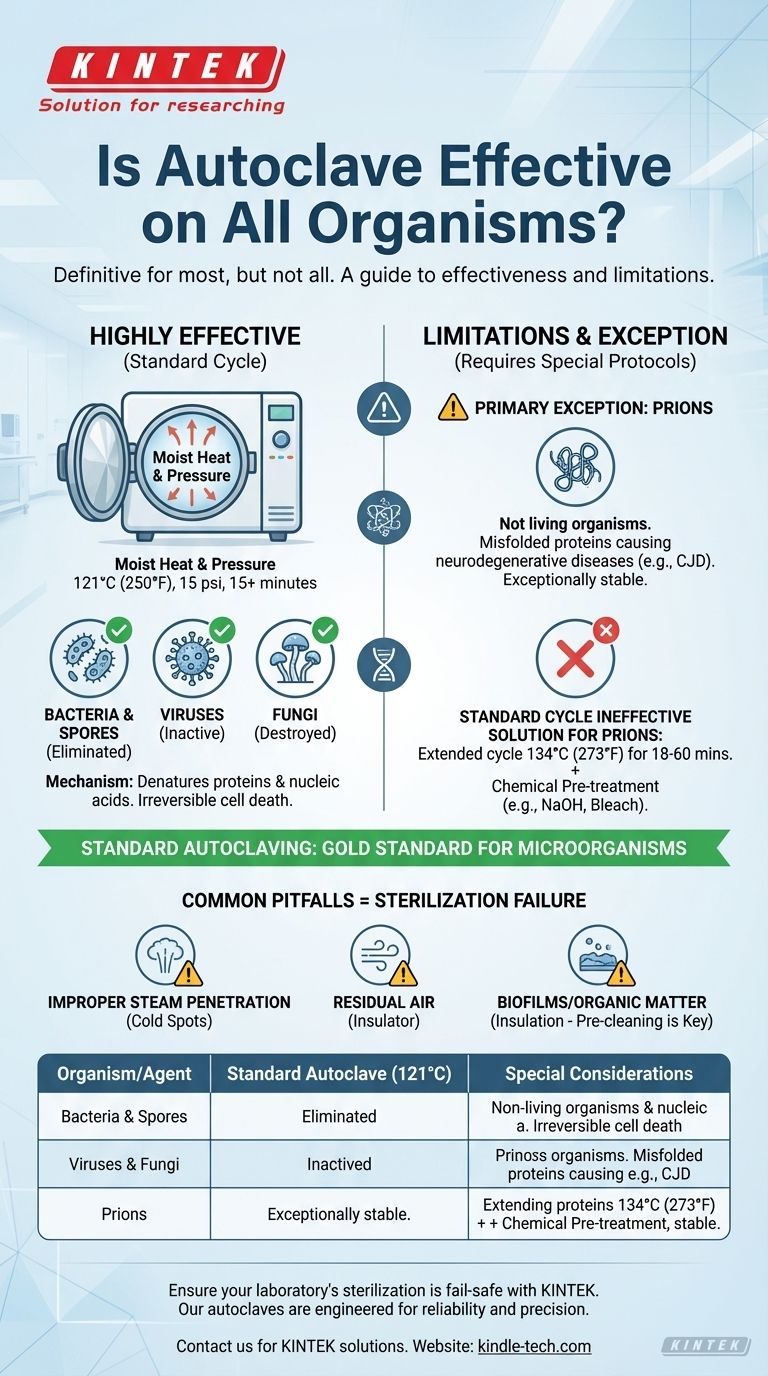
In practice, autoclaving is the definitive method for sterilizing against nearly all microorganisms, but it is not universally effective against every potential biological threat. The combination of high-pressure steam and extreme heat is designed to destroy bacteria, viruses, fungi, and even highly resistant bacterial spores. However, a specific class of infectious agents requires more rigorous protocols.
While standard autoclaving is the gold standard for eliminating bacteria, viruses, and spores, it is not reliably effective against prions. True and complete sterilization depends not only on the target organism but also on the correct application of the autoclaving process itself.
How Autoclaving Achieves Sterilization
Autoclaving works by applying moist heat under pressure, a combination far more effective than dry heat alone.
The Power of Pressurized Steam
An autoclave is essentially a highly controlled pressure cooker. By increasing the pressure, it allows water to remain in its liquid (steam) phase well above its normal 100°C boiling point.
A typical cycle runs at 121°C (250°F) at 15 psi for at least 15 minutes. This intense, moisture-rich environment rapidly penetrates and destroys microorganisms.
The Mechanism of Destruction
The hot steam denatures and coagulates essential proteins and nucleic acids within the cells of microorganisms. This process is irreversible and quickly leads to cell death, effectively sterilizing the equipment or media inside.
The Limits of Standard Autoclaving
While incredibly effective, the standard 121°C cycle has known limitations, primarily concerning a unique class of infectious agents and the physics of the process itself.
The Primary Exception: Prions
Prions are not living organisms but are misfolded proteins that can cause fatal neurodegenerative diseases, such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD).
These proteins are exceptionally stable and are not reliably inactivated by the standard autoclaving cycles used for bacteria and spores. Their structure makes them highly resistant to heat, radiation, and chemical degradation.
Other Hyper-Resistant Organisms
In extreme environments, some hyperthermophilic archaea can survive temperatures of 121°C. However, these are not pathogenic and are not a concern for medical or typical laboratory sterilization. The primary concern in these settings remains prions.
Common Pitfalls That Cause Sterilization Failure
Even for common bacteria, an autoclave is only effective if used correctly. Process failures are a more frequent cause of contamination than the inherent resistance of an organism.
Improper Steam Penetration
If steam cannot directly contact every surface of an object, sterilization will fail. Overpacking the autoclave, using sealed containers, or wrapping instruments in improper materials can create cold spots shielded from steam.
Residual Air
Air is a poor conductor of heat and acts as an insulator. If air is not fully evacuated from the chamber and from within porous loads, it prevents steam from reaching the required temperature, leading to a failed cycle. This is why modern autoclaves use vacuum cycles to remove air before injecting steam.
Presence of Biofilms or Organic Matter
A heavy layer of soil, tissue, or a hardened biofilm can physically insulate microorganisms from the steam. This is why thorough pre-cleaning of instruments before they are placed in an autoclave is a non-negotiable step in any professional setting.
How to Inactivate Prions
Given their extreme resistance, special protocols recommended by organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and CDC are required for items potentially contaminated with prions.
Extended Time and Higher Temperatures
Prion inactivation demands more aggressive conditions. One common protocol involves autoclaving at 134°C (273°F) for a minimum of 18 minutes, and some guidelines call for cycles as long as 60 minutes.
Chemical Pre-Treatment
For high-risk materials, a combination of chemical and heat treatment is often necessary. Soaking instruments in sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or sodium hypochlorite (bleach) before the extended autoclave cycle provides the highest level of assurance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Sterilization Goal
Your sterilization protocol must match the potential risk and the materials involved.
- If your primary focus is routine lab work or medical care: Standard autoclaving at 121°C for 15-30 minutes is highly effective for eliminating bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores.
- If your primary focus is decontaminating items exposed to CJD or other prion diseases: You must use specialized, high-temperature, extended-duration cycles, often combined with chemical pre-treatment as per institutional and CDC/WHO guidelines.
- If your primary focus is ensuring maximum reliability in any setting: Always prioritize proper cleaning, correct loading to ensure steam penetration, and regular validation of your autoclave's performance using biological indicators.
Ultimately, mastering sterilization comes from understanding that the process is just as important as the machine itself.

Summary Table:
| Organism/Agent | Standard Autoclave Effectiveness (121°C) | Special Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Bacteria & Spores | Highly Effective | Standard cycle is sufficient. |
| Viruses & Fungi | Highly Effective | Standard cycle is sufficient. |
| Prions | Not Reliably Effective | Requires 134°C for 18-60 min, often with chemical pre-treatment. |
| Hyperthermophiles | May Survive | Not a concern for medical/lab settings. |
Ensure your laboratory's sterilization is fail-safe with KINTEK.
Our autoclaves are engineered for reliability and precision, providing the consistent performance needed for critical applications. Whether you require standard sterilization or are working with highly resistant agents, KINTEK's lab equipment is designed to meet the highest standards of safety and efficacy.
Contact us today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your workflow and protect your research. Get in touch via our contact form.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a laboratory pressure steam sterilizer in dark fermentation? Boost Hydrogen Yield
- What are the uses of autoclave in laboratory equipment? Ensure Sterile Conditions for Your Research
- Is a sterilizer an autoclave? Understand the Key Differences for Your Lab
- What is the maximum pressure in an autoclave? A Guide to Safe and Effective Sterilization
- How long does a typical autoclave run? Understand the Full Cycle for Safe Sterilization
- What is the best sterilization method in microbiology? Match the Method to Your Material for Optimal Results
- What are the 3 most common machines used in sterilization? Choose the Right Method for Your Materials
- What are the key parameters for ensuring safe autoclave decontamination? Master Bio-Hazardous Waste Safety



















