In short, an autoclave is a highly effective and economical sterilization tool, but its reliance on high-pressure steam makes it unsuitable for materials sensitive to heat and moisture. Its primary advantages are its speed, thorough penetration, and low operating costs, while its main disadvantages are the potential for moisture retention and the risk of damaging non-compatible items like carbon steel or certain plastics.
The core decision of whether to use an autoclave comes down to a simple trade-off: you gain unparalleled sterilization power and efficiency in exchange for strict limitations on the types of materials you can process.

How an Autoclave Achieves Sterilization
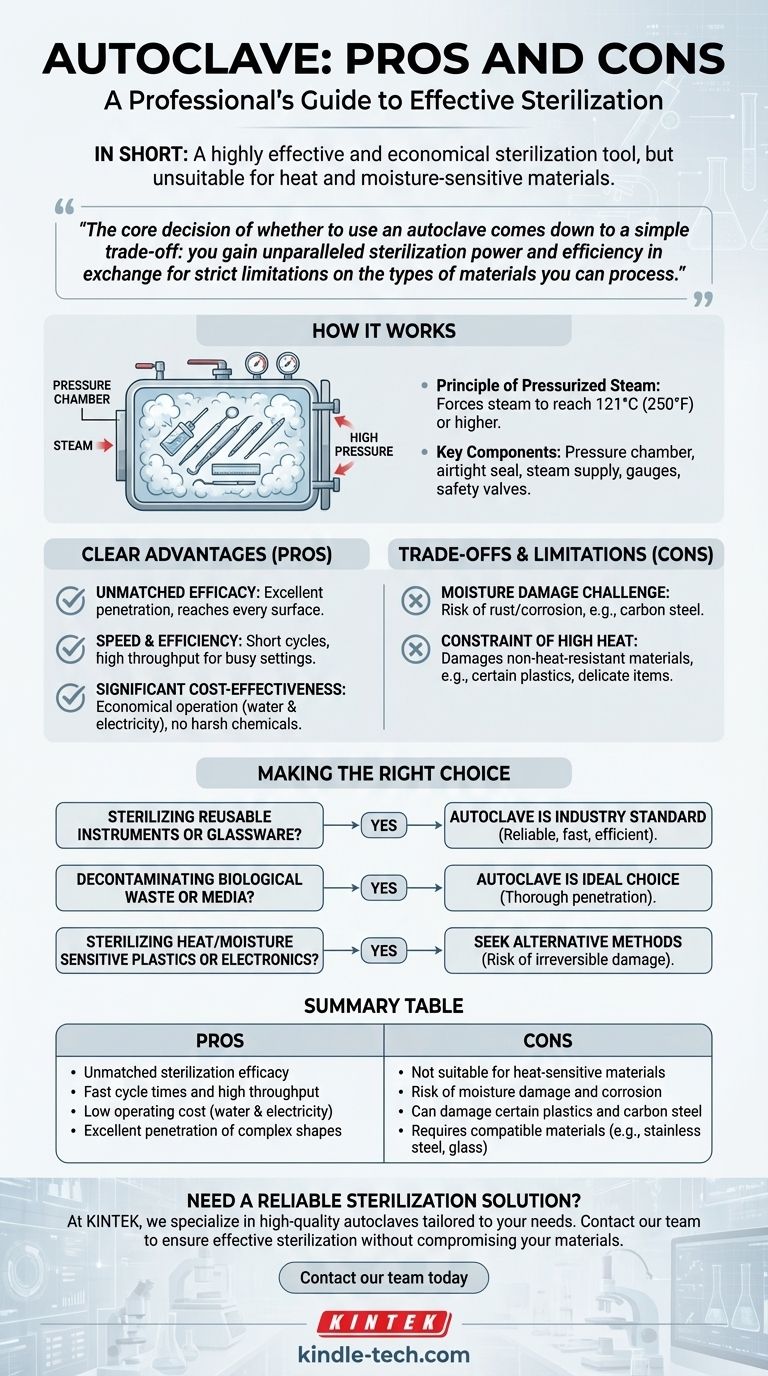
An autoclave is essentially a highly specialized pressure chamber. It doesn't just use heat; it uses high-pressure steam to sterilize equipment and supplies, making it a cornerstone technology in medicine, research, and various industries.
The Principle of Pressurized Steam
The key to an autoclave's effectiveness is its ability to create an environment where water boils at a temperature much higher than its normal 100°C (212°F). By increasing the pressure inside its chamber, the autoclave forces steam to reach temperatures of 121°C (250°F) or higher.
This superheated, pressurized steam is incredibly effective at penetrating all surfaces of an object, regardless of its shape. The combination of intense heat and moisture rapidly denatures the essential proteins and enzymes within microorganisms, killing them completely.
Key Components and Function
Several components work together to create this sterilizing environment. The central element is the pressure chamber, a robust vessel with an inner chamber and an outer jacket. A secure lid or door creates an airtight seal.
An electric generator or steam supply heats water to create steam, while pressure gauges and safety valves ensure the system operates within safe limits. This controlled system guarantees that the required temperature and pressure are maintained for the necessary duration to achieve sterilization.
The Clear Advantages of Autoclaving
The widespread use of autoclaves is due to a powerful combination of efficacy, speed, and cost-effectiveness.
Unmatched Sterilization Efficacy
Pressurized steam provides excellent penetration. It reliably reaches every surface of an instrument, including the interiors of hollow objects and the threads of screws, which can be challenging for chemical or dry-heat methods.
Speed and Efficiency
Compared to other methods, an autoclave sterilization cycle is relatively short. This allows for a high throughput of instruments and media, which is critical in busy hospital, laboratory, and veterinary settings.
Significant Cost-Effectiveness
Autoclaves are economical to operate. They primarily consume water and electricity, eliminating the need for expensive and often hazardous chemical sterilants or other disposables.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Despite its power, an autoclave is not a universal solution. Its operating principle introduces specific limitations that are critical to understand.
The Challenge of Moisture Damage
The process inherently involves steam, which condenses back into water. This moisture retention can be a significant problem for certain materials.
Carbon steel instruments, for example, are highly susceptible to rust and corrosion when exposed to the moisture in an autoclave. This makes the device unsuitable for such items.
The Constraint of High Heat
The high temperatures required for sterilization will damage any material that is not heat-resistant. This is the most significant limitation of the technology.
Only specific items, such as stainless steel instruments, glassware, and certain types of high-temperature plastics, can safely withstand an autoclave cycle. Attempting to sterilize incompatible materials will lead to melting, warping, or complete destruction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the decision to use an autoclave depends entirely on the nature of the materials you need to sterilize.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing reusable surgical instruments or laboratory glassware: The autoclave is the industry standard for its unmatched reliability, speed, and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is decontaminating biological waste or preparing culture media: An autoclave is the ideal choice due to its ability to thoroughly penetrate and neutralize all microorganisms.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive plastics, delicate electronics, or moisture-sensitive metals: You must seek alternative methods, as an autoclave will cause irreversible damage to these items.
Understanding these material compatibility rules is the key to leveraging the autoclave's power safely and effectively.
Summary Table:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Unmatched sterilization efficacy | Not suitable for heat-sensitive materials |
| Fast cycle times and high throughput | Risk of moisture damage and corrosion |
| Low operating cost (water & electricity) | Can damage certain plastics and carbon steel |
| Excellent penetration of complex shapes | Requires compatible materials (e.g., stainless steel, glass) |
Need a Reliable Sterilization Solution for Your Lab?
Choosing the right equipment is critical for safety and efficiency. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality autoclaves and lab equipment tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're processing stainless steel instruments, glassware, or media, our experts can help you find a solution that ensures effective sterilization without compromising your materials.
Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success with reliable, cost-effective sterilization equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the common categories of autoclave loads for waste decontamination? Optimize MBL Safety and Sterilization
- What are the parameters of an autoclave machine? Master Temperature, Pressure & Time for Sterility
- Why is an autoclave required for the preparation of stainless steel coupons? Ensure Accurate Antimicrobial Test Data
- What is the difference between an autoclave and a sterilizer? Understanding Sterilization Methods
- What are the three advantages of the steam autoclave? Unmatched Speed, Cost-Effectiveness & Safety
- What function does a high-pressure laboratory autoclave serve in walnut shell pretreatment? Enhance Biomass Reactivity.
- Where are autoclaves used? Ensuring Sterility from Hospitals to High-Tech Labs
- What are the different types of autoclaves in hospitals? Choose the Right Sterilization for Your Needs



















