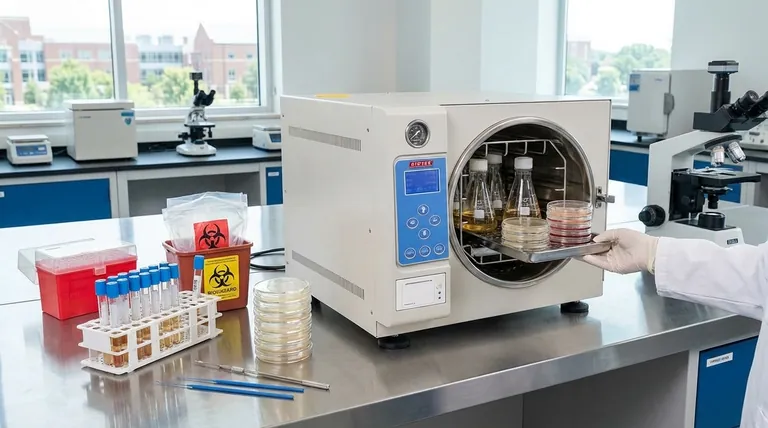
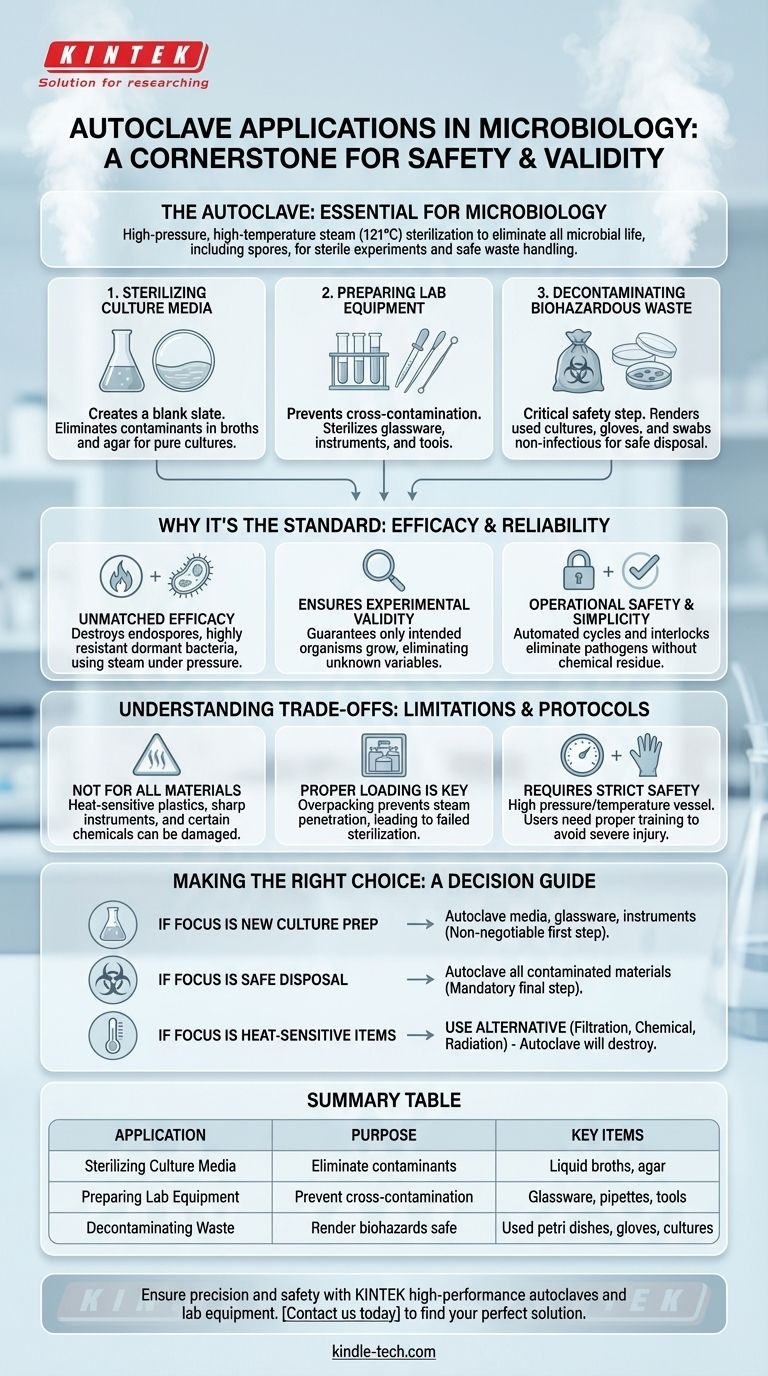
In a microbiology lab, an autoclave is primarily used for three critical tasks: sterilizing culture media before inoculation, preparing glassware and instruments for use, and decontaminating biohazardous waste before disposal. This process uses high-pressure, high-temperature steam to eliminate all forms of microbial life, including highly resistant bacterial spores, ensuring a sterile environment for experiments and a safe procedure for waste handling.
The autoclave is more than a sterilization device; it is the cornerstone of experimental validity and laboratory safety in microbiology. Its function is to create a controlled, sterile foundation, without which research and diagnostic work would be impossible.

The Core Functions of an Autoclave in Microbiology
Understanding the specific applications of an autoclave reveals its central role in the daily workflow of any microbiology laboratory. Its use is divided between preparing for experiments and safely concluding them.
Sterilizing Culture Media
Before you can grow a specific microorganism, its food source—the culture medium—must be a completely blank slate. Autoclaving is the standard method for sterilizing liquid broths, agar, and other media.
This step eliminates any pre-existing bacteria, fungi, or spores that could contaminate the experiment, compete with the target organism, or produce misleading results.
Preparing Laboratory Equipment
Any item that will come into direct or indirect contact with a microbial culture must be sterile. This prevents cross-contamination between experiments.
Common examples include sterilizing glass flasks, test tubes, and pipettes. Metal instruments like inoculation loops, forceps, and spreaders are also routinely autoclaved to ensure no viable microbes are transferred.
Decontaminating Biohazardous Waste
Perhaps the most critical safety function is the sterilization of used materials. All items contaminated with microorganisms are considered biohazardous waste.
This includes used petri dishes with bacterial or fungal colonies, contaminated gloves, swabs, and liquid cultures. Autoclaving this waste renders it non-infectious, allowing for safe disposal and protecting both lab personnel and the environment.
Why Autoclaving is the Standard
While other sterilization methods exist, autoclaving remains the gold standard in microbiology for several key reasons. Its reliability and efficacy are unmatched for most laboratory applications.
Unmatched Efficacy
The combination of high heat (typically 121°C or 250°F) and pressurized steam effectively denatures proteins and destroys the cellular structures of all microorganisms.
Crucially, this process is lethal to bacterial endospores, which are dormant, highly resistant forms of bacteria that can survive boiling and many chemical disinfectants.
Ensuring Experimental Validity
A successful microbiology experiment depends on controlling variables. Sterilization by autoclave ensures that the only organism growing in your culture is the one you intentionally introduced.
Without this guarantee, you could never be certain if your observations were due to your target microbe or an unknown contaminant.
Operational Safety and Simplicity
Modern autoclaves are engineered with safety interlocks and automated cycles, making them a reliable and straightforward part of the lab routine.
They eliminate pathogens without leaving chemical residues, which could interfere with subsequent experiments or pose a hazard to technicians.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its widespread use, an autoclave is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly and safely.
Not Suitable for All Materials
The intense heat and moisture will destroy or damage many materials. Heat-sensitive plastics will melt, sharp instruments can be dulled over time, and certain chemicals or reagents will degrade.
These items require alternative sterilization methods, such as filtration for liquids or chemical disinfection for surfaces.
The Importance of Proper Loading
Sterilization is only effective if the steam can contact every surface. Overpacking the autoclave chamber or improperly sealing containers can create air pockets that prevent steam penetration.
This can lead to a failed sterilization cycle, where items appear processed but are not truly sterile, creating a significant risk of contamination.
Requires Strict Safety Protocols
An autoclave is a pressure vessel operating at high temperatures. Improper use, such as attempting to open the door while it is still pressurized, can lead to severe burns and injury. Users must be properly trained on its safe operation and maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying sterilization correctly depends entirely on your objective and the materials you are working with.
- If your primary focus is preparing for a new culture: Autoclaving your media, glassware, and instruments is the non-negotiable first step to ensure a clean experimental start.
- If your primary focus is safe disposal: Autoclaving all used and contaminated materials is the mandatory final step to neutralize biohazards and comply with safety regulations.
- If your primary focus is working with heat-sensitive items: You must use an alternative method, as autoclaving will destroy your materials; consider filtration, ethylene oxide, or radiation.
Ultimately, mastering the use of the autoclave is fundamental to performing safe, repeatable, and valid science in microbiology.
Summary Table:
| Application | Purpose | Key Items |
|---|---|---|
| Sterilizing Culture Media | Eliminate contaminants for pure cultures | Liquid broths, agar |
| Preparing Lab Equipment | Prevent cross-contamination between experiments | Glassware, pipettes, metal tools |
| Decontaminating Waste | Render biohazards safe for disposal | Used petri dishes, gloves, cultures |
Ensure your microbiology lab operates with precision and safety. KINTEK specializes in high-performance autoclaves and lab equipment designed to meet the rigorous demands of sterilization. From preparing culture media to safely disposing of biohazardous waste, our solutions help you maintain experimental validity and protect your team. Contact us today to find the perfect autoclave for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the size of the autoclave? Choose the Right Capacity for Your Lab
- Is autoclave the same as sterilization? Unlocking the Key Differences for Lab Safety
- How do you autoclave lab equipment? A Step-by-Step Guide to Sterile Results
- What is autoclave in laboratory? Achieve Total Sterility for Your Lab
- Is a sterilizer an autoclave? Understand the Key Differences for Your Lab



















