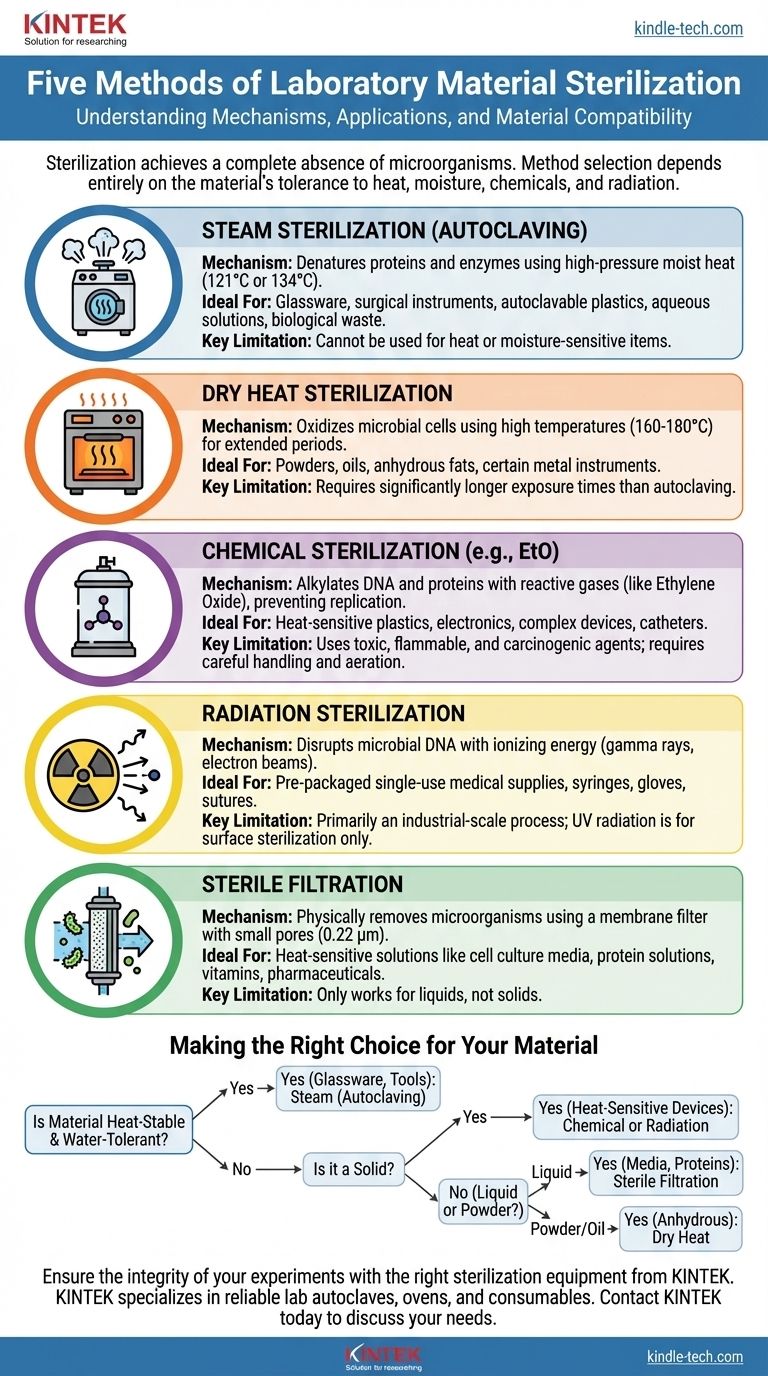
In laboratory settings, sterilization is not a one-size-fits-all process. The five principal methods used to achieve sterility are steam sterilization (autoclaving), dry heat, chemical sterilization (gas or liquid), radiation, and sterile filtration. Each method works through a different mechanism, making it suitable for a specific set of materials and applications.
The core challenge of sterilization is not simply killing microbes, but doing so without destroying the item being sterilized. Your choice of method is therefore dictated entirely by the material's tolerance to heat, moisture, chemicals, and radiation.

Understanding the Goal: True Sterility
Before comparing methods, it's crucial to define the objective. Sterilization is an absolute term.
What "Sterile" Actually Means
Sterility is the complete absence of all viable microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and even highly resistant bacterial spores. This is a much higher standard than disinfection, which only reduces the number of pathogenic organisms to a safe level.
A Process of Elimination, Not Instant Death
Sterilization is a process based on probability. The goal is to reduce the microbial population to a point where the probability of a single viable organism surviving is exceptionally low, typically less than one in a million. This is known as the Sterility Assurance Level (SAL).
A Breakdown of the Five Sterilization Methods
Each method leverages a different mechanism to inactivate or remove microorganisms. Your task is to match the mechanism to the material.
Method 1: Steam Sterilization (Autoclaving)
This is the most common and reliable method used in labs. An autoclave works like a sophisticated pressure cooker, using high-pressure steam to reach temperatures (typically 121°C or 134°C) that are not achievable with boiling water alone.
The combination of extreme heat and moisture rapidly denatures essential proteins and enzymes, killing all microbial life. It is the gold standard for sterilizing glassware, surgical instruments, autoclavable plastics, aqueous solutions, and biological waste.
Method 2: Dry Heat Sterilization
Dry heat sterilization uses a hot air oven to expose materials to very high temperatures (typically 160-180°C) for a much longer period than an autoclave.
Because there is no moisture to aid in heat penetration, the killing mechanism is primarily oxidation, which is a slower process. Dry heat is ideal for materials that cannot tolerate moisture, such as powders, oils, and certain types of glassware or metal instruments that might be damaged by steam.
Method 3: Chemical Sterilization
This method is essential for items that cannot withstand high temperatures. It uses reactive gases or chemical vapors to inactivate microbes.
The most common agent is Ethylene Oxide (EtO) gas. This gas is a powerful alkylating agent that disrupts the DNA and proteins of microorganisms, preventing them from replicating. It is used for heat-sensitive items like plastic petri dishes, catheters, and complex electronic devices.
Method 4: Radiation Sterilization
Radiation sterilization uses energy to disrupt the fundamental building blocks of microbial life. There are two main types.
Ionizing radiation (gamma rays or electron beams) uses high energy to break chemical bonds, directly damaging microbial DNA and other cellular components. This is a highly effective, industrial-scale process used for pre-packaged, single-use medical supplies like syringes, gloves, and sutures.
Non-ionizing radiation (Ultraviolet light, or UV-C) has lower energy but is effective for surface and air sterilization, such as inside a biological safety cabinet. It works by causing damage to microbial DNA but has very poor penetration power.
Method 5: Sterile Filtration
Unlike the other four methods, filtration does not kill microorganisms; it physically removes them.
Liquids are passed through a membrane filter with a pore size small enough (typically 0.22 micrometers) to trap bacteria. This is the only method suitable for sterilizing heat-labile solutions, such as cell culture media, protein solutions, vitamins, and pharmaceuticals, whose chemical composition would be destroyed by heat, chemicals, or radiation.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Choosing a method involves balancing efficacy, material compatibility, and safety.
The Primary Factor: Material Stability
The first and most important question is whether your material is thermolabile (heat-sensitive) or thermostable (heat-stable). If it can withstand heat and moisture, autoclaving is almost always the preferred choice. If not, you must turn to "cold" methods like chemicals, radiation, or filtration.
Penetration vs. Surface Treatment
Steam, EtO gas, and ionizing radiation are excellent because they can penetrate deep into materials and packaging. In contrast, UV radiation is a surface-level treatment only and is easily blocked by glass, dirt, or shadows. Filtration only works for liquids.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Steam and dry heat are the safest and most environmentally friendly methods, using only water and electricity. Chemical sterilization with agents like EtO is highly effective but involves toxic, flammable, and carcinogenic substances that require careful handling and aeration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
Your decision should be a logical process based on the nature of your item.
- If your material is heat-stable and water-tolerant (e.g., glassware, metal tools, waste): Steam sterilization (autoclaving) is your most reliable and cost-effective method.
- If your material is a heat-sensitive solid (e.g., plastic devices, electronics): Industrial-scale chemical (EtO) or radiation sterilization are the standard choices.
- If your material is a heat-sensitive liquid (e.g., culture media, protein solution): Sterile filtration is the only method that preserves the integrity of your solution.
- If your material cannot tolerate moisture (e.g., powders, oils, anhydrous fats): Dry heat sterilization is the appropriate choice.
- If you are treating a surface or the air in a confined space (e.g., a biosafety cabinet): UV radiation serves as an effective, but supplemental, decontamination method.
Matching the sterilization method to the material is the foundation of safe, effective, and reproducible scientific work.
Summary Table:
| Method | Mechanism | Ideal For | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steam (Autoclaving) | Denatures proteins with moist heat | Glassware, instruments, waste | Cannot be used for heat/moisture-sensitive items |
| Dry Heat | Oxidizes cells with high temperatures | Powders, oils, anhydrous materials | Requires longer exposure times |
| Chemical (e.g., EtO) | Alkylates DNA/proteins with gas | Heat-sensitive plastics, electronics | Uses toxic/carcinogenic agents |
| Radiation | Damages DNA with ionizing energy | Pre-packaged single-use items | Industrial-scale process; UV is surface-only |
| Sterile Filtration | Physically removes bacteria from liquids | Heat-sensitive solutions (media, proteins) | Only works for liquids, not solids |
Ensure the integrity of your experiments with the right sterilization equipment from KINTEK.
Choosing the correct sterilization method is critical for laboratory safety and reproducibility. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables, including autoclaves for steam sterilization and ovens for dry heat processes. We understand the unique needs of research and quality control labs.
Let our experts help you select the perfect equipment to protect your sensitive materials and ensure true sterility.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory's sterilization needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- Why is a laboratory high-pressure autoclave sterilizer necessary? Ensure Accuracy in Antibacterial Research
- What is the function of laboratory autoclaves in SCWR research? Predict Material Compatibility and Corrosion Kinetics
- What extreme conditions does a laboratory autoclave simulate? Testing Wear Resistance of Nuclear Fuel Cladding
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment



















