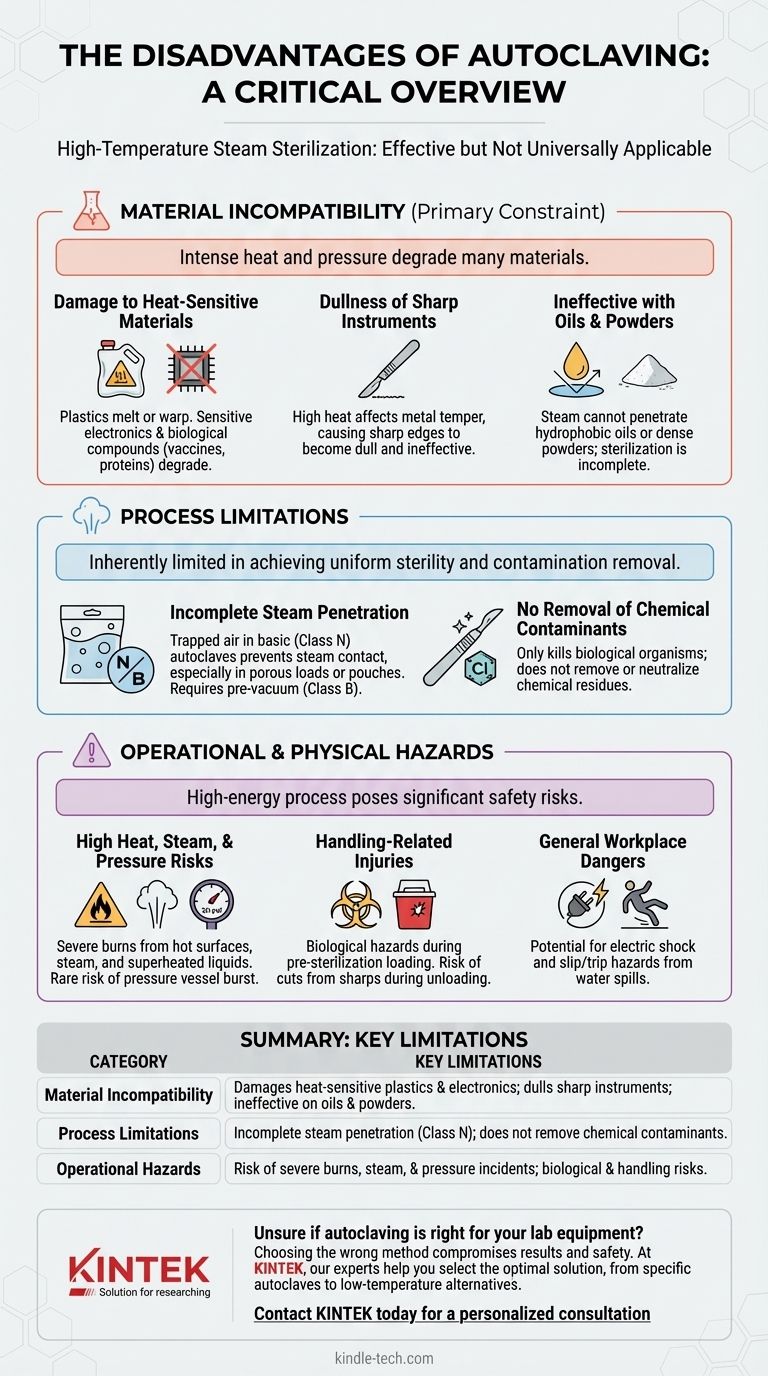
While autoclaving is a gold standard for sterilization, it is not a universally applicable solution. Its primary disadvantages stem from the very conditions that make it effective: the use of high-temperature, high-pressure steam. This process can damage or destroy many common materials, is ineffective for non-aqueous substances like oils, and poses significant physical hazards to operators if not handled with extreme care.
The core limitation of an autoclave is its destructive potential. The intense heat and steam required to achieve sterility will also degrade, melt, or dull many materials, making material compatibility—not microbial effectiveness—the most critical consideration for its use.

Material Incompatibility: The Primary Constraint
The most frequent challenge with autoclaving is its effect on the items being sterilized. The process is inherently aggressive and is only suitable for materials that can withstand its conditions.
Damage to Heat-Sensitive Materials
Many modern lab and medical items are not built for extreme heat. Plastics may melt or warp, and sensitive electronic components will be irreversibly damaged.
Furthermore, many complex biological and chemical compounds, such as vaccines, serums, and certain proteins, will degrade or denature, rendering them useless. These require alternative methods like sterile filtration.
Dullness of Sharp Instruments
High-grade carbon steel instruments, like scalpels and some scissors, lose their sharp edges in an autoclave. The high heat affects the temper of the metal, causing it to become dull and less effective.
Ineffectiveness with Oils and Powders
Autoclaving relies on pressurized steam to make direct contact with every surface. Oily or fatty substances are hydrophobic (repel water) and prevent steam penetration, making sterilization incomplete. Likewise, dense powders cannot be effectively sterilized by steam.
Understanding the Process Limitations
Beyond simple material damage, the autoclaving process itself has inherent limitations that can lead to sterilization failure if not properly understood.
The Problem of Incomplete Steam Penetration
For sterilization to be successful, steam must reach every surface. Basic autoclaves (Class N) lack a vacuum cycle to remove air before introducing steam.
This makes them unsuitable for sterilizing textiles, hollow instruments, or items sealed in pouches, as trapped air pockets will prevent proper steam contact and result in a failed cycle. More advanced Class B autoclaves with pre-vacuum cycles are required for these loads.
No Removal of Chemical Contaminants
It is critical to distinguish between sterilization and decontamination. An autoclave kills biological organisms like bacteria and viruses, but it does not remove or neutralize chemical contamination. Any chemical residue on an instrument will remain after the cycle is complete.
Operational and Physical Hazards
Operating an autoclave involves managing significant energy and presents several physical risks. These are not disadvantages of the sterilization outcome but are critical risks of the process itself.
High Heat, Steam, and Pressure Risks
Autoclaves operate at temperatures above 121°C (250°F) and pressures over 20 psi. The primary hazards are severe burns from contact with hot chamber walls or materials, steam burns during door opening, and scalds from superheated liquids that can boil over explosively. In rare cases of malfunction, the pressurized chamber can burst.
Handling-Related Injuries
Operators face biological hazards when loading infectious materials before they are sterilized. After the cycle, mishandling of sharps that were not properly contained can lead to cuts and puncture wounds.
General Workplace Dangers
Other associated hazards include the risk of electric shock from faulty wiring, especially in a wet environment, and slips or trips from water spilled during loading or unloading.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct sterilization method requires matching the process to the material and the objective.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-resistant glassware, steel surgical tools, or microbiological media: Autoclaving is the ideal, most reliable, and cost-effective method.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive plastics, sharp carbon-steel instruments, or electronics: You must use a low-temperature alternative like ethylene oxide (EtO) gas, hydrogen peroxide plasma, or irradiation.
- If your primary focus is processing oily substances, powders, or heat-labile solutions like vaccines: Autoclaving is unsuitable; consider dry heat sterilization for oils and powders, and sterile filtration for sensitive liquids.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing porous loads or items in pouches: You must use a Class B autoclave with a pre-vacuum cycle, as a simpler Class N unit will not guarantee sterility.
Ultimately, understanding an autoclave's limitations is the first step toward ensuring both effective sterilization and the integrity of your materials.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Limitations |
|---|---|
| Material Incompatibility | Damages heat-sensitive plastics & electronics; dulls sharp instruments; ineffective on oils & powders. |
| Process Limitations | Incomplete steam penetration in basic models; does not remove chemical contaminants. |
| Operational Hazards | Risk of severe burns from high heat/steam; potential for pressure-related incidents; biological & physical handling risks. |
Unsure if autoclaving is right for your lab equipment?
Choosing the wrong sterilization method can lead to damaged equipment, compromised results, and safety risks. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables for your specific sterilization needs. Our experts can help you select the optimal solution—whether it's a specific class of autoclave or an alternative low-temperature sterilization system—to ensure the integrity of your materials and the safety of your team.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and protect your laboratory investments.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How much time is required for autoclave sterilization of instruments? Understand the Full Cycle for Safety
- What is the pressure of autoclave at 121 C? The Key to Effective Steam Sterilization
- What equipment is used for laboratory sterilization? A Guide to Autoclaves, Ovens & Filtration
- What are the settings for autoclave sterilization? Ensure Reliable Sterility with Proper Parameters
- Why is the standard autoclave temperature set to 121? The Science of Effective Sterilization



















