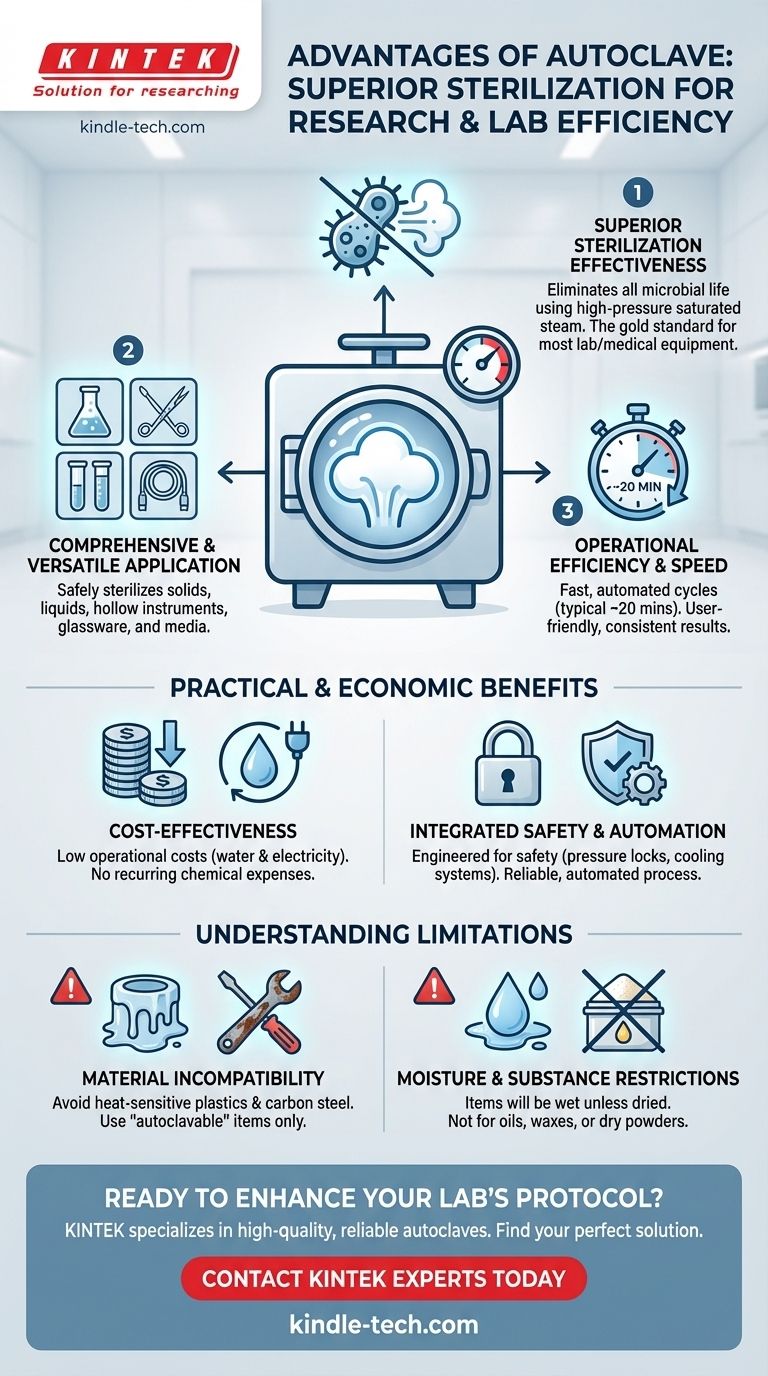
The primary advantages of an autoclave are its remarkable efficiency, economic operation, and unmatched sterilization effectiveness. It achieves this by using high-pressure saturated steam for rapid, deep penetration on a wide variety of materials without the need for additional chemicals.
An autoclave's core advantage is its ability to reliably and efficiently terminate all forms of microbial life using the physical power of pressurized steam, making it the gold standard for sterilizing most laboratory and medical equipment.

How Autoclaving Achieves Superior Sterilization
The effectiveness of an autoclave is not just about high heat; it's about the combination of heat, pressure, and moisture working in concert. This trio creates an environment that is lethal to microorganisms.
The Power of Saturated Steam
An autoclave works by boiling water to create steam, then trapping that steam in a chamber to increase the pressure and temperature. This saturated steam is a highly efficient vehicle for transferring thermal energy.
This method allows heat to penetrate dense materials and reach all surfaces of complex instruments, something dry heat struggles to do. It ensures a complete and total sterilization that is difficult to achieve with other methods.
Comprehensive and Versatile Application
A key advantage is the sheer breadth of materials that can be safely sterilized. Autoclaves are not limited to a single type of object.
They are used to sterilize solids, liquids, hollow instruments, glassware, surgical tools, and microbial growth media. This versatility makes them indispensable in microbiology, medical fields, dentistry, and veterinary science.
Operational Efficiency and Speed
Compared to many other sterilization methods, autoclaving is remarkably fast. A typical sterilization cycle is often around 20 minutes, though this can be adjusted based on the load's size and density.
Modern autoclaves are fully automated, with user-friendly interfaces that allow operators to select pre-set programs, ensuring consistent and reliable results with minimal hands-on time.
The Practical and Economic Benefits
Beyond its scientific effectiveness, the autoclave is a cornerstone technology due to its practical design and long-term cost benefits.
Cost-Effectiveness
The operational costs are relatively low. Autoclaves run on water and electricity, eliminating the ongoing expense of purchasing sterilization chemicals or other disposables.
This makes them a highly economical choice for any facility that performs a high volume of sterilizations.
Integrated Safety and Automation
Modern autoclaves are engineered with safety as a priority. They include mechanisms to prevent excessive pressure buildup and have locking doors that cannot be opened until the internal temperature and pressure have returned to safe levels.
Many also feature cooling systems that lower the water temperature before it is discharged, protecting a facility's plumbing and drainage systems from damage.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, autoclaving is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for proper use and to prevent damage to your equipment.
Material Incompatibility
The combination of high heat and moisture can be destructive to certain materials. Heat-sensitive plastics will melt, and carbon steel instruments are prone to rust and corrosion from the moisture.
Only items rated as "autoclavable," such as stainless steel and specific types of heat-resistant plastics (like polypropylene), should be processed.
The Challenge of Moisture Retention
Because the process relies on steam, items will be wet at the end of a cycle unless a specific drying phase is used. This retained moisture can be problematic for certain applications or for instruments that need to be packaged and stored immediately.
Not Suitable for All Substances
The autoclave is designed for sterilizing materials that contain water or can withstand steam penetration. It is ineffective for substances that repel moisture, such as oils, waxes, and dry powders, which require dry-heat sterilization instead.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right sterilization method depends entirely on the materials you work with and your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing reusable, heat-stable instruments, glassware, and media: The autoclave is the gold standard for its unmatched efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is processing moisture-sensitive or rust-prone items: You must acknowledge the autoclave's limitations and consider alternative methods like dry-heat sterilization or chemical sterilants.
- If your primary focus is operational cost and environmental impact: The autoclave is a superior choice, as it avoids the recurring expense and disposal challenges associated with chemical-based sterilization.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental principles of steam sterilization empowers you to leverage its advantages while respecting its limitations.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Sterilization Effectiveness | Eliminates all microbial life using high-pressure saturated steam. |
| Versatility | Safely sterilizes a wide range of materials, from solids and liquids to hollow instruments. |
| Operational Efficiency | Fast, automated cycles (e.g., ~20 minutes) with minimal hands-on time. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Low operational costs using just water and electricity, no recurring chemical expenses. |
| Safety & Automation | Integrated safety features and user-friendly controls for reliable, consistent results. |
Ready to enhance your lab's sterilization protocol?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality autoclaves and lab equipment designed for reliability and efficiency. Our autoclaves deliver the precise steam sterilization your laboratory needs for instruments, glassware, and media, ensuring safety and cost-effectiveness.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect autoclave solution for your specific application and operational goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave equipped with a stirring device for molten salt testing? Dynamic Accuracy
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment
- What is the primary function of a laboratory autoclave in the pre-treatment of medical plastic waste for liquid fuel?
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing



















