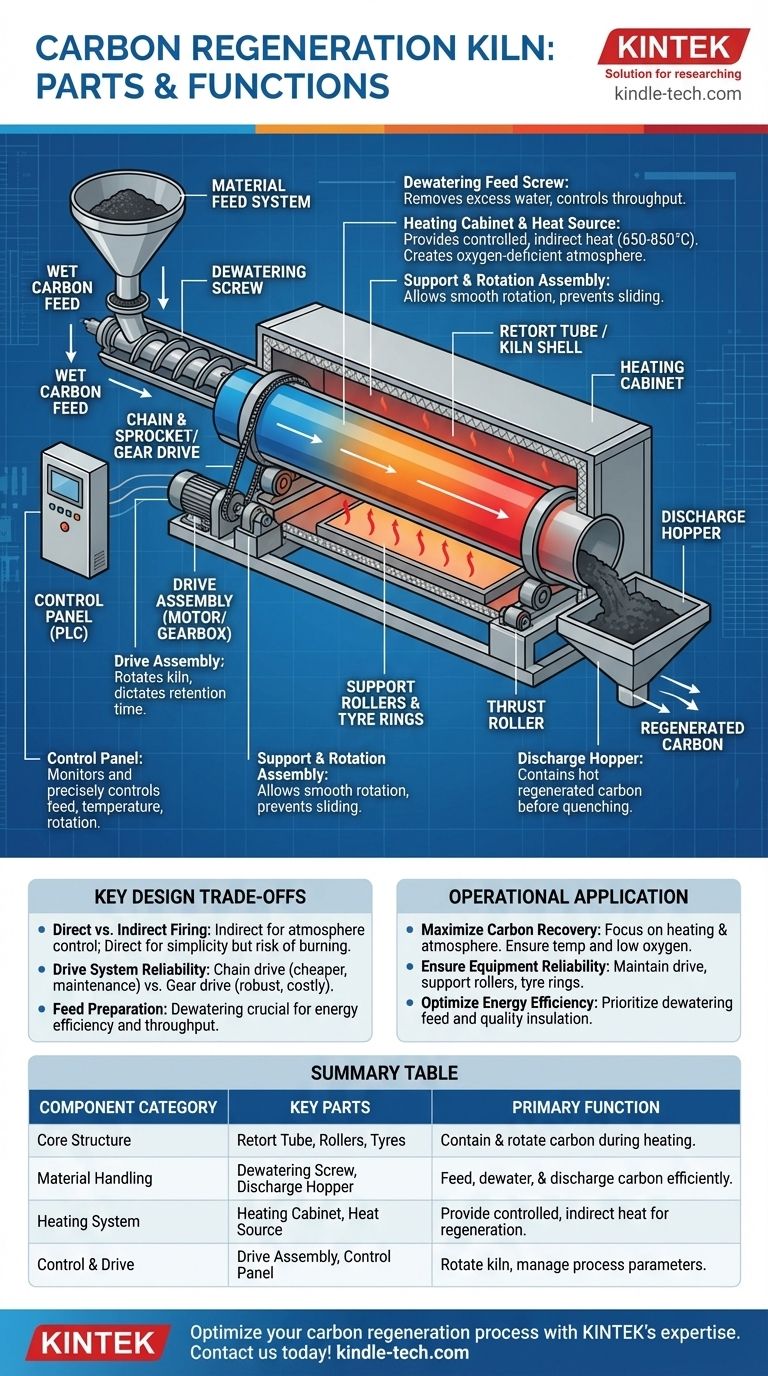
At its core, a carbon regeneration kiln is a system of integrated components designed to precisely heat activated carbon in a controlled atmosphere. The main parts include a material feed system (often a dewatering screw), a rotating central chamber (the retort tube or kiln shell), support and drive assemblies to turn the chamber, an external heating cabinet with a heat source, and a discharge hopper for the regenerated carbon.
A carbon regeneration kiln is not merely a furnace; it is a sophisticated processing machine. Each component serves a specific function in a multi-stage process designed to remove adsorbed organics without destroying the carbon's valuable porous structure.

The Core Structure: Containment and Rotation
The fundamental purpose of the kiln's structure is to contain the carbon and move it through a controlled temperature profile. This is achieved through a combination of static and rotating components.
The Retort Tube or Kiln Shell
This is the central rotating chamber that holds and transports the carbon. In many carbon kilns, this is a retort tube, meaning the heat is applied externally, protecting the carbon from direct flame contact.
Larger industrial kilns may use a kiln shell, a large steel cylinder lined with refractory (heat-resistant) material to insulate the process and protect the steel shell from high temperatures.
The Support and Rotation Assembly
This system allows the heavy retort or shell to rotate smoothly and reliably. It consists of support rollers and tyre rings (or "tires"), which are large steel rings attached to the shell that ride on the rollers.
A thrust roller is also used to prevent the kiln from sliding downhill due to its slight operational angle.
The Material Handling System: From Feed to Discharge
Moving carbon into, through, and out of the kiln efficiently is critical for consistent results and preventing energy waste.
The Feed System
Carbon is typically introduced via a dewatering feed screw. This component is vital as it removes excess water from the wet carbon before it enters the high-heat zone.
Feeding wet carbon directly into a hot kiln is extremely inefficient, as a massive amount of energy is wasted boiling off water instead of heating the carbon. The feed screw's speed is often variable, allowing operators to control the throughput, or the amount of carbon processed per hour.
The Discharge Hopper
After passing through the kiln, the hot, regenerated carbon exits into a discharge hopper. This component safely contains the product before it is typically quenched in water and returned to the process circuit.
The Heating and Atmosphere System: The Heart of Regeneration
This is where the actual reactivation occurs. The system must deliver precise heat and control the atmosphere inside the retort to vaporize adsorbed organics without burning the carbon itself.
The Heating Cabinet and Heat Source
The retort tube is enclosed within an insulated heating cabinet. This cabinet contains the heat source, which can be a series of gas burners or electric heating elements.
This indirect heating design is crucial. It allows for a controlled, oxygen-deficient atmosphere inside the retort, which prevents the carbon from combusting at the high temperatures required for regeneration (typically 650-850°C).
Atmosphere Control
The goal is to create an atmosphere rich in steam and low in oxygen. As the dewatered carbon enters, the remaining moisture turns to steam. This steam helps in the volatilization and removal of adsorbed organic compounds from the carbon's pores.
The Drive and Control Systems: Ensuring Precision
These systems are the "brain and muscle" of the kiln, ensuring it operates according to the precise parameters needed for effective regeneration.
The Drive Assembly
This is the motor and gearbox that rotates the kiln shell. Common types include a chain and sprocket drive or a more robust gear drive.
The rotation speed is critical; it dictates the retention time of the carbon inside the kiln, ensuring it is heated for the correct duration. Many kilns include a main and back-up drive unit for redundancy.
The Control Panel
Modern kilns feature a fully integrated control panel, often a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller). This allows operators to monitor and precisely control all critical variables, including feed rate, kiln temperature zones, and rotation speed.
Understanding the Key Design Trade-offs
Choosing or operating a kiln involves balancing performance, cost, and reliability. The design of these components reflects important trade-offs.
Direct vs. Indirect Firing
Indirectly fired kilns (with a retort tube inside a heating cabinet) offer superior atmosphere control, protecting the carbon from combustion. This is standard for carbon regeneration. Direct-fired kilns, where a flame acts inside the shell, are simpler but risk burning the carbon, leading to significant product loss.
Drive System Reliability
A simple chain and sprocket drive may be cheaper initially but can require more maintenance and is a common point of failure. A direct-mount gear drive assembly is more robust and reliable but comes at a higher capital cost.
Feed Preparation
Skimping on the dewatering feed system is a false economy. While it adds complexity, its ability to reduce the water content entering the kiln has a massive positive impact on energy efficiency and throughput, directly affecting operational costs.
How This Applies to Your Operation
Understanding how these parts function together allows you to focus on the variables that matter most for your specific goals.
- If your primary focus is maximizing carbon recovery: Pay close attention to the heating system and atmosphere control. Ensure temperatures are high enough to clean the carbon but that the oxygen-deficient atmosphere prevents it from burning.
- If your primary focus is ensuring equipment reliability: The drive assembly, support rollers, and tyre rings are your critical components. A robust preventative maintenance schedule for these mechanical parts is essential to avoid costly downtime.
- If your primary focus is optimizing energy efficiency: The dewatering feed screw and the quality of the heating cabinet's insulation are paramount. Every drop of water removed before the kiln and every degree of heat kept within the system directly reduces your energy consumption.
By viewing the kiln as an interconnected system, you can diagnose problems and optimize its performance far more effectively.
Summary Table:
| Component Category | Key Parts | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Core Structure | Retort Tube / Kiln Shell, Support Rollers, Tyre Rings | Contain and rotate carbon through the heating process |
| Material Handling | Dewatering Feed Screw, Discharge Hopper | Feed, dewater, and discharge carbon efficiently |
| Heating System | Heating Cabinet, Heat Source (burners/elements) | Provide controlled, indirect heat to regenerate carbon |
| Control & Drive | Drive Assembly (motor/gearbox), PLC Control Panel | Rotate the kiln and precisely manage temperature, speed, and feed rate |
Optimize your carbon regeneration process with KINTEK's expertise. Our specialized lab equipment and consumables are designed to meet the precise needs of carbon regeneration, ensuring maximum efficiency, reliability, and carbon recovery. Whether you're focused on energy savings, equipment durability, or process control, KINTEK has the solutions to support your laboratory's success. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your operation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do you carbonize charcoal? Master the 3-Step Pyrolysis Process for High-Purity Carbon
- What temperature is a carbon regeneration kiln? Master the 650°C-800°C Range for Optimal Results
- What is the temperature of a carbon regeneration kiln? Mastering the 750-800°C Reactivation Process
- What are the principles of a rotary kiln? Master the Mechanics of High-Temperature Processing
- How to regenerate activated carbon? Master the 3-Stage Thermal Process for Cost Savings



















