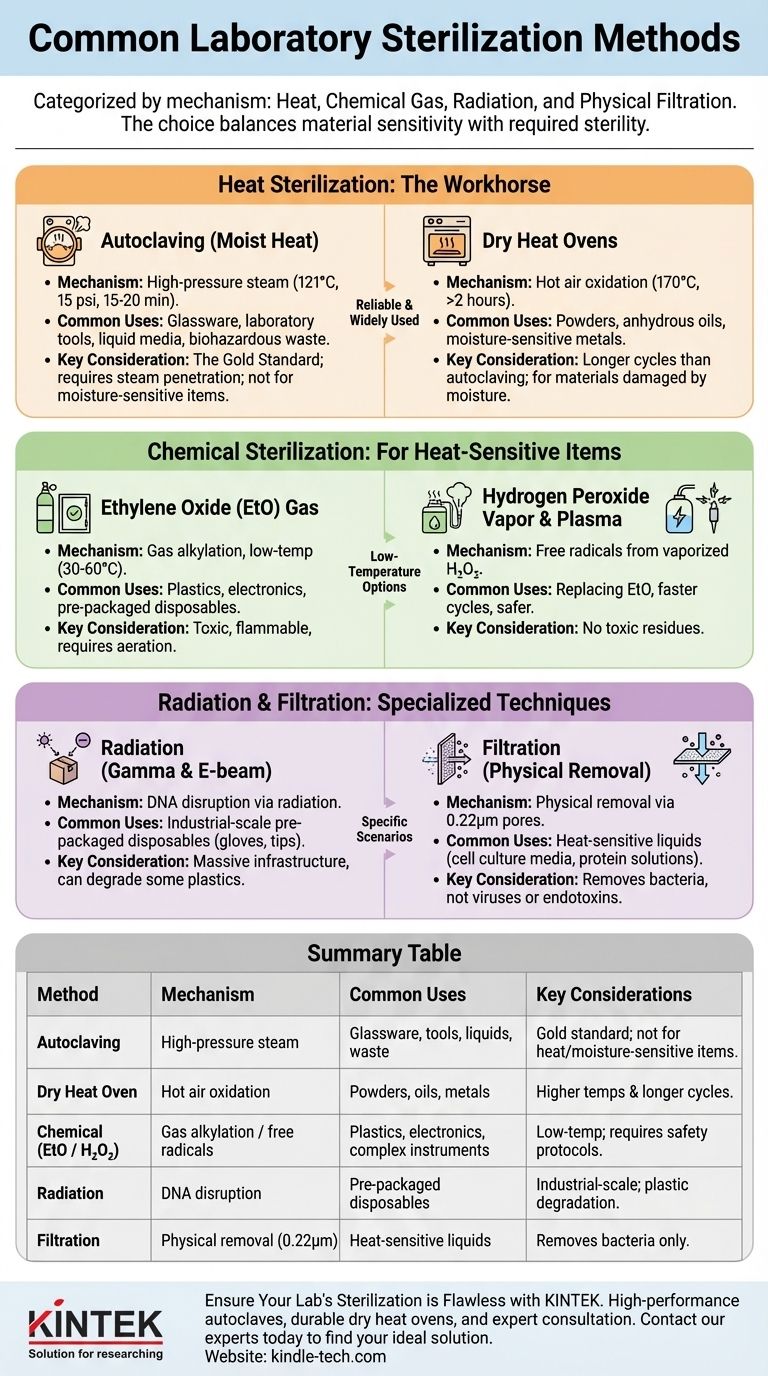
The most common laboratory sterilization methods are categorized by their mechanism: heat (both moist and dry), chemical gas, radiation, and physical filtration. Moist heat sterilization via an autoclave is the most prevalent method for general lab equipment and liquids, while other techniques are reserved for items that cannot withstand high temperatures and pressure.
Choosing a sterilization method is not about finding the single "best" option, but about selecting the most appropriate one for the material you are sterilizing. The decision is a critical balance between the material's sensitivity to heat or chemicals and the required level of sterility for your application.

Heat Sterilization: The Workhorse of the Lab
Heat is the most reliable and widely used sterilization agent in a laboratory setting. It works by irreversibly denaturing the essential proteins and enzymes that microorganisms need to survive.
Autoclaving (Moist Heat): The Gold Standard
An autoclave is a pressure chamber that uses high-pressure steam to sterilize items. The standard cycle is 121°C (250°F) at 15 psi for 15-20 minutes.
The presence of steam is critical. It allows for rapid and efficient heat penetration into dense materials, making it far more effective than dry heat at the same temperature.
Autoclaving is the preferred method for sterilizing most glassware (bottles, flasks), laboratory tools (forceps), liquid media, and biohazardous waste.
Dry Heat Ovens: For Materials Sensitive to Moisture
Dry heat sterilization is performed in an oven and requires higher temperatures and much longer exposure times than autoclaving. A typical cycle is 170°C (340°F) for at least two hours.
This method kills microbes through oxidation. Because hot air is less efficient at transferring heat than steam, the longer cycle is necessary to ensure all organisms are destroyed.
Dry heat is used for materials that are damaged by moisture or cannot be penetrated by steam, such as anhydrous oils, powders, and certain metal instruments.
Chemical Sterilization: For Heat-Sensitive Items
When an item cannot withstand the high temperatures of an autoclave or dry heat oven, chemical sterilants are used. These are most often employed for plastics, electronics, and complex medical instruments.
Ethylene Oxide (EtO) Gas: A Low-Temperature Option
Ethylene Oxide (EtO) is a colorless gas that effectively sterilizes at low temperatures (30-60°C). It is an alkylating agent that disrupts microbial DNA and proteins, preventing replication.
EtO can penetrate breathable packaging like plastic wrap, making it ideal for sterilizing pre-packaged disposable items like syringes, catheters, and plastic petri dishes.
The major disadvantage is its toxicity and flammability. Items sterilized with EtO require a lengthy aeration period to remove residual gas before they can be safely handled.
Hydrogen Peroxide Vapor & Plasma: A Faster, Safer Alternative
This method involves vaporizing an aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide. In some systems, radiofrequency energy is used to excite the vapor into a low-temperature plasma state.
The process creates free radicals that are highly reactive and destructive to microorganisms. The primary byproducts are non-toxic water and oxygen.
Vaporized hydrogen peroxide is rapidly replacing EtO for many applications due to its faster cycle times and significantly improved safety profile, with no toxic residues.
Radiation and Filtration: Specialized Techniques
These methods are used in specific scenarios where heat or chemicals are not suitable.
Radiation (Gamma & E-beam): For Industrial-Scale Sterilization
Irradiation uses high-energy gamma rays or electron beams to destroy microorganisms by breaking the covalent bonds in their DNA. This is a highly effective, low-temperature method.
Due to the massive infrastructure required (e.g., a cobalt-60 source), this technique is almost exclusively used at an industrial scale by manufacturers of medical devices and lab disposables.
You have likely used many items sterilized by radiation, such as pre-packaged sterile gloves, swabs, and pipette tips.
Filtration: Removing, Not Killing
Sterile filtration is unique because it physically removes microorganisms rather than killing them. A liquid or gas is passed through a filter with a pore size small enough to trap bacteria, typically 0.22 micrometers (µm).
This is the only viable method for sterilizing heat-sensitive liquids, such as cell culture media containing vitamins or antibiotics, protein solutions, and certain drugs.
It is critical to remember that filtration does not remove viruses or endotoxins unless specialized ultra-filters are used. The resulting liquid is sterile, but the filter itself becomes highly contaminated.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single method is perfect for every situation. Choosing correctly requires understanding the limitations of each technique.
Material Compatibility is Paramount
The nature of the item being sterilized is the first consideration. An autoclave will melt most standard plastics and damage sensitive electronics. Radiation can make some polymers brittle, and chemical gases may be absorbed by certain materials.
Penetration and Complexity
An autoclave's steam must be able to contact all surfaces. Tightly wrapped or improperly loaded items may not be sterilized. Similarly, complex instruments with long, narrow lumens can be challenging for gas sterilants to penetrate.
Safety, Cost, and Turnaround
Autoclaves represent a moderate capital cost but are cheap to run. Chemical sterilizers like EtO systems are expensive and carry significant safety and regulatory burdens. Filtration is inexpensive for small volumes but time-consuming and costly for large-scale production.
How to Select the Correct Sterilization Method
The decision hinges on the nature of your item and the goal of your experiment. Use this as your guide.
- If you are sterilizing robust materials like glassware, liquids, or waste: Use an autoclave for its unmatched reliability and efficiency.
- If you are sterilizing heat-sensitive liquids like media with vitamins or protein solutions: Use sterile filtration to remove bacteria while preserving the chemical integrity of your solution.
- If you are sterilizing heat-sensitive solid items like certain plastics or electronics: Chemical methods like hydrogen peroxide or ethylene oxide are necessary.
- If you are simply reducing the microbial load on a surface (disinfection): A 70% ethanol solution or UV light is often sufficient and much faster than sterilization.
Choosing the correct method is a fundamental pillar of reproducible, safe, and effective laboratory science.
Summary Table:
| Method | Mechanism | Common Uses | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autoclaving (Moist Heat) | High-pressure steam | Glassware, tools, liquid media, waste | Gold standard; not for heat/moisture-sensitive items |
| Dry Heat Oven | Hot air oxidation | Powders, oils, moisture-sensitive metals | Requires higher temps and longer cycles than autoclaving |
| Chemical (EtO / H₂O₂) | Gas alkylation / free radicals | Plastics, electronics, complex instruments | Low-temperature; requires aeration/safety protocols |
| Radiation (Gamma/E-beam) | DNA disruption via radiation | Pre-packaged disposables (gloves, tips) | Industrial-scale; can degrade some plastics |
| Filtration | Physical removal via 0.22µm pores | Heat-sensitive liquids (media, drugs) | Removes bacteria but not viruses or endotoxins |
Ensure Your Lab's Sterilization is Flawless with KINTEK
Choosing the right sterilization method is critical for the integrity of your experiments and the safety of your lab. Whether you need a reliable autoclave for daily glassware sterilization, a dry heat oven for sensitive materials, or guidance on chemical methods, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your laboratory's unique needs.
We provide:
- High-performance autoclaves for efficient and reliable steam sterilization.
- Durable dry heat ovens designed for precise, moisture-free sterilization cycles.
- Expert consultation to help you select the perfect sterilization technique for your specific materials and protocols.
Don't let improper sterilization compromise your research. Contact our lab equipment experts today to find the ideal sterilization solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Can autoclave sterilize liquid? Master Safe and Effective Liquid Sterilization
- What is the use of autoclave in medical? The Critical Role of Sterilization in Patient Safety
- How does the lab autoclave work? Achieve Complete Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What is a lab autoclave? Your Guide to Sterilization with Pressurized Steam
- How do you sterilize glassware by autoclave? Master the 3-Step Process for Reliable Sterility



















