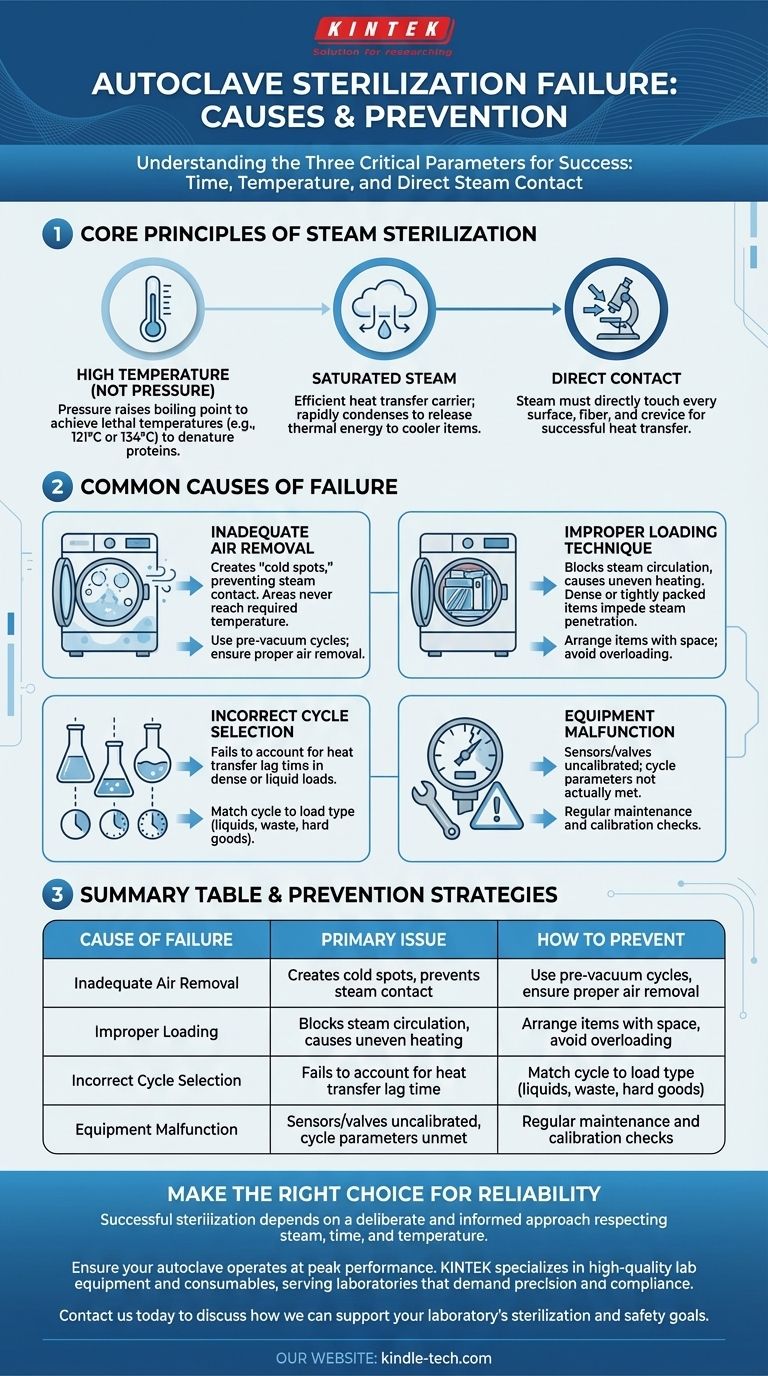
Autoclave sterilization failure is almost always preventable. It typically results from a failure to meet one of the three critical parameters for steam sterilization: time, temperature, or direct steam contact. These issues are most often caused by improper loading, incorrect cycle selection for the material, or inadequate air removal from the chamber.
The core principle of steam sterilization is not just heat, but the transfer of heat via saturated steam. Failure occurs whenever something—be it trapped air, improper loading, or an incorrect cycle—prevents this steam from making direct, sustained contact with every surface at the required temperature for the necessary amount of time.

Understanding the Core Principles
To troubleshoot failures, you must first understand why steam sterilization works. The process relies on a few fundamental scientific principles that, if compromised, will lead to an unsuccessful cycle.
It's High Temperature, Not High Pressure
The high pressure inside an autoclave serves a single purpose: to raise the boiling point of water. This allows the chamber to achieve temperatures (e.g., 121°C or 134°C) that are high enough to denature the essential proteins and enzymes within microorganisms, effectively killing them.
The pressure itself does not sterilize; it is merely the tool used to achieve lethal temperatures.
The Critical Role of Saturated Steam
Saturated steam—steam at the highest possible temperature for a given pressure—is an incredibly efficient carrier of thermal energy. When it makes contact with a cooler item, it rapidly condenses into water, transferring a large amount of heat directly to that surface.
Dry, superheated steam or wet steam with too much water content are both less effective at this critical heat transfer process.
The Necessity of Direct Contact
Sterilization is a surface-level event. For the heat transfer to occur, saturated steam must make direct contact with every fiber, crack, and crevice of the items being sterilized. If contact is blocked, that area will not reach the target temperature and will not be sterilized.
Common Causes of Sterilization Failure
Most failures can be traced back to one of these operational errors, which directly interfere with the core principles of time, temperature, or steam contact.
Inadequate Air Removal
This is one of the most common causes of failure. If air is not completely removed from the chamber and the load, it creates "cold spots." These pockets of air prevent steam from reaching surfaces, meaning those areas never achieve the required sterilization temperature, even if the autoclave's primary sensor reads correctly.
Improper Loading Technique
How you load the autoclave is paramount. Overloading the chamber or placing items too close together prevents steam from circulating freely and penetrating the entire load.
Dense materials, tightly packed instruments, or waste bags laid flat instead of on their side can create barriers that steam cannot bypass, leaving the interiors unsterilized.
Incorrect Cycle Selection
Different materials require different sterilization cycles. A cycle designed for glassware is insufficient for a large bag of biological waste or a flask of liquid media.
This is due to heat transfer lag time—the time it takes for the center of the load to reach the target temperature. Dense and liquid loads heat up much more slowly than the chamber air, requiring longer exposure times to ensure full sterilization.
Ignoring Material and Load Characteristics
The nature of the load itself dictates the required parameters. A load with a high concentration of microorganisms (bioburden) or highly resistant bacterial spores requires a more rigorous cycle than clean glassware.
Similarly, the type of material (e.g., hard goods, liquids, porous items) determines how easily steam can penetrate and how long the cycle must run.
Equipment Malfunction or Poor Calibration
A sterilization cycle is only as reliable as the machine performing it. If temperature sensors, pressure valves, or timers are not calibrated regularly, the autoclave may report a successful cycle when the required conditions were never actually met.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To prevent failure, you must think critically about the specific load you are sterilizing before every cycle.
- If your primary focus is hard goods (glassware, instruments): Ensure items are clean and arranged with adequate spacing to guarantee steam can reach every surface.
- If your primary focus is liquids or media: Use a dedicated liquid cycle with a slow exhaust to prevent boiling over, and never seal containers tightly.
- If your primary focus is porous loads or waste: Select a cycle with a pre-vacuum stage for air removal and a longer sterilization time to overcome heat lag.
- If your primary focus is reliability: Always verify cycle parameters against the manufacturer's recommendations and maintain a strict schedule for equipment calibration and maintenance.
Ultimately, successful sterilization depends on a deliberate and informed approach that respects the fundamental principles of steam, time, and temperature.
Summary Table:
| Cause of Failure | Primary Issue | How to Prevent |
|---|---|---|
| Inadequate Air Removal | Creates cold spots, prevents steam contact | Use pre-vacuum cycles, ensure proper air removal |
| Improper Loading | Blocks steam circulation, causes uneven heating | Arrange items with space, avoid overloading |
| Incorrect Cycle Selection | Fails to account for heat transfer lag time | Match cycle to load type (liquids, waste, hard goods) |
| Equipment Malfunction | Sensors/valves uncalibrated, cycle parameters unmet | Regular maintenance and calibration checks |
Ensure your autoclave operates at peak performance and reliability. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories that demand precision and compliance. Our autoclaves are designed to meet rigorous sterilization standards, with features that prevent common failures. Let our experts help you select the right equipment and establish best practices for your specific needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sterilization and safety goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer Lab Microcomputer Sterilizer
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a high-pressure static autoclave in PWR coolant corrosion experiments? Essential Nuclear Testing
- What is the role of a Teflon-lined autoclave in g-C3N4 synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Hydrothermal Condensation
- What is the process of autoclaving? A Step-by-Step Guide to Sterilization
- How long does autoclaving take? Mastering Sterilization Times for Your Lab
- What core conditions must a high-pressure autoclave meet for supercritical water corrosion? Master 27 MPa & 600°C Tests
- How do you autoclave lab equipment? A Step-by-Step Guide to Sterile Results
- What is the alternative method of sterilization for culture media if autoclaving is not suitable? Protect Heat-Sensitive Components
- What specific reaction conditions does a PTFE-lined autoclave provide for NVP/C synthesis? Optimize Battery Cathodes



















