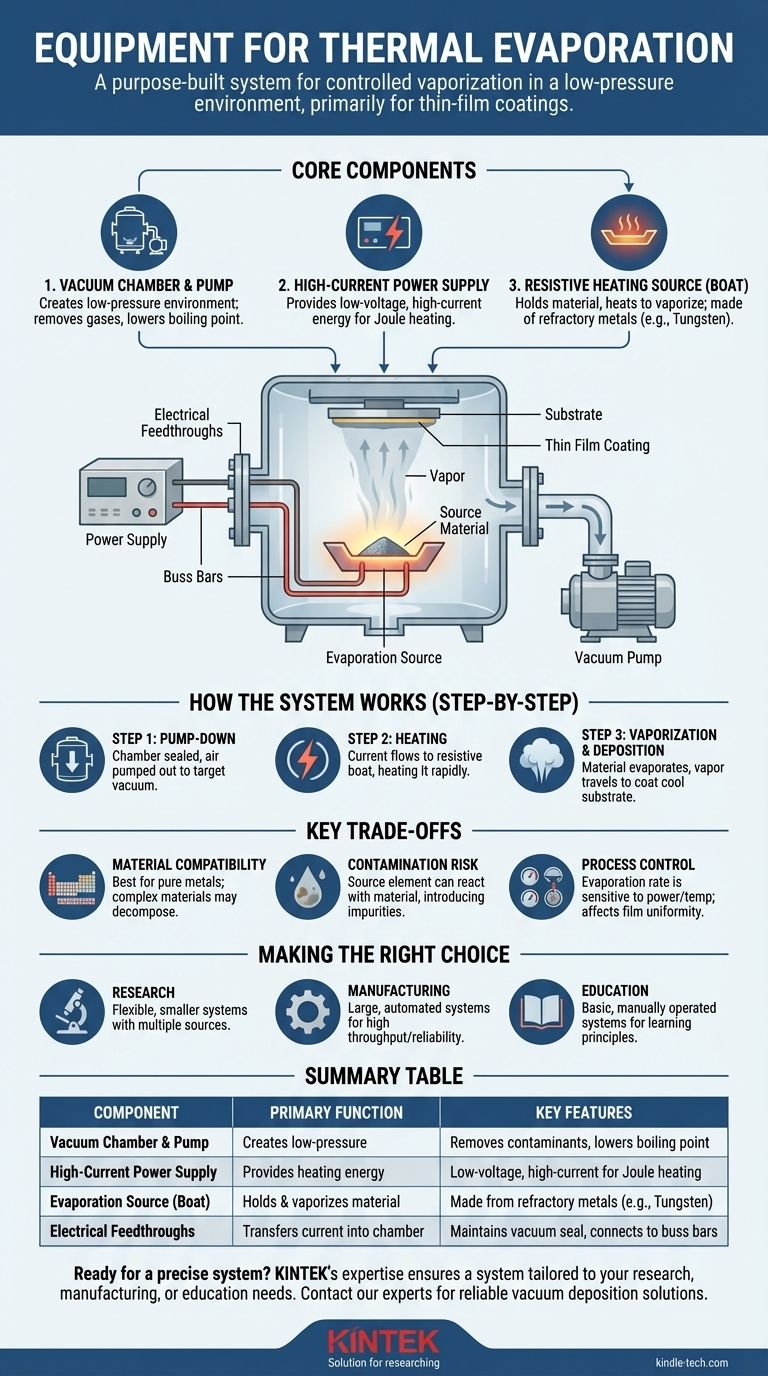
In a technical context, the equipment for evaporation is a purpose-built system centered around three key components: a vacuum chamber, a high-current power supply, and a resistive heating source. This setup is designed to heat a material until it turns into a vapor within a controlled, low-pressure environment, a process most commonly used for creating thin-film coatings.
The essential equipment for evaporation works as a unified system. It uses a vacuum to lower a material's boiling point and remove contaminants, while an electrical source heats a container—often called a "boat"—to vaporize the material for deposition.
The Core Components of a Thermal Evaporation System
Thermal evaporation isn't just about heat; it's about applying that heat in a highly controlled environment. Each component has a specific role in achieving this control.
The Vacuum Chamber and Pumping System
The entire process occurs inside a sealed vacuum chamber. A vacuum is critical for two reasons.
First, it removes atmospheric gases like oxygen and water vapor, which could otherwise contaminate or react with the hot source material and the resulting film.
Second, it drastically lowers the pressure. This allows materials to vaporize at a much lower temperature than they would at normal atmospheric pressure. It also allows the vaporized atoms to travel in straight lines to their target without colliding with air molecules.
The Power Supply
An evaporation power supply is a specialized unit that provides low-voltage, high-current electricity.
This electrical energy is not for powering the chamber itself, but for directly heating the evaporation source through a principle called Joule heating. The high current is what generates the intense heat required for vaporization.
The Evaporation Source (The "Boat")
The source is the element that both holds the material to be evaporated and generates the heat. It is typically a small boat, basket, or filament made from a highly resistive material.
These sources are usually made of refractory metals like tungsten, molybdenum, or tantalum. These materials are chosen because they have extremely high melting points and will not evaporate themselves at the temperatures needed to vaporize the source material.
Electrical Feedthroughs and Buss Bars
To get the high current from the power supply (outside the chamber) to the evaporation source (inside the vacuum), you need specialized hardware.
Electrical feedthroughs are sealed connectors that allow electrical current to pass through the chamber wall without creating a vacuum leak. These connect to internal buss bars, which are thick, highly conductive metal rods that carry the current to the resistive source with minimal energy loss.
How the System Works in Practice
Understanding the components is key, but seeing how they work in sequence reveals the full picture of the process.
Step 1: Pump-Down
First, the source material is placed in the boat, and the target to be coated (the substrate) is placed in the chamber. The chamber is then sealed and pumped down to a target pressure using a vacuum pump system.
Step 2: Heating
Once the desired vacuum level is reached, the power supply is turned on. Current flows from the feedthroughs, through the buss bars, and into the resistive boat. The boat's high resistance causes it to heat up rapidly, often glowing white-hot.
Step 3: Vaporization and Deposition
As the boat heats, it transfers that thermal energy to the source material it holds. The material's temperature rises until it begins to evaporate, releasing a stream of vapor. This vapor travels in a straight line-of-sight path until it coats the cooler substrate, condensing back into a solid to form a thin film.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
While powerful, thermal evaporation is not a universal solution. Success depends on understanding its limitations.
Material Compatibility
This method works best for pure metals and some simple compounds that vaporize without breaking down. Complex alloys or certain chemical compounds may decompose when heated, meaning the resulting vapor and film will have a different chemical composition than the starting material.
Contamination Risk
The hot source element can sometimes react with the source material, introducing impurities into the film. Choosing the right boat material for the material being evaporated is critical for ensuring a pure final product.
Process Control
Controlling the thickness and uniformity of the deposited film requires careful management of the evaporation rate. This rate is highly sensitive to the power input and temperature, which can make achieving perfectly repeatable results a challenge without sophisticated monitoring equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific equipment configuration you need depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: A flexible, smaller system with multiple source options and good instrumentation is ideal for experimenting with different materials and processes.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: You need a large, highly automated system optimized for reliability, throughput, and depositing a single, well-characterized material.
- If your primary focus is educational learning: A basic, manually operated system is often the best choice to clearly demonstrate the core principles of vacuum technology and phase transition.
Ultimately, understanding how these components function as an integrated system is the key to mastering the evaporation process for any application.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Chamber & Pump | Creates a low-pressure environment | Removes contaminants, lowers boiling point |
| High-Current Power Supply | Provides heating energy | Low-voltage, high-current for Joule heating |
| Evaporation Source (Boat) | Holds and vaporizes the material | Made from refractory metals (e.g., Tungsten) |
| Electrical Feedthroughs | Transfers current into the chamber | Maintains vacuum seal, connects to buss bars |
Ready to integrate a precise thermal evaporation system into your lab? Whether your focus is on research, manufacturing, or education, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment ensures you get a system tailored to your specific needs. We specialize in providing reliable vacuum deposition solutions that enhance your thin-film coating processes. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's goals with the right equipment and consumables.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is the meaning of thermal evaporation? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin Film Coating
- What is the evaporation process in semiconductors? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between sputtering and thermal evaporation? Choose the Right PVD Method for Your Thin Film
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What is thermal evaporation used to deposit? A Guide to Metals, Compounds, and Key Applications



















