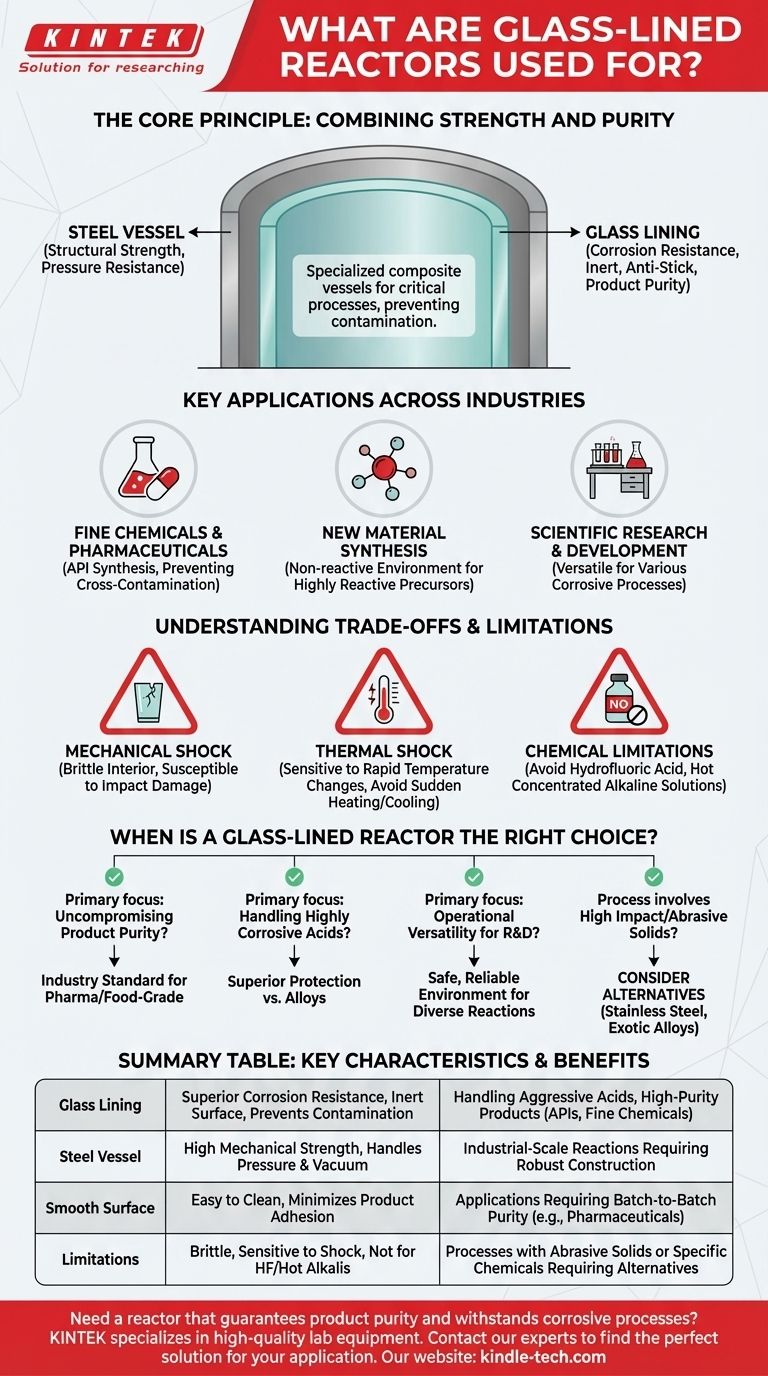
At their core, glass-lined reactors are specialized vessels used for critical chemical processes where corrosion resistance and product purity are non-negotiable. They are essential equipment in industries ranging from fine chemicals and biopharmaceuticals to new material synthesis and scientific research, serving as a controlled environment for mixing, reacting, and distilling aggressive or sensitive substances.
The fundamental value of a glass-lined reactor is its dual nature: it combines the structural strength and pressure resistance of a steel vessel with the superior corrosion resistance and inert, anti-stick properties of a glass surface.

The Core Principle: Combining Strength and Purity
A glass-lined reactor is not made of solid glass. It is a composite material system designed to leverage the best properties of both steel and glass.
The Strength of Steel
The outer vessel of the reactor is constructed from steel. This provides the necessary mechanical strength to safely handle high pressures, vacuums, and significant temperature variations required for industrial chemical processes.
The Inertness of Glass
The interior of the steel vessel is fused with a layer of specialized glass. This glass lining is the component that comes into contact with the process chemicals. Its primary job is to create a barrier that is exceptionally resistant to corrosion from a wide range of acids and other chemicals.
Ensuring Product Purity
Because the glass surface is highly inert, it prevents metal ions from the steel vessel from leaching into and contaminating the product. This is absolutely critical in applications like pharmaceuticals, where even trace amounts of metallic contamination can render a batch unusable. The smooth surface also minimizes product buildup and simplifies cleaning between batches.
Key Applications Across Industries
The unique properties of glass-lined reactors make them indispensable in several demanding fields.
Fine Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals
In the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and other high-value chemicals, preventing cross-contamination and metallic impurities is paramount. The inert nature of the glass lining ensures the final product meets stringent purity standards.
New Material Synthesis
When developing new materials, chemists often work with highly reactive or corrosive precursors. A glass-lined reactor provides a non-reactive environment, ensuring that the vessel itself does not interfere with the intended chemical reaction.
Scientific Research and Development
For laboratories and pilot plants, versatility is key. A single glass-lined reactor can be used for a wide array of different chemical processes involving various corrosive agents, making it a cost-effective and flexible asset for experimentation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, glass-lined reactors are not indestructible. Understanding their limitations is crucial for safe and efficient operation.
Vulnerability to Mechanical Shock
The glass lining is strong against chemical attack but is inherently brittle. Dropping a tool or any sharp impact on the interior surface can cause chipping or cracking, which compromises the entire vessel. This is known as "impact damage."
Sensitivity to Thermal Shock
Exposing the reactor to rapid and extreme temperature changes can create stress between the steel and the glass lining, leading to cracks. Heating and cooling must be performed gradually and within specified limits to avoid thermal shock.
Chemical Limitations
While resistant to most acids, the glass lining can be attacked by a few specific substances. Hydrofluoric acid and hot, concentrated alkaline solutions (high pH) will corrode the glass and must be avoided.
When is a Glass-Lined Reactor the Right Choice?
Choosing the correct reactor is a critical decision based on your specific process requirements.
- If your primary focus is uncompromising product purity: The inert, non-contaminating surface of a glass-lined reactor is the industry standard for pharmaceutical and food-grade applications.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive acids: The exceptional chemical resistance of the borosilicate glass lining offers superior protection compared to most metal alloys.
- If your primary focus is operational versatility for R&D: A single glass-lined reactor provides a safe and reliable environment for a diverse range of chemical reactions.
- If your process involves high impact or abrasive solids: You should consider more robust alternatives like stainless steel or exotic alloys, as the brittleness of glass is a significant liability.
Ultimately, selecting a glass-lined reactor is a strategic choice for processes where chemical resistance and purity are more critical than mechanical toughness.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Lining | Superior corrosion resistance, inert surface, prevents contamination | Handling aggressive acids, high-purity products (APIs, fine chemicals) |
| Steel Vessel | High mechanical strength, handles pressure and vacuum | Industrial-scale reactions requiring robust construction |
| Smooth Surface | Easy to clean, minimizes product adhesion | Applications requiring batch-to-batch purity (e.g., pharmaceuticals) |
| Limitations | Brittle (susceptible to impact/thermal shock), not for HF/hot alkalis | Processes with abrasive solids or specific chemicals requiring alternative materials |
Need a reactor that guarantees product purity and withstands corrosive processes? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including glass-lined reactors designed for the demanding needs of pharmaceutical, chemical, and research laboratories. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your application and ensure the integrity of your critical processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- Why are high-pressure autoclaves essential for preparing bio-based polyamide curing agents from dimeric acid?
- What is the function of a constant temperature hydrothermal reactor? Master Coal Fly Ash Activation
- What is the role of high-pressure reactors in the study of alloy oxidation? Essential Tools for Supercritical Research
- How does a high-pressure reactor demonstrate its value in accelerated aging? Predict Catalyst Durability Fast
- What is the purpose of using high-purity argon gas in a high-pressure reactor? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Data



















