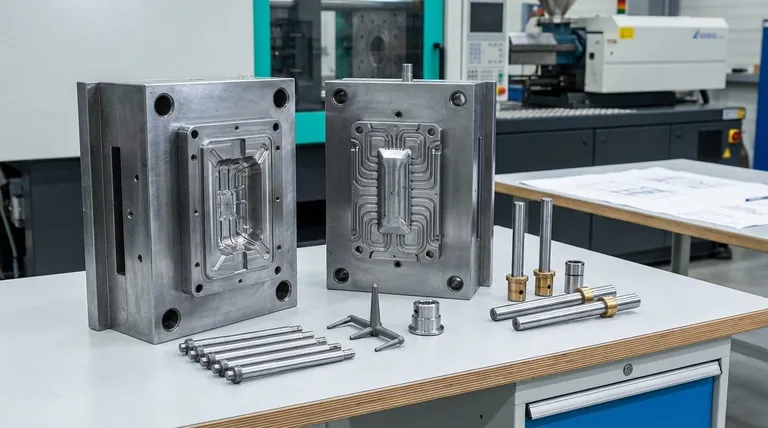
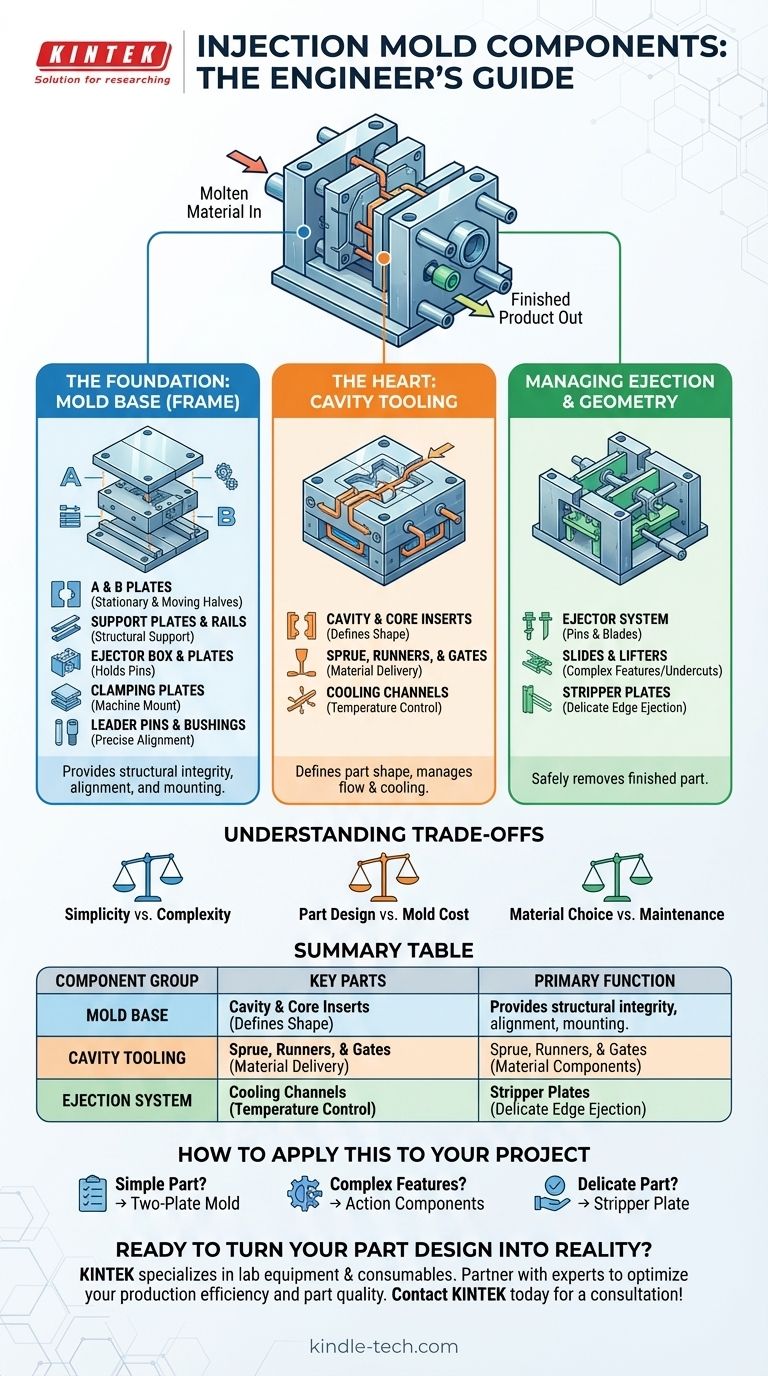
At its core, an injection mold is a sophisticated assembly of precision-machined parts designed for a single purpose: to shape molten material into a finished product. These components can be organized into three fundamental groups: the mold base (the structural frame), the cavity tooling (which defines the part's shape), and the ejection system (which removes the finished part). Together, these systems must withstand immense pressure and temperature changes with perfect alignment, cycle after cycle.
Understanding a mold isn't just about naming its parts; it's about recognizing it as an integrated system. The base provides the structure and alignment, the tooling defines the geometry, and the ejection system ensures the part can be removed cleanly, with every component influencing the final product's quality and cost.
The Foundation: The Mold Base (Frame)
The mold base, sometimes called the mold frame or die set, is the standardized foundation that holds all the custom tooling. It provides the structural integrity, alignment, and mechanism for mounting the entire assembly into an injection molding machine.
A and B Plates
These are the two main halves of the mold. The "A" side, or stationary half, contains the cavity insert and attaches to the machine's stationary platen. The "B" side, or moving half, contains the core insert and the ejection system.
Support Plates and Rails
Located behind the core and cavity inserts, these plates provide critical structural support. They prevent the plates from flexing or deforming under the immense pressure of plastic injection, which can reach thousands of PSI.
Ejector Box and Plates
Housed on the "B" side of the mold, the ejector box contains the ejector plate and the ejector retainer plate. These two plates move together, holding the ejector pins and pushing them forward to eject the finished part.
Clamping Plates
These are the outermost plates on both the "A" and "B" sides of the mold base. They are used to physically clamp the entire mold assembly into the injection molding machine.
Leader Pins and Bushings
These are critical alignment components. Leader pins on one half of the mold fit perfectly into bushings on the other half as the mold closes. This ensures precise alignment between the cavity and core, which is essential for consistent part quality.
The Heart of the Mold: Cavity Tooling
This is the custom, part-specific tooling that sits within the mold base. The quality and precision of these components directly determine the final part's dimensions, features, and surface finish.
Cavity and Core Inserts
These are the two components that form the actual shape of the part. The cavity is the female half that typically forms the exterior surface of the part, while the core is the male half that forms the interior surface.
Sprue, Runners, and Gates
This is the delivery system that transports molten plastic from the machine's nozzle to the cavity. The sprue is the initial channel, the runners distribute the plastic to different cavities, and the gate is the final, narrow opening into the cavity itself.
Cooling Channels
These are pathways drilled through the mold plates and inserts through which a fluid (usually water) circulates. Controlling the mold's temperature is critical for managing part shrinkage, preventing defects, and achieving a fast, repeatable cycle time.
Managing Ejection and Complex Geometry
Beyond the basic structure, many molds include components to handle the ejection of the part and to form complex features like undercuts.
The Ejector System (Pins and Blades)
Ejector pins are the most common method for pushing the part out of the core after it has cooled. These hardened steel pins are housed in the ejector plates and travel forward through the core to make contact with the part.
Slides and Lifters
These are "action" components—moving parts within the mold used to create undercuts or features that would otherwise lock the part in the mold. Slides move perpendicular to the mold's opening direction, while lifters move at an angle.
Stripper Plates
For parts that are delicate or have a continuous outer edge (like a bottle cap), a stripper plate may be used instead of ejector pins. This plate surrounds the core and pushes the entire edge of the part forward, providing a gentle and uniform ejection force.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice and number of components in a mold represent a series of critical engineering trade-offs between part design, tool cost, and long-term maintenance.
Simplicity vs. Complexity
A simple, open-and-shut two-plate mold is relatively inexpensive to build and easy to maintain. Adding components like slides, lifters, or a third plate for a hot runner system dramatically increases the tool's complexity, upfront cost, and potential for wear.
Part Design vs. Mold Cost
The design of the plastic part dictates the complexity of the mold. A simple feature like a snap-fit latch requires an undercut, which in turn requires a slide or lifter in the mold. This single design choice can add thousands of dollars to the cost of the tool.
Material Choice and Maintenance
The steel used for the cavity and core inserts affects the mold's longevity and cycle time. Hardened tool steels last for millions of cycles but are expensive. Softer steels are cheaper but wear out faster. Complex molds with many moving parts require more frequent preventative maintenance to ensure alignment and function.
How to Apply This to Your Project
The ideal mold configuration depends entirely on your project's specific needs for part geometry, production volume, and budget.
- If your primary focus is a simple part with no undercuts: A basic two-plate mold with a standard pin ejection system offers the most cost-effective and reliable solution.
- If your primary focus is a complex part with side features: You will require a mold with action components like slides or lifters, which increases cost but enables greater design freedom.
- If your primary focus is a delicate, thin-walled, or cylindrical part: A stripper plate mold provides gentle, even ejection, preventing warping or damage that could be caused by localized ejector pin force.
By understanding how these individual components function as a system, you can design more manufacturable parts and communicate more effectively with your tooling and manufacturing partners.
Summary Table:
| Mold Component Group | Key Parts | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Mold Base (Frame) | A/B Plates, Support Plates, Leader Pins, Clamping Plates | Provides structural integrity, alignment, and mounting for the machine. |
| Cavity Tooling | Cavity/Core Inserts, Sprue/Runners/Gates, Cooling Channels | Defines the part's shape and manages the flow and cooling of molten plastic. |
| Ejection System | Ejector Pins/Plates, Slides, Lifters, Stripper Plates | Safely removes the finished, cooled part from the mold cavity. |
Ready to turn your part design into a reality?
Understanding mold components is the first step. The next is partnering with an expert who can help you navigate the trade-offs between part design, tool cost, and production volume.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our expertise ensures you get the right mold configuration for your specific application, balancing performance with budget. Let's discuss how the right mold design can optimize your production efficiency and part quality.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- XRF & KBR steel ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- Assemble Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hydrothermal Synthesis Reactor Polytetrafluoroethylene Carbon Paper and Carbon Cloth Nano-growth
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
People Also Ask
- What functions do PTFE insulation sleeves serve in solid-state battery molds? Enhance Battery Assembly Precision
- How do high-precision molds contribute to Li6PS5Cl electrolyte membrane formation? Achieve Perfect Density and Thickness
- What are the key functions of high-temperature graphite molds? Optimize Vacuum Hot Pressing for W-50%Cu Composites
- What is a press die set? A Precision System for Efficient Mass Production
- What is the tooling of a mold? A Guide to Core Components and Cost-Effective Production
- How should KBr powder be pre-treated before it is used to make a pellet? Optimize Your FTIR Spectra Quality
- What role do high-pressure mold components play in the thermal pressing of nano-crystalline tungsten? Maximize Density
- What role do graphite molds play during vacuum hot press sintering? Optimize TiCN-Reinforced Composites



















