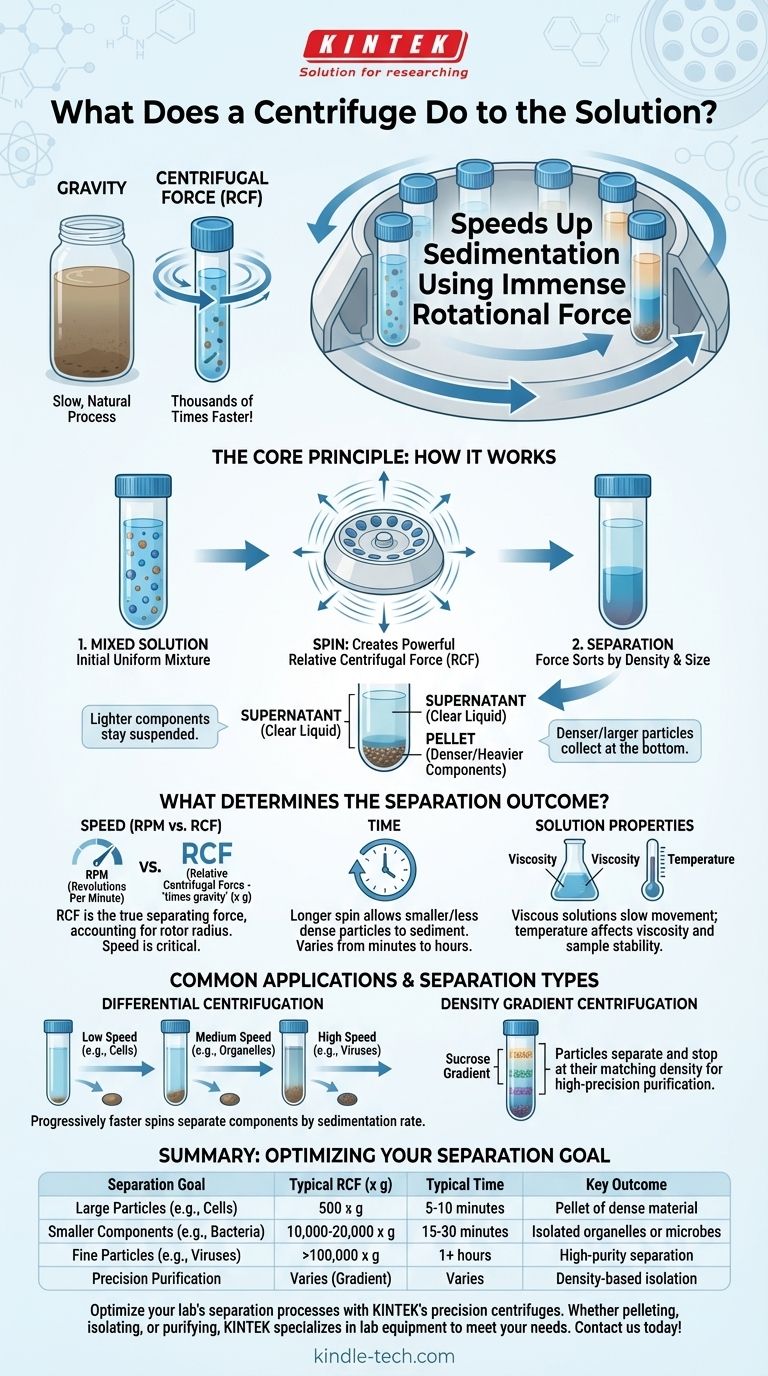
In essence, a centrifuge separates components within a solution based on their physical properties. It uses immense rotational force to accelerate the natural process of sedimentation, forcing denser, larger, or heavier particles to collect at the bottom of the container while leaving lighter components suspended in the liquid above.
A centrifuge is an instrument that dramatically speeds up gravity. It spins samples at high velocity to generate a powerful centrifugal force, which sorts the mixed particles in a solution by their density, size, and shape.

The Core Principle: How Centrifugation Works
To understand what a centrifuge does, we must first understand the force it creates. This process is an enhancement of a natural phenomenon we see every day.
From Gravity to Centrifugal Force
Imagine letting a jar of muddy water sit undisturbed. Over time, the heavier sand and silt will settle to the bottom due to gravity, leaving clearer water on top. A centrifuge does the same thing, but thousands of times faster.
By spinning samples at high speeds, it creates a powerful outward force known as Relative Centrifugal Force (RCF). This force is much stronger than Earth's gravity and acts on every particle within the solution.
The Deciding Factors: Density and Size
Not all particles react to this force equally. Denser and larger particles experience a greater effect from the RCF and move outward (toward the bottom of the tube) more quickly.
This difference in movement, or sedimentation rate, is the key to separation. Heavier components like whole cells will separate much faster and at lower speeds than smaller components like proteins or viruses.
The Resulting Separation: Supernatant and Pellet
After centrifugation, the solution is physically separated into two distinct parts.
The solid, compacted material that collects at the bottom of the tube is called the pellet.
The remaining clear liquid on top is called the supernatant. These two components can then be easily separated by carefully pouring off (decanting) the supernatant.
What Determines the Separation Outcome?
Achieving the desired separation isn't just about turning the machine on. The outcome is carefully controlled by several key parameters that you must understand and set correctly.
The Role of Speed (RPM vs. RCF)
Speed is the most critical factor. It's often expressed in Revolutions Per Minute (RPM), which simply describes how fast the motor is spinning the rotor.
However, the more scientifically accurate measure is Relative Centrifugal Force (RCF), often measured in "times gravity" (x g). RCF accounts for the radius of the rotor, giving you the true separating force being applied to your sample. Two different centrifuges running at the same RPM can produce very different RCFs.
The Importance of Time
The duration of the centrifugation run is also crucial. A longer spin time allows smaller or less dense particles more time to sediment and form a compact pellet.
Separating large particles like yeast cells might only take a few minutes, while separating tiny extracellular vesicles could require several hours at much higher forces.
The Impact of the Solution Itself
The properties of the liquid, or solvent, also play a role. A highly viscous solution, like one containing glycerol, will slow down particle movement.
Temperature can also be a factor, as it affects the viscosity of the solution and the stability of biological samples. This is why many high-speed centrifuges are refrigerated.
Common Applications and Types of Separation
The basic principle of pelleting is simple, but centrifugation can be used for far more sophisticated separations, making it a cornerstone of modern biology and chemistry.
Differential Centrifugation
This is the most common technique. A mixture is subjected to progressively faster centrifugation speeds to separate components based on their different sedimentation rates.
A low-speed spin might first pellet whole cells. The supernatant is then removed and spun at a much higher speed to pellet smaller components, like mitochondria or other organelles.
Density Gradient Centrifugation
This advanced method is used for purification. The sample is layered on top of a solution with a density gradient (e.g., a sucrose or cesium chloride gradient).
During centrifugation, particles travel through the gradient and stop when they reach a point equal to their own density. This allows for extremely precise separation of particles with very similar sizes but different densities.
Everyday Examples
You encounter centrifugation in many contexts outside of a research lab. It's used to separate red blood cells from plasma in blood banks, cream from milk in the dairy industry, and solids from liquids in wastewater treatment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The parameters you choose depend entirely on what you want to achieve with your solution.
- If your primary focus is separating large, dense particles (like cells): A short spin (5-10 minutes) at a low RCF (e.g., 500 x g) is typically sufficient.
- If your primary focus is collecting smaller components (like organelles or bacteria): You will need a longer spin (15-30 minutes) at a moderate RCF (e.g., 10,000-20,000 x g).
- If your primary focus is isolating very small particles (like viruses or proteins): This requires an ultracentrifuge capable of extremely high RCFs (>100,000 x g) for runs lasting one to several hours.
- If your primary focus is purifying a specific molecule with high precision: Density gradient centrifugation is the most appropriate and powerful technique.
By applying force far greater than gravity, a centrifuge transforms a uniform solution into distinct, separable layers, making it an indispensable tool for analysis and purification.
Summary Table:
| Separation Goal | Typical RCF (x g) | Typical Time | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large Particles (e.g., Cells) | 500 x g | 5-10 minutes | Pellet of dense material |
| Smaller Components (e.g., Bacteria) | 10,000-20,000 x g | 15-30 minutes | Isolated organelles or microbes |
| Fine Particles (e.g., Viruses) | >100,000 x g | 1+ hours | High-purity separation |
| Precision Purification | Varies (Gradient) | Varies | Density-based isolation |
Optimize your lab's separation processes with KINTEK's precision centrifuges. Whether you're pelleting cells, isolating organelles, or purifying biomolecules, KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables to meet your laboratory needs. Contact us today to find the right centrifuge for your application and enhance your workflow efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the speed of a sieving machine? Optimize Vibration for Maximum Efficiency and Accuracy
- What are the different types of sieving machines? Choose the Right Motion for Your Material
- What is the principle of sieving machine? Achieve Accurate Particle Size Separation
- What is the use of vibrating sieve machine? Achieve Precise Particle Size Analysis for Your Lab
- What is powder sieving? A Guide to Accurate Particle Size Separation



















