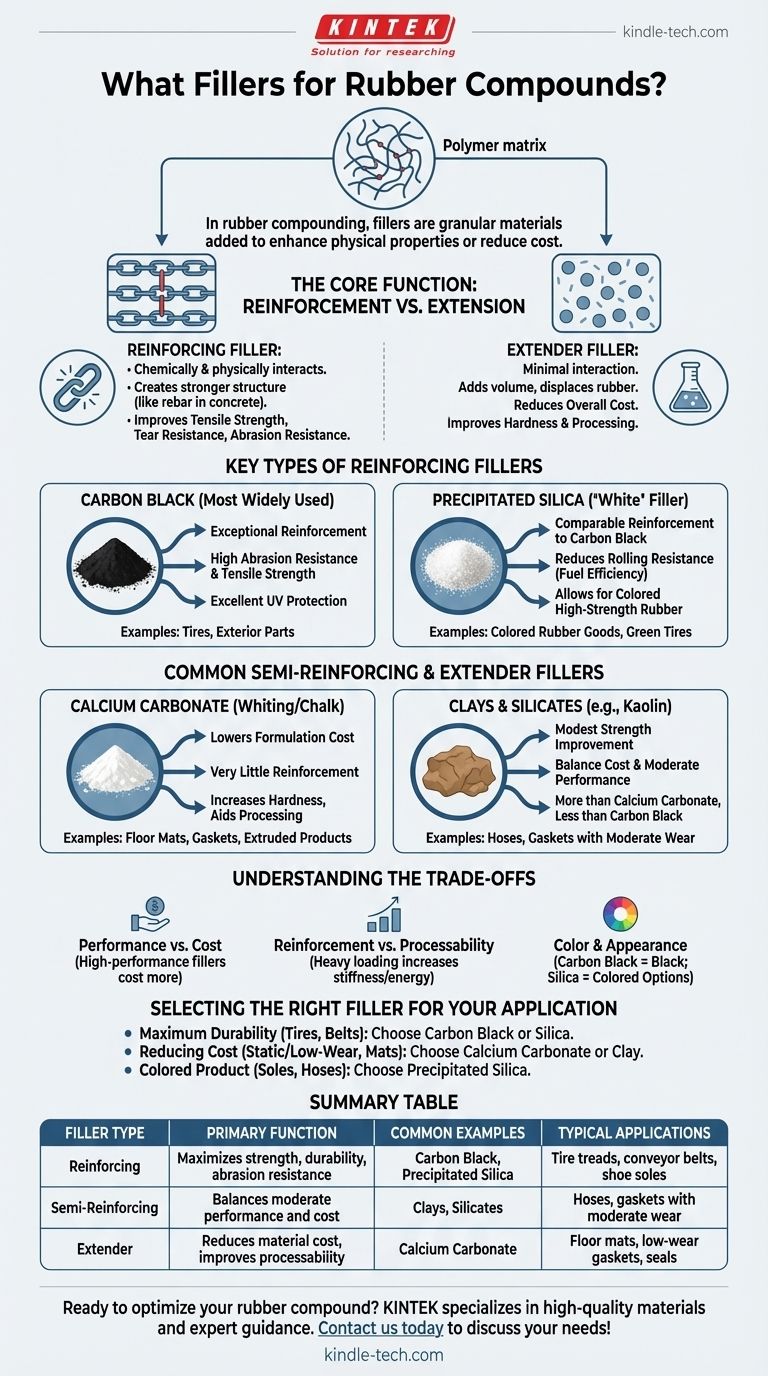
In rubber compounding, fillers are granular materials added to the polymer to enhance physical properties or reduce cost. The most common and effective fillers are carbon blacks and silicas, used for high reinforcement, while materials like calcium carbonate, clays, and silicates are used for less demanding applications.
The choice of a rubber filler is a fundamental decision that dictates the final compound's performance and cost. It's a strategic trade-off between achieving maximum strength and durability versus managing material expense and processability.

The Core Function of Fillers: Reinforcement vs. Extension
Fillers are not just inert "stuffing." They form a crucial part of the rubber matrix, fundamentally altering its behavior. Their primary function falls into one of two categories: reinforcing the compound or extending it to reduce cost.
What is a Reinforcing Filler?
A reinforcing filler chemically and physically interacts with the rubber polymer chains. This interaction creates a stronger, more robust internal structure.
Think of it like rebar in concrete. The filler particles lock the long, flexible polymer chains together, restricting their movement under stress.
This reinforcement significantly improves key mechanical properties like tensile strength, tear resistance, and abrasion resistance, making the final product far more durable.
What is an Extender (or Non-Reinforcing) Filler?
An extender filler, often called a non-reinforcing or semi-reinforcing filler, has minimal interaction with the polymer matrix.
Its primary purpose is to add volume and displace the more expensive rubber polymer. This directly reduces the overall cost of the compound.
While they don't provide the high-level strength of reinforcing fillers, they can improve other characteristics like hardness and processing smoothness.
Key Types of Reinforcing Fillers
When performance is the top priority, only a few types of fillers are considered. These are the workhorses of high-performance rubber applications.
Carbon Black
Carbon black is the most widely used reinforcing filler in the rubber industry, produced from the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons.
It provides exceptional reinforcement, leading to high abrasion resistance and tensile strength. It also offers excellent UV protection, which is why most exterior rubber parts, like tires, are black.
Precipitated Silica
Silica is the second major reinforcing filler, often called a "white" filler. It offers a level of reinforcement comparable to carbon black.
Its key advantage is its ability to reduce rolling resistance in tires, which improves fuel efficiency. Because it isn't black, it is the filler of choice for producing high-strength, colored rubber goods.
Common Semi-Reinforcing and Extender Fillers
For countless applications where cost is a primary driver and mechanical demands are lower, extender fillers are the standard choice.
Calcium Carbonate
Also known as whiting or chalk, calcium carbonate is one of the most common extender fillers. It is primarily used to lower the formulation cost.
It offers very little reinforcement but can increase hardness and aid in processing, often providing a smooth surface finish to extruded products.
Clays and Silicates
Various types of clays (like kaolin clay) and other mineral silicates are used as semi-reinforcing fillers.
They provide a modest improvement in strength—more than calcium carbonate but significantly less than carbon black or silica. They are a good middle-ground option for balancing cost and moderate performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a filler is never about finding a single "best" option. It's about balancing competing priorities for your specific application.
Performance vs. Cost
This is the most fundamental trade-off. High-performance reinforcing fillers like specialized carbon blacks and silicas are significantly more expensive than extender fillers like ground calcium carbonate. The required durability of the final product dictates the acceptable cost.
Reinforcement vs. Processability
Heavily loading a rubber compound with reinforcing fillers makes it very stiff and difficult to mix and process. This can increase energy consumption and cycle times during manufacturing. Extender fillers often result in softer, more easily processed compounds.
Color and Appearance
The choice is simple: if your product needs to be any color other than black, you cannot use carbon black. Your only option for high-strength colored products is to use silica or other non-black fillers.
Selecting the Right Filler for Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on the goal of your rubber compound.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and abrasion resistance (e.g., tire treads, conveyor belts): Your best choice is a reinforcing filler like carbon black or precipitated silica.
- If your primary focus is reducing material cost in a static, low-wear application (e.g., floor mats, gaskets): An extender filler like calcium carbonate or a basic clay is the most economical choice.
- If your primary focus is creating a colored product with good physical properties (e.g., shoe soles, hoses): Precipitated silica is the necessary reinforcing filler for this purpose.
Choosing the right filler is the first step in designing a compound that meets its performance targets without exceeding its budget.
Summary Table:
| Filler Type | Primary Function | Common Examples | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reinforcing | Maximizes strength, durability, abrasion resistance | Carbon Black, Precipitated Silica | Tire treads, conveyor belts, shoe soles |
| Semi-Reinforcing | Balances moderate performance and cost | Clays, Silicates | Hoses, gaskets with moderate wear |
| Extender | Reduces material cost, improves processability | Calcium Carbonate | Floor mats, low-wear gaskets, seals |
Ready to optimize your rubber compound? The right filler choice is critical to balancing performance, cost, and processability for your specific product. KINTEK specializes in supplying high-quality materials and expert guidance for laboratory and industrial rubber compounding. Let our team help you select the ideal fillers to meet your application's demands—contact us today to discuss your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Open Type Two Roll Mixing Mill Machine for Rubber Crusher
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
People Also Ask
- What is meant by two high rolling mill? A Guide to Core Material Processing
- What is a two roll mill for rubber compounding? A Foundational Tool for Polymer Processing
- What is the disadvantage of a two-roll mill? Limited Thickness Reduction Due to Roll Flattening
- What is the use of two roll mill? Essential for Polymer Mixing, R&D, and Quality Control
- What is a two-high roll mill? Master Precise Material Compounding and Testing



















