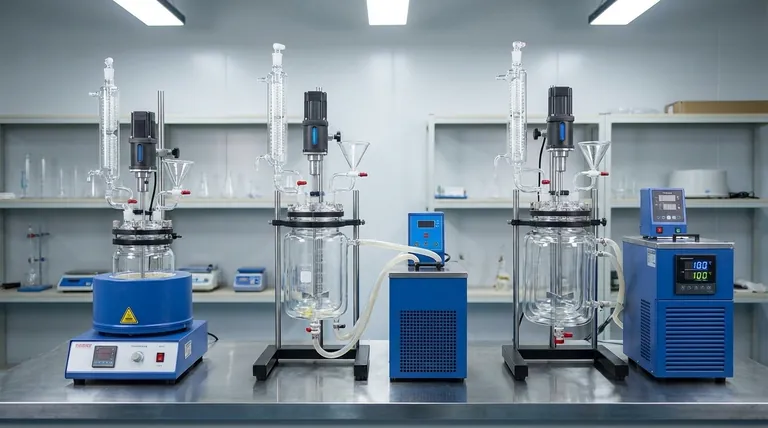
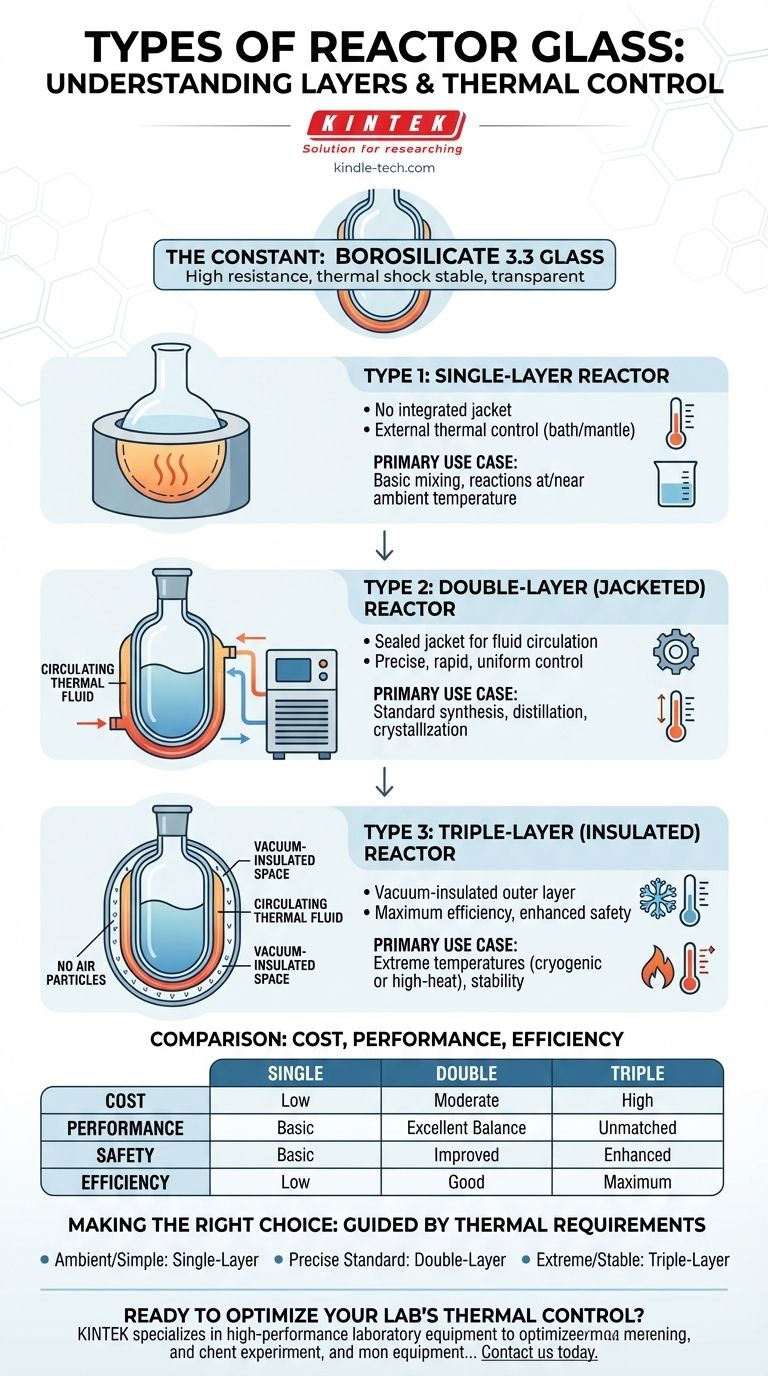
When selecting a glass reactor, the "types" of glass refer not to the material itself, but to the construction of the vessel's layers. The three primary types are single-layer, double-layer (jacketed), and triple-layer (jacketed and vacuum insulated), each designed for a different level of thermal control.
The choice between reactor types is fundamentally a decision about temperature control. You are not choosing different kinds of glass, but rather different systems of heating, cooling, and insulation built around a standard borosilicate glass vessel.

The Core Material vs. The System Design
Before comparing reactor types, it's critical to understand that the glass vessel at the heart of the system is almost always the same.
The Constant: Borosilicate 3.3 Glass
The reaction vessel itself is typically made from Borosilicate 3.3 glass. This material is the industry standard due to its exceptional properties.
It offers high resistance to chemical attack, withstands significant thermal shock, and its transparency allows for direct observation of the chemical process.
The Variable: The "Layers" are Jackets
The terms single, double, and triple-layer do not describe the glass of the inner vessel. They describe the external jackets built around it, which create a system for managing temperature.
A Breakdown of Reactor Types by Layer
Each layer adds a specific function, primarily related to heating or cooling the reactor's contents efficiently and safely.
Type 1: The Single-Layer Reactor
This is the simplest design, consisting of a single-walled glass vessel with no integrated thermal jacket.
To control temperature, the entire reactor must be placed within an external heating or cooling medium, such as a heating mantle or a water/oil bath.
This type is best suited for basic applications at or near room temperature where precise, uniform thermal control is not the primary concern.
Type 2: The Double-Layer (Jacketed) Reactor
This is the most common type of glass reactor. It features an outer jacket that creates a sealed space around the inner reaction vessel.
A thermal fluid (like water, glycol, or silicone oil) is pumped from a circulating chiller/heater through this jacket. This allows for precise, rapid, and uniform heating or cooling of the reactor's contents.
The jacketed reactor is the workhorse for most standard chemical synthesis, distillations, and crystallization processes.
Type 3: The Triple-Layer (Insulated) Reactor
This design adds a third, outermost layer to a jacketed reactor, creating a vacuum-insulated space between the thermal jacket (layer two) and the ambient environment (layer three).
This vacuum acts as a powerful insulator, dramatically reducing heat loss to the surroundings. It keeps cold processes cold and hot processes hot with maximum efficiency.
It is essential for very low-temperature (cryogenic) reactions or high-temperature processes where thermal stability and energy efficiency are paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right reactor involves balancing performance needs with cost and operational complexity.
Cost vs. Performance
A single-layer reactor is the least expensive but offers the poorest temperature control. A double-layer reactor provides an excellent balance of cost and precise thermal performance. A triple-layer reactor is the most expensive but delivers unmatched efficiency and stability for extreme-temperature applications.
Safety and Efficiency
The vacuum insulation of a triple-layer reactor not only saves energy but also enhances safety. The outer surface remains close to room temperature, preventing burns from hot processes and eliminating condensation or frost during cold processes.
Operational Footprint
Single-layer reactors rely on large, open baths, which can be cumbersome. Jacketed reactors require a dedicated fluid circulator, which adds to the system's footprint but provides far superior control in a closed loop.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection should be guided entirely by the thermal requirements of your specific application.
- If your primary focus is simple mixing or reactions at ambient temperature: A single-layer reactor offers the most cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature control for standard synthesis or crystallization: The double-layer (jacketed) reactor is the industry standard and provides the best balance of performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature work (cryogenic or high-heat) or maximizing thermal efficiency: A triple-layer reactor is necessary for its superior insulation and process stability.
Understanding that the 'layers' refer to thermal control systems, not the glass itself, empowers you to select the right tool for your specific scientific objective.
Summary Table:
| Reactor Type | Key Feature | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Layer | No integrated jacket; requires external bath | Basic mixing or reactions at/near ambient temperature |
| Double-Layer (Jacketed) | Sealed jacket for circulating thermal fluid | Precise temperature control for standard synthesis, distillation, crystallization |
| Triple-Layer (Insulated) | Vacuum-insulated outer layer for maximum efficiency | Extreme temperature work (cryogenic or high-heat) requiring stability |
Ready to optimize your lab's thermal control? KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory equipment, including a full range of single, double, and triple-layer glass reactors designed for precise chemical synthesis and crystallization. Our solutions ensure safety, efficiency, and reliability for your most demanding processes. Contact us today to discuss your specific application needs and find the perfect reactor system for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a high-pressure reactor in h-BN magnetic nanocomposite synthesis? Master Precision Deposition
- What is the role of a PTFE-lined stainless steel high-pressure autoclave in ZrW2O8 synthesis? Achieve High Purity
- Why are stainless steel autoclaves key to PCL-TPE preparation? Mastering High-Vacuum Polycondensation
- What is the function of high-pressure reactors in semiconductor catalyst preparation? Optimize Your Heterojunctions
- Why is a High-temperature and High-pressure Autoclave necessary for zirconium alloy testing? Ensure Nuclear Safety.



















