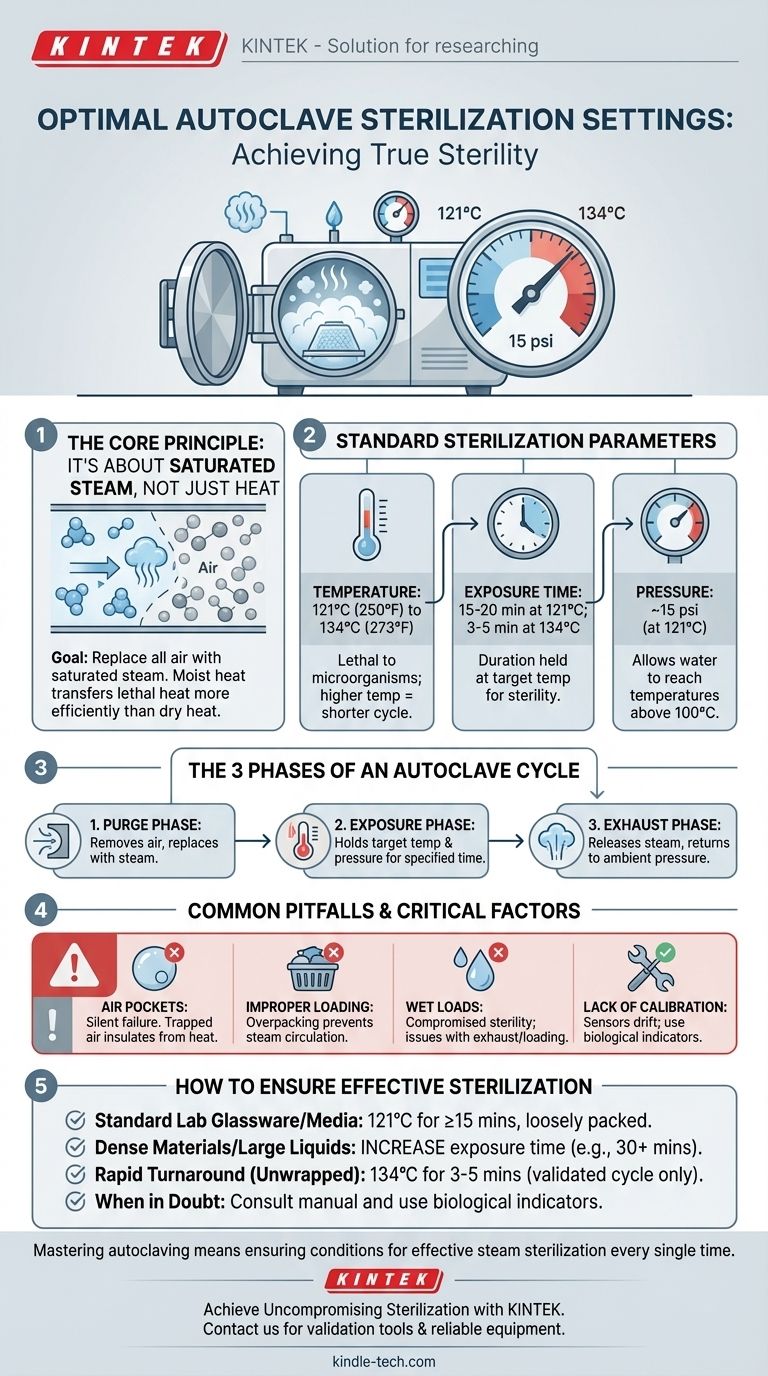
For effective autoclave sterilization, the universally recognized setting is a temperature between 121°C (250°F) and 134°C (273°F). The duration of the cycle is determined by the temperature used and the type of material being sterilized, but a common baseline is 15-20 minutes at 121°C. These numbers, however, are only part of the equation for achieving true sterility.
Achieving reliable sterilization is not about simply setting a temperature dial. The true goal is to replace all air within the chamber with saturated steam, as steam is the agent that transfers lethal heat efficiently enough to kill all microbial life. Your settings are merely the tools to achieve this state.

The Core Principle: It's About Steam, Not Just Heat
The effectiveness of an autoclave relies on a physical principle: moist heat is far more effective at denaturing proteins and killing microorganisms than dry heat. The entire process is designed to create an environment of pure, pressurized steam.
Why Saturated Steam is Essential
Dry, hot air is a poor conductor of heat. Air pockets trapped within the autoclave chamber or inside your materials act as an insulating barrier, protecting microbes from the lethal temperature.
Saturated steam, however, transfers heat energy with extreme efficiency upon contact, rapidly raising the temperature of all surfaces to the target sterilization level.
The Three Phases of an Autoclave Cycle
Every autoclave run follows a critical three-part sequence to ensure air is removed and steam can do its job.
- Purge Phase: The cycle begins by actively removing air from the chamber and replacing it with steam. This is the most critical step for preventing sterilization failure.
- Exposure (Sterilization) Phase: Once all air is purged, the chamber is held at the target temperature and pressure for the specified duration. This is when the microbial killing occurs.
- Exhaust Phase: Finally, the steam is released, and the pressure is returned to an ambient level, allowing you to safely remove the cooled, sterile items.
Standard Sterilization Parameters
While every autoclave and load is different, there are industry-standard baselines that serve as a starting point.
Standard Temperature and Time
The most common and widely tested setting is 121°C (250°F) for a minimum of 15 minutes of exposure time.
For more robust or heat-resistant items, a higher temperature of 132-134°C (270-273°F) for 3-5 minutes can be used. This is often employed for unwrapped instruments where a rapid turnaround is needed (flash sterilization).
The Role of Pressure
Pressure itself does not sterilize. Its sole purpose is to allow water to reach temperatures above its normal boiling point of 100°C.
At sea level, achieving 121°C requires a pressure of approximately 15 psi (pounds per square inch) above atmospheric pressure. This value is a consequence of the temperature, not an independent setting.
Adjusting for Load Type and Size
The standard times assume steam can instantly penetrate the entire load. This is not always the case.
Dense materials, large liquid volumes, or tightly wrapped instrument packs create a "heat transfer lag." You must increase the exposure time—not the temperature—to ensure the center of the load reaches the target temperature for the required duration.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Relying on default settings without understanding the process can lead to failed sterilization cycles. Awareness of these common failure points is crucial for reliable outcomes.
Air Pockets: The Silent Failure
The most common reason for failure is incomplete air removal during the purge phase. If air is trapped in an inverted beaker or a densely packed bag, it will not become sterile, even if the autoclave reports a successful cycle.
Improper Loading
Never overpack an autoclave chamber. Tightly packed items prevent steam from circulating and penetrating the load, creating insulated cold spots where microorganisms can survive. Always leave space between items.
Wet Loads
If your sterilized packs come out wet, it often indicates an issue with the exhaust phase or improper loading. Wetness compromises the sterile barrier of the packaging and can lead to recontamination.
Lack of Regular Calibration
An autoclave is a precision instrument. Temperature and pressure sensors can drift over time, leading to cycles that do not reach the required parameters. Regular calibration and validation using biological indicators are non-negotiable for any critical application.
How to Ensure Effective Sterilization
Your approach must adapt to your specific load and equipment. Use these principles as your guide.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing standard lab glassware or media: Start with the baseline of 121°C for at least 15 minutes, ensuring all items are loosely packed to allow for steam circulation.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing dense materials or large liquid volumes: Significantly increase the exposure time to account for slow heat penetration, often to 30 minutes or more.
- If your primary focus is rapid turnaround for unwrapped metal instruments: Use a higher temperature like 134°C for a shorter duration (3-5 minutes), but only if your autoclave has a pre-validated cycle for this.
- If you are ever in doubt: Always consult the manufacturer's manual for your specific autoclave and confirm your process with biological indicators.
Mastering autoclaving means moving beyond simply setting the dials and instead ensuring the conditions for effective steam sterilization are met every single time.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Standard Setting | Purpose & Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 121°C (250°F) to 134°C (273°F) | Lethal to microorganisms; higher temperatures allow for shorter cycles. |
| Exposure Time | 15-20 min at 121°C; 3-5 min at 134°C | Duration the load must be held at temperature for sterility. |
| Pressure | ~15 psi (at 121°C) | Allows water to reach temperatures above 100°C. |
| Critical Factor | Saturated Steam | Essential for efficient heat transfer; air removal is paramount. |
Achieve Uncompromising Sterilization in Your Laboratory
Ensuring your autoclave operates at peak performance is critical for lab safety and integrity. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including reliable autoclaves and validation tools, to meet your precise sterilization needs.
Let our experts help you select the right equipment and establish validated cycles for your specific applications—from glassware and media to dense materials and liquids.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss your laboratory's sterilization requirements and ensure reliable, effective results every time.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 16L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the size of the autoclave? Choose the Right Capacity for Your Lab
- What precautions should be taken during autoclave in laboratory? A Complete Safety Guide to Prevent Burns and Explosions
- How does an autoclave sterilize instruments supplies and equipment? A Guide to High-Pressure Steam Sterilization
- How do you sterilize glassware by autoclave? Master the 3-Step Process for Reliable Sterility
- Why is proper maintenance and cleaning of the autoclave important? Ensure Sterilization Efficacy and Safety



















