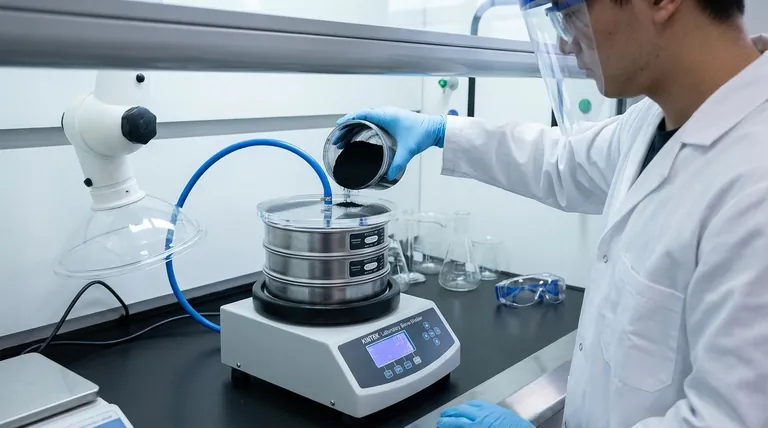
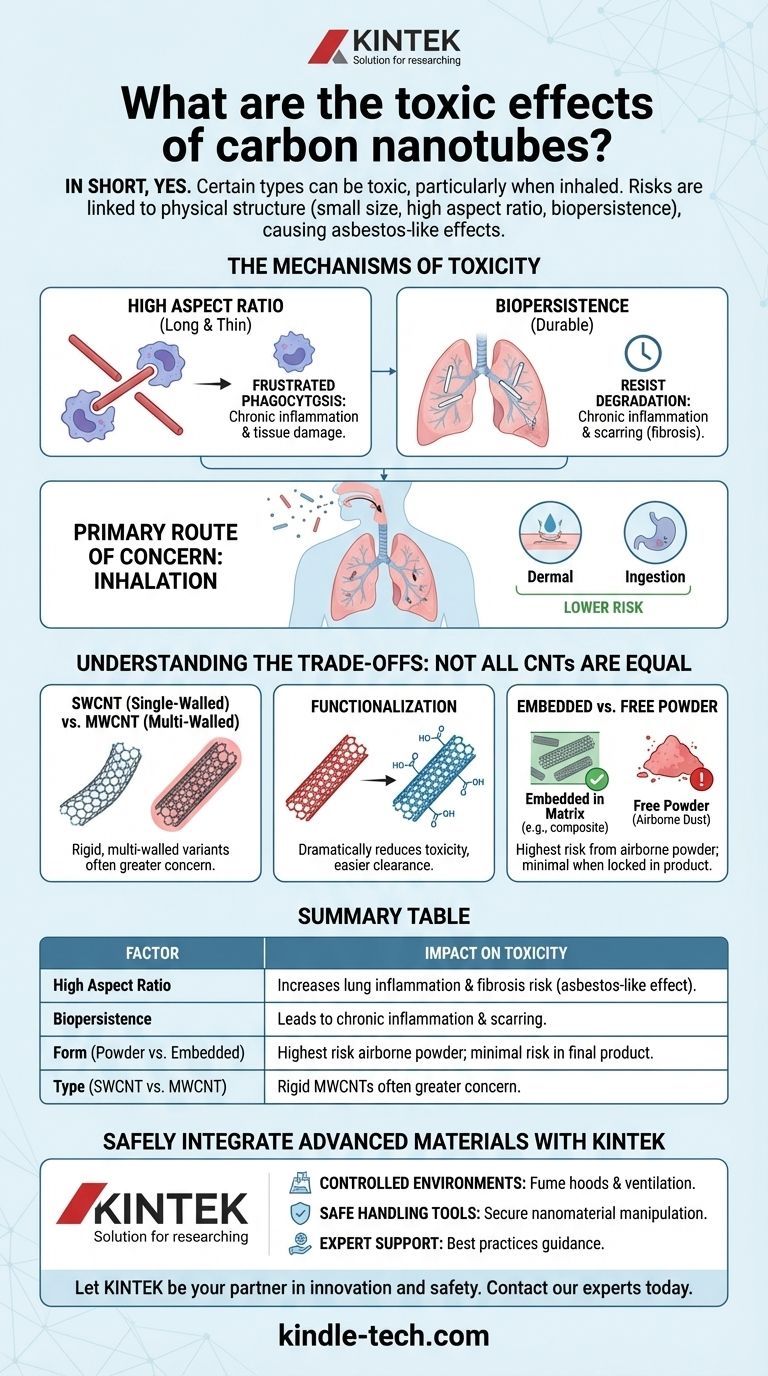
In short, yes, certain types of carbon nanotubes can be toxic, particularly when inhaled. Their potential health risks are primarily linked to their physical structure—specifically their small size, high aspect ratio (long and thin), and biopersistence—which can cause asbestos-like effects in the lungs, including inflammation, fibrosis, and an increased risk of cancer.
The toxicity of carbon nanotubes is not inherent to the carbon itself, but is a function of their physical form. The primary danger arises when long, thin, and rigid nanotubes are inhaled as airborne particles, posing a significant risk to researchers and manufacturing workers, but a minimal risk when securely embedded within a final product.

The Mechanisms of CNT Toxicity
The concern over carbon nanotube (CNT) toxicity is rooted in how their physical shape interacts with the body's natural defense mechanisms. The parallel drawn to asbestos fibers is not an accident; it is based on a similar structural mechanism of harm.
The Role of Shape and Size
The most critical factor for CNT toxicity is the high aspect ratio—being very long and thin. When these fibers are inhaled, the lung's immune cells (macrophages) attempt to engulf and clear them.
However, if a nanotube is longer than the macrophage itself (typically >15-20 µm), the cell cannot fully envelop it. This leads to a process called frustrated phagocytosis, where the macrophage repeatedly tries and fails to clear the fiber, releasing inflammatory signals and damaging enzymes that harm the surrounding lung tissue.
Biopersistence: The Inability to Degrade
Another key factor is biopersistence. Many materials we inhale can be broken down by the body's enzymes or dissolved over time.
Pristine carbon nanotubes are highly durable and can resist biological degradation. This means that once they are lodged in the lung tissue, they can remain there for long periods, causing chronic inflammation and scarring (fibrosis).
The Primary Route of Concern: Inhalation
By far, the most studied and significant route of exposure is inhalation. Airborne, individual CNT fibers or small agglomerates can travel deep into the lungs, reaching the alveolar region where gas exchange occurs.
Other exposure routes like dermal (skin) contact or ingestion are generally considered much lower risk. The skin provides a strong barrier, and ingested nanotubes typically pass through the digestive system with minimal absorption.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Not All CNTs are Equal
It is a critical mistake to treat all carbon nanotubes as having the same risk profile. The actual toxicity is highly dependent on a range of factors, turning a simple "yes/no" question into a complex risk assessment.
Single-Walled vs. Multi-Walled
Single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) are often more flexible and can contain metallic catalyst residues from their synthesis, which can add to their chemical toxicity.
Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) are typically more rigid. The long, straight, and rigid variants are the ones most often compared to asbestos fibers and are considered a greater concern for causing the physical damage described above.
The Importance of Functionalization
Raw, pristine CNTs are often modified in a process called functionalization, where chemical groups are attached to their surface.
This process can dramatically reduce toxicity. Functionalization can make CNTs more water-soluble, less likely to agglomerate, and easier for the body to clear, thereby mitigating the primary mechanisms of harm.
Embedded vs. Free Powder
The context of exposure is paramount. The highest risk is to workers in research or manufacturing who might handle raw, dry CNT powders, which can easily become airborne.
In contrast, the risk to an end-user of a product where CNTs are embedded within a polymer matrix (like a carbon fiber bicycle frame or a piece of electronic equipment) is negligible. The nanotubes are locked in place and not available for inhalation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating the risk of CNTs requires you to consider the specific material you are using and its application throughout the product lifecycle.
- If your primary focus is worker safety in R&D or manufacturing: Prioritize engineering controls like fume hoods and ventilation, mandate personal protective equipment (PPE) like respirators, and whenever possible, source CNTs in a safer form, such as a liquid dispersion or a polymer masterbatch, to prevent airborne dust.
- If your primary focus is material selection for a composite: Select CNTs that are functionalized to reduce toxicity and ensure they are well-dispersed and locked within the material matrix. The primary risk is in the manufacturing phase, not the final product.
- If your primary focus is environmental impact: Consider the entire lifecycle. While CNTs might have a lower production footprint than some alternatives, proper disposal and understanding their long-term fate in the environment are necessary for a complete picture.
Ultimately, managing the risk of carbon nanotubes is about controlling exposure and choosing the right form of the material for the job.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Toxicity |
|---|---|
| High Aspect Ratio (Long & Thin) | Increases risk of lung inflammation and fibrosis (asbestos-like effect). |
| Biopersistence (Durability in Body) | Leads to chronic inflammation and scarring as fibers are not easily broken down. |
| Form (Powder vs. Embedded) | Highest risk from airborne powder; minimal risk when locked in a final product. |
| Type (SWCNT vs. MWCNT) | Rigid, multi-walled nanotubes (MWCNTs) are often of greater concern. |
Safely Integrate Advanced Materials into Your Workflow
Navigating the handling and application of materials like carbon nanotubes requires the right equipment and expertise. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to the unique needs of research and manufacturing laboratories.
We help you mitigate risk and enhance safety by providing:
- Controlled Environments: Fume hoods and ventilation systems to manage airborne particles.
- Safe Handling Tools: Equipment designed for the secure manipulation of nanomaterials.
- Expert Support: Guidance on best practices for material handling and storage.
Let KINTEK be your partner in innovation and safety. Whether you are developing new composites or conducting cutting-edge research, we have the solutions to support your goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and ensure a safe, productive working environment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Small Lab Rubber Calendering Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a sputtering target? The Key to High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- Is deposition a physical process? Understand the Key Differences Between PVD and CVD
- What is the effect of deposition rate on thin film? Control Microstructure for Better Performance
- Why are carbon nanotubes good for electronics? Unlocking Next-Generation Speed and Efficiency
- What are carbon nanotubes advantages and disadvantages? Balancing Performance and Practicality
- How do sputtering targets work? The Foundation of High-Performance Thin Film Coatings
- What is the difference between Moissanite and CVD diamond? A Guide to Choosing Your Perfect Gemstone
- What are the advantages of thin film technology? Achieve Breakthroughs in Electronics, Energy, and More



















