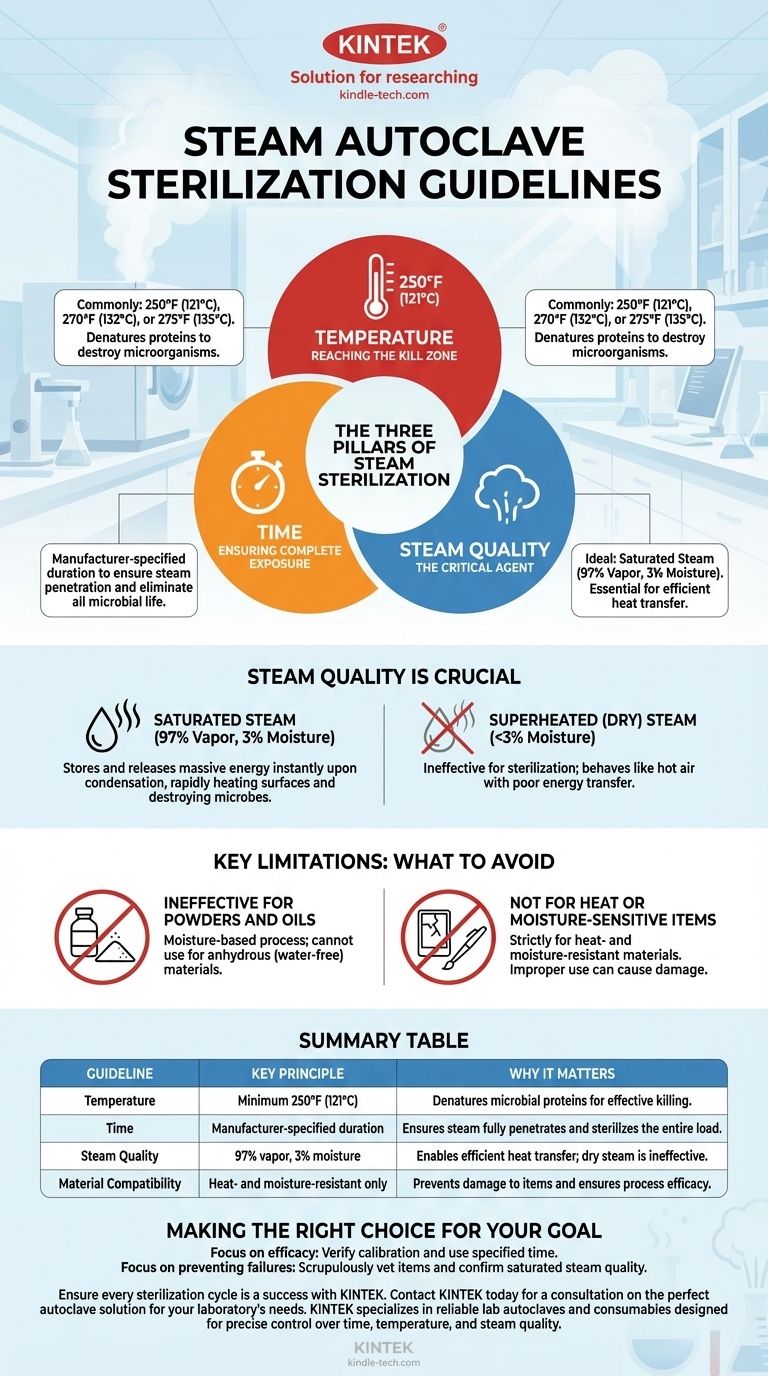
The fundamental guidelines for steam autoclave sterilization center on achieving the correct balance of three critical factors: time, temperature, and steam quality. Items must be exposed to a minimum temperature of 250°F (121°C) for a specific duration, using steam that has the proper moisture content to effectively transfer heat and destroy all microorganisms.
The core principle is not just about applying heat, but about using the unique energy of high-quality saturated steam. Sterilization fails when any one of the three pillars—time, temperature, or steam quality—is compromised.
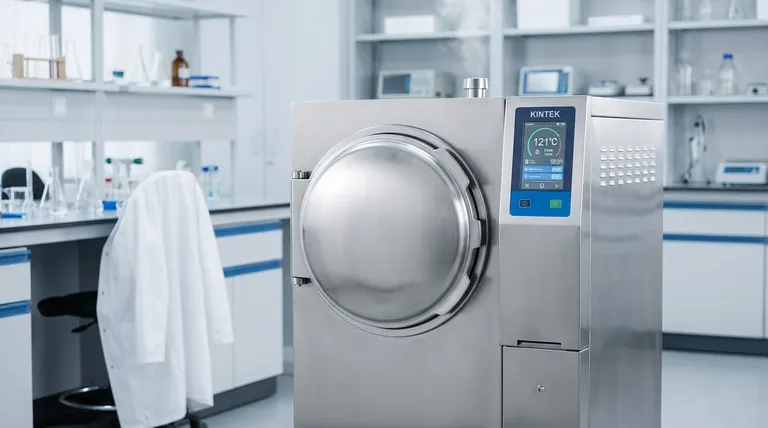

The Three Pillars of Steam Sterilization
Successful steam sterilization is a precise process. Understanding each component is essential for ensuring that items are not just treated, but are rendered completely sterile.
Temperature: Reaching the Kill Zone
The temperatures used in steam autoclaves are well above the boiling point of water and are designed to denature the proteins within bacteria, viruses, and spores.
Commonly recommended temperatures for steam sterilization are 250°F (121°C), 270°F (132°C), or 275°F (135°C). The specific temperature required will depend on the item being sterilized and the cycle chosen.
Time: Ensuring Complete Exposure
Reaching the target temperature is not enough; it must be held for a minimum duration to guarantee that the steam fully penetrates the load and eliminates all microbial life.
The necessary exposure time is determined by the manufacturer of the sterilizer and the nature of the items. Following these recommendations precisely is critical for a successful cycle.
Steam Quality: The Critical Agent
Steam is the vehicle that transfers lethal energy to the microorganisms. Its quality is arguably the most critical and nuanced factor in the entire process.
The ideal composition for sterilization is saturated steam, consisting of approximately 97% steam (vapor) and 3% moisture (liquid water). This small amount of moisture is essential for efficient heat transfer.
Steam is far more effective than hot air because it contains a massive amount of stored energy. This energy is released instantly when the steam condenses on a cooler surface, rapidly heating it and destroying microbes.
Key Limitations and What to Avoid
An autoclave is a powerful tool, but it is not suitable for all materials. Using it improperly can lead to sterilization failure or damage to the items.
Ineffective for Powders and Oils
Steam sterilization is fundamentally a moisture-based process. It cannot be used for oils, powders, or any other anhydrous (water-free) material, as the steam cannot condense and transfer its energy effectively.
Not for Heat or Moisture-Sensitive Items
Any item that can be damaged by high temperatures or moisture should not be autoclaved. This process is strictly for heat- and moisture-resistant materials.
The Danger of Superheated (Dry) Steam
If the steam has less than 3% moisture, it is considered superheated or "dry" steam. This type of steam behaves more like hot air and is very poor at transferring energy, rendering it ineffective for sterilization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure every cycle is effective, apply these guidelines based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is ensuring maximum efficacy: Verify that your autoclave is calibrated to reach the correct temperature and that you are using the manufacturer-specified time for your specific load.
- If your primary focus is preventing sterilization failures: Scrupulously vet every item to ensure it is moisture-resistant and confirm your steam source provides high-quality saturated steam, not ineffective dry steam.
Ultimately, mastering steam sterilization is about controlling the precise interplay of time, temperature, and high-energy saturated steam.
Summary Table:
| Guideline | Key Principle | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Minimum 250°F (121°C) | Denatures microbial proteins for effective killing. |
| Time | Manufacturer-specified duration | Ensures steam fully penetrates and sterilizes the entire load. |
| Steam Quality | 97% vapor, 3% moisture (saturated steam) | Enables efficient heat transfer; dry steam is ineffective. |
| Material Compatibility | Heat- and moisture-resistant only | Prevents damage to items and ensures process efficacy. |
Ensure every sterilization cycle is a success with the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab autoclaves and consumables designed for precise control over time, temperature, and steam quality. Let our experts help you achieve guaranteed sterility and protect your critical work. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation on the perfect autoclave solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Why is a 24-hour hydrothermal treatment in an autoclave necessary for BMO nanosheets? Unlock Superior Photocatalysis
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing
- What is the necessity of using a steam autoclave for dental alloys? Ensure Pure Bacterial Adhesion Data
- How does an autoclave ensure the reliability of experimental results? Achieving a Sterile Baseline for Lab Research
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization



















